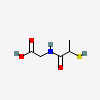
Tiopronin
- tiopronin
- 1953-02-2
- N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine
- Acadione
- Thiopronine
- Create:2005-03-25
- Modify:2025-01-18

- 2 Mercaptopropionylglycine
- 2 Thiol propionamido acetic Acid
- 2 Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
- 2-Mercaptopropionylglycine
- 2-Thiol-propionamido-acetic Acid
- 2-Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
- Acadione
- Acid, 2-Thiol-propionamido-acetic
- Acid, 2-Thiolpropionamidoacetic
- alpha Mercaptopropionylglycine
- alpha-Mercaptopropionylglycine
- Captimer
- Meprin
- Mercaptopropionylglycine
- Thiola
- Thiopronine
- Tiopronin
- Tiopronine
- tiopronin
- 1953-02-2
- N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine
- Acadione
- Thiopronine
- Captimer
- Mucolysin
- Tiopronine
- Capen
- Thiopronin
- Epatiol
- Thiola
- Sutilan
- Thiosol
- Glycine, N-(2-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)-
- Thiolpropionamidoacetic acid
- Tioglis
- Vincol
- 2-(2-sulfanylpropanoylamino)acetic acid
- Tiopronin (Thiola)
- Meprin (detoxicant)
- N-(2-Mercapto-1-oxopropyl)glycine
- tiopronina
- Tiopronino
- Tioproninum
- (2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine
- NSC-760416
- C5W04GO61S
- CCRIS 1935
- DTXSID4023678
- THIOLA EC
- EINECS 217-778-4
- Tiopronine [INN-French]
- Tioproninum [INN-Latin]
- 2-(2-sulfanylpropanamido)acetic acid
- 2-(2-Mercaptopropanamido)acetic acid
- Tiopronino [INN-Spanish]
- BRN 1859822
- CHEMBL1314
- UNII-C5W04GO61S
- alpha-mercaptopropionyl glycine
- GLYCINE, N-(2-MERCAPTOPROPIONYL)-
- DTXCID803678
- N-(2-mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
- MERCAPTOPROPIONYLGLYCINE-
- CHEBI:32229
- NSC 760416
- NCGC00159422-02
- NCGC00159422-04
- Tiopronine (INN-French)
- Tioproninum (INN-Latin)
- Tiopronino (INN-Spanish)
- TIOPRONIN (MART.)
- TIOPRONIN [MART.]
- Glycine, N-(2-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)- (9CI)
- alpha-Mercaptopropionylglycine
- CAS-1953-02-2
- A-MERCAPTOPROPIONYL GLYCINE
- Tiopronin; 2-(2-Sulfanylpropanoylamino)acetic acid
- 2 Mercaptopropionylglycine
- 2-Mercaptopropionylglycine
- Tiopronin [INN:DCF:JAN]
- alpha Mercaptopropionylglycine
- 2 Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
- 2-Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
- Tiopronin Base
- Acid, 2-Thiolpropionamidoacetic
- 2 Thiol propionamido acetic Acid
- 2-Thiol-propionamido-acetic Acid
- Acid, 2-Thiol-propionamido-acetic
- (S)-2-(2-Mercaptopropanamido)acetic Acid
- MFCD00004861
- Thiola (TN)
- Tiopronin (JAN/INN)
- TIOPRONIN [INN]
- TIOPRONIN [JAN]
- TIOPRONIN [MI]
- TIOPRONIN [VANDF]
- 2-mercapto-propionylglycine
- TIOPRONIN [WHO-DD]
- (2-mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
- SCHEMBL19989
- MLS006010632
- N-(2-Sulfanylpropanoyl)glycine
- TIOPRONIN [ORANGE BOOK]
- n-(2-mercaptopropionyl) glycine
- N-(2-mercaptopropanoyl) glycine
- G04BX16
- Acadione; Capen; Epatiol; Vincol
- (+)-(2-Mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
- (-)-(2-Mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
- HMS3264B11
- HMS3655L15
- Pharmakon1600-01506190
- BCP13354
- HY-B0373
- 2-(2-Mercaptopropanamido)aceticacid
- Tox21_111654
- BDBM50020805
- MFCD30157366
- NSC760416
- s2062
- (2-Mercaptopropionylamino)acetic acid
- AKOS015895408
- N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine, 99%
- Tox21_111654_1
- AC-2087
- CCG-214007
- DB06823
- (2-Mercapto-propionylamino)-acetic acid
- NCGC00159422-03
- AS-12522
- SMR001550282
- SY262996
- DB-352240
- NS00005173
- SW219206-1
- T2614
- Tiopronin, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard
- C73708
- D01430
- SBI-0653504.0001
- AB00376096_02
- EN300-7408657
- Q414456
- SR-01000942263
- J-012651
- SR-01000942263-1
- BRD-A85295731-001-02-3
- BRD-A85295731-001-03-1
- BRD-A85295731-001-04-9
- BRD-A85295731-001-05-6
- BRD-A85295731-001-06-4
- Z2681891170
- TIOPRONIN, Dextiopronin, Tiopronin (n-2-mercaptopropionyl glycine)
- 1939-02-2
- 2254742-22-6
- 