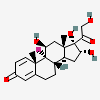
Triamcinolone
- triamcinolone
- 124-94-7
- Fluoxyprednisolone
- Aristocort
- Triamcinolon
- Create:2005-03-26
- Modify:2025-01-11
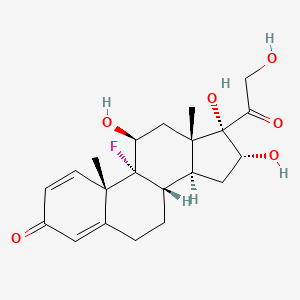
- Aristocort
- Triamcinolone
- Volon
- triamcinolone
- 124-94-7
- Fluoxyprednisolone
- Aristocort
- Triamcinolon
- Kenacort
- Rodinolone
- Delphicort
- Ledercort
- Tricortale
- Adcortyl
- Celeste
- Triamcet
- Volon
- Triam-Tablinen
- Cinolone-T
- SK-Triamcinolone
- Triamcinlon
- Omcilon
- Fluoxiprednisolone
- Triamcinolona
- Triamcinolonum
- Triamcinolonum [INN]
- Tiamcinolonum
- Triamcinalone
- Tiamcinolonum [INN-Latin]
- Triamcinolona [INN-Spanish]
- 9alpha-Fluoro-16alpha-hydroxyprednisolone
- CL 19823
- Kenacort-AG
- HSDB 3194
- UNII-1ZK20VI6TY
- 9-alpha-Fluoro-16-alpha-hydroxyprednisolone
- (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,16R,17S)-9-fluoro-11,16,17-trihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
- EINECS 204-718-7
- 1ZK20VI6TY
- NSC 13397
- NSC-13397
- BRN 2341955
- CHEBI:9667
- Prednisolone, 9-fluoro-16alpha-hydroxy-
- DTXSID1040742
- Triamcinolone, topical
- 9-Fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- NSC13397
- Triamcinolone (Standard)
- Aristocort Tablets
- MLS000028542
- MLS001066543
- (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,16R,17S)-9-fluoro-11,16,17-trihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
- DTXCID9020742
- 124-94-7 (free)
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-16.alpha.-hydroxyprednisolone
- 4-08-00-03629 (Beilstein Handbook Reference)
- Triamcinolone [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- SMR000058333
- 9-Fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- Prednisolone, 9-fluoro-16.alpha.-hydroxy-
- Tiamcinolonum (INN-Latin)
- Triamcinolona (INN-Spanish)
- 51855-44-8
- TRIAMCINOLONE (MART.)
- TRIAMCINOLONE [MART.]
- TRIAMCINOLONE (USP-RS)
- TRIAMCINOLONE [USP-RS]
- Triamcinolone (USP:INN:BAN:JAN)
- TRIAMCINOLONE (EP MONOGRAPH)
- TRIAMCINOLONE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- TRIAMCINOLONE (USP MONOGRAPH)
- TRIAMCINOLONE [USP MONOGRAPH]
- 11beta,16alpha,17alpha,21-Tetrahydroxy-9alpha-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17alpha,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- Kenacort (TN)
- Triamcinolone (Aristocort)
- Triamcinolone Acetonide Imp. A (EP); Triamcinolone; Triamcinolone Acetonide Impurity A
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-
- NCGC00094799-01
- CAS-124-94-7
- Prestwick_438
- 9-alpha-Fluoro-11-beta,16-alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- 11-beta,16-alpha,17-alpha,21-Tetrahydroxy-9-alpha-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- Prestwick0_000120
- Prestwick1_000120
- Prestwick2_000120
- Prestwick3_000120
- TRIAMCINOLONE [MI]
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxy-
- TRIAMCINOLONE [INN]
- TRIAMCINOLONE [JAN]
- SCHEMBL4447
- CHEMBL1451
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11-beta,16-alpha)-
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11beta,16alpha)
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11beta,16alpha)-
- TRIAMCINOLONE [HSDB]
- Lopac0_001179
- BSPBio_000140
- TRIAMCINOLONE [VANDF]
- cid_31307
- MLS002695935
- SPBio_002079
- TRIAMCINOLONE [WHO-DD]
- BPBio1_000154
- GTPL2870
- BDBM41132
- HY-B0328R
- Triamcinolone (JP17/USP/INN)
- HMS1568G22
- HMS2090D12
- HMS2095G22
- HMS2231E20
- HMS3263L19
- HMS3712G22
- TRIAMCINOLONE [GREEN BOOK]
- TRIAMCINOLONE [ORANGE BOOK]
- BCP11941
- EX-A4109
- HY-B0328
- Tox21_111332
- Tox21_300178
- Tox21_501179
- MFCD00010477
- s1933
- AKOS015895436
- Tox21_111332_1
- AC-2072
- CCG-205253
- DB00620
- LP01179
- SDCCGSBI-0051146.P002
- 11.beta.,16.alpha.,17.alpha., 21-Tetrahydroxy-9.alpha.-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- BRN-2341955
- SMP1_000300
- NCGC00021580-03
- NCGC00021580-04
- NCGC00021580-05
- NCGC00021580-06
- NCGC00021580-07
- NCGC00021580-08
- NCGC00021580-16
- NCGC00178404-03
- NCGC00254049-01
- NCGC00261864-01
- AS-13657
- NCI60_000750
- CS-0695010
- EU-0101179
- NS00007956
- D00385
- E70344
- EN300-7400440
- SR-01000000079
- Q1074056
- SR-01000000079-3
- BRD-K77554836-001-03-3
- BRD-K77554836-001-11-6
- BRD-K77554836-001-14-0
- TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IMPURITY A [EP IMPURITY]
- Triamcinolone, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard
- Triamcinolone, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- WLN: L E5 B666 OV KU MUTJ A1 BF CQ E1 FV1Q FQ GQ
- Triamcinolone, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,17,21-tetrahydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- Pregna-1,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxy-
- (11beta,16alpha)-9-Fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- 11.beta.,17.alpha.,21-Tetrahydroxy-9.alpha.-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
- 9-FLUORO-11,BETA,,16.ALPHA.,17,21-TETRAHYDROXYPREGNA-1,4-DIENE-3,20-DIONE
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,17.alpha.,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- Pregna-1,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3, 20-dione, 9-fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxy-
- (1R,2S,10S,11S,13R,14S,15S,17S)-1-fluoro-13,14,17-trihydroxy-14-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-3,6-dien-5-one
- (1S,2R,3aS,3bS,9aS,9bR,10S,11aS)-9b-fluoro-1,2,10-trihydroxy-1-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-9a,11a-dimethyl-1H,2H,3H,3aH,3bH,4H,5H,7H,9aH,9bH,10H,11H,11aH-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-one
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17.alpha., 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
- PREGNA-1,4-DIENE-3,20-DIONE, 9-FLUORO-11,16,17,21-TETRAHYDROXY-, (11.BETA.,16.ALPHA.)
- Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11beta,16alpha)-, tetrahydro deriv.
184.21 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
210.98 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
180.29 Ų [M+H-H2O]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
206.4 Ų [M+K]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
345.15 100
325.1397 84.76
357.1681 100
225.1258 66.33
339.1583 44.66
237.127 33.67
321.1478 33.28
375.18 999
395.187 867
357.1692 481
376.1825 282
396.1887 243
357.1681 999
225.1258 662
339.1583 446
237.127 336
321.1478 332
357.16901 100
225.12694 91.19
339.15826 65.12
321.14761 64.19
147.07985 60.04
147.08086 100
223.11201 49.88
171.08051 46.05
121.06519 39.95
225.1274 39.09
Triamcinolone Acetonide (active moiety of)
Triamcinolone Diacetate (narrower)
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07X - Corticosteroids, other combinations
D07XB - Corticosteroids, moderately potent, other combinations
D07XB02 - Triamcinolone
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A01 - Stomatological preparations
A01A - Stomatological preparations
A01AC - Corticosteroids for local oral treatment
A01AC01 - Triamcinolone
C - Cardiovascular system
C05 - Vasoprotectives
C05A - Agents for treatment of hemorrhoids and anal fissures for topical use
C05AA - Corticosteroids
C05AA12 - Triamcinolone
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07A - Corticosteroids, plain
D07AB - Corticosteroids, moderately potent (group ii)
D07AB09 - Triamcinolone
R - Respiratory system
R01 - Nasal preparations
R01A - Decongestants and other nasal preparations for topical use
R01AD - Corticosteroids
R01AD11 - Triamcinolone
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01B - Antiinflammatory agents
S01BA - Corticosteroids, plain
S01BA05 - Triamcinolone
- Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
Use (kg) in USA (2002): 2300
Consumption (g per capita) in the USA (2002): 0.00815
Calculated removal (%): 45.6

H351 (63.3%): Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity]
H361 (31.7%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity]
P203, P280, P318, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 60 reports by companies from 7 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Carc. 2 (63.3%)
Repr. 2 (31.7%)
IMAP assessments - Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-: Environment tier I assessment
IMAP assessments - Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-: Human health tier I assessment
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Topical triamcinolone has not been studied during breastfeeding. Since only extensive application of the most potent corticosteroids may cause systemic effects in the mother, it is unlikely that short-term application of topical corticosteroids would pose a risk to the breastfed infant by passage into breastmilk. However, it would be prudent to use the least potent drug on the smallest area of skin possible. It is particularly important to ensure that the infant's skin does not come into direct contact with the areas of skin that have been treated. Current guidelines allow topical corticosteroids to be applied to the nipples just after nursing for eczema, with the nipples cleaned gently before nursing. Only water-miscible cream or gel products should be applied to the breast because ointments may expose the infant to high levels of mineral paraffins via licking.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
Topical application of a corticosteroid with relatively high mineralocorticoid activity (isofluprednone acetate) to the mother's nipples resulted in prolonged QT interval, cushingoid appearance, severe hypertension, decreased growth and electrolyte abnormalities in her 2-month-old breastfed infant. The mother had used the cream since birth for painful nipples.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Adequate endogenous adrenocorticoid levels are necessary for normal lactation.
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Because no information is available on the use of oral triamcinolone during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Use of triamcinolone as a nasal spray or local injections, such as for tendinitis, would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Expert opinion considers inhaled and oral corticosteroids acceptable to use during breastfeeding. Local injections, such as for tendinitis, would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Single injections of triamcinolone acetonide into the breast for treating granulomatous mastitis appear to be acceptable. Medium to large doses of corticosteroids given systemically or injected into joints or the breast have been reported to cause temporary reduction of lactation. See also Triamcinolone, Topical.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
None reported with any corticosteroid.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
A mother was nursing her 14-month-old 3 to 7 times daily. She had 5.7 mg of betamethasone sodium phosphate and acetate mixture injected into her shoulder for bursitis with no effect on lactation. Four weeks later, she continued to have pain in her thoracic cervical regions and was diagnosed with neural sensitization. She had 80 to 120 mg of triamcinolone diacetate injected into her cervical and thoracic spine epidurally and into the facets. Three days later, she noticed a decrease in milk supply and a reduced ejection reflex which continued to worsen over the next 5 days. She began using a breast pump with frequent pumping and domperidone as a galactogogue. Her milk slowly increased over several days and was normal by 21 days after the injection when she stopped domperidone. At that time, her serum prolactin levels were elevated. The decrease in the mother's milk supply was possibly caused by the corticosteroid injections. Medium to large doses of corticosteroids given systemically or injected into joints or the breast have been reported to cause temporary reduction of lactation.
A study of 46 women who delivered an infant before 34 weeks of gestation found that a course of another corticosteroid (betamethasone, 2 intramuscular injections of 11.4 mg of betamethasone 24 hours apart) given between 3 and 9 days before delivery resulted in delayed lactogenesis II and lower average milk volumes during the 10 days after delivery. Milk volume was not affected if the infant was delivered less than 3 days or more than 10 days after the mother received the corticosteroid. An equivalent dosage regimen of triamcinolone might have the same effect.
A study of 87 pregnant women found that betamethasone given as above during pregnancy caused a premature stimulation of lactose secretion during pregnancy. Although the increase was statistically significant, the clinical importance appears to be minimal. An equivalent dosage regimen of triamcinolone might have the same effect.
A nursing mother who was 7 months postpartum had triamcinolone 40 mg injected into the first dorsal compartment of the wrist along with 2 mL of 1% lidocaine for de Quervain tenosynovitis. Twenty-four hours after the injection, the patient reported a 90% decrease in lactation as measured by breast pumping before and after the injection. She continued to pump her breasts and began taking fenugreek to stimulate lactation. Within 1 week, her milk supply increased by 50% and by 1 month after the injection, she was able to meet her infants breastfeeding needs.
A woman with idiopathic granulomatous mastitis received an injection of 40 mg of triamcinolone acetonide into erythematous areas of the affected breast. Her milk production decreased from the injected left breast. She had originally been able to express 60 mL on that side with an electric breast pump, and after the injection she was only able to express 10 mL. Her milk supply on the affected side recovered over the course of 2 weeks. Production on the unaffected right breast did not decrease.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=GFNANZIMVAIWHM-OBYCQNJPSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusTriamcinolone [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000124947Tetrahydrotriamcinolonehttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0051855448ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_useTriamcinolonehttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00620
- DTP/NCILICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- EPA DSSToxTriamcinolonehttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID1040742CompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeTriamcinolone (EC: 204-718-7)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/33162
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)TRIAMCINOLONEhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3194
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingTriamcinolonehttp://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014758HMDB0014758_nmr_one_2210https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014758#spectra
- CCSbaseCCSbase Classificationhttps://ccsbase.net/
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licenceTRIAMCINOLONEhttps://platform.opentargets.org/drug/CHEMBL1451
- Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)LICENSET3DB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (T3DB) and the original publication.http://www.t3db.ca/downloadsTriamcinolonehttp://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D4756
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jspTriamcinolonehttps://ctdbase.org/detail.go?type=chem&acc=D014221
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloadsTRIAMCINOLONEhttps://www.dgidb.org/drugs/rxcui:10759
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)Triamcinolonehttps://idrblab.net/ttd/data/drug/details/D03BLF
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)Triamcinolone, Topicalhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/n/lactmed/LM266/Triamcinolonehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/n/lactmed/LM267/
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/TriamcinoloneNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- SpectraBaseTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/J5OnNzXaaecTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/8d8y76T7PsNTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/48VGqiq2yRV9.alpha.-fluoro-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17.alpha.,21-tetrahydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3-onehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/EXPueI2VwPQTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/7pjlAmtK1uFTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/DeIcVd3RrUWTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/4LvoYm5KMSGTriamcinolonehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/FiYTJcJcbwL
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.kegDrugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeiahttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08311.keg
- MassBank Europe
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmltriamcinolonehttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/10759
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=D07XB02Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=A01AC01Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=C05AA12Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=D07AB09Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=R01AD11Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=S01BA05Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=H02AB08Triamcinolonehttps://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=R03BA06
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policiestriamcinolonehttps://www.pharmgkb.org/chemical/PA451749
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/abouttriamcinolonehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/MMZVS1LLWYGT
- Springer Nature
- The Cambridge Structural Database
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidatatriamcinolonehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1074056
- Wikipedia4-Hydroxynonenalhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4-HydroxynonenalTriamcinolonehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triamcinolone
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlTriamcinolonehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68014221Glucocorticoidshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68005938Anti-Inflammatory Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000893
- PubChemPFAS and Fluorinated Compounds in PubChemhttps://gitlab.com/uniluxembourg/lcsb/eci/pubchem-docs/-/raw/main/pfas-tree/PFAS_Tree.pdf?inline=false
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 388480566https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/388480566
- NCBI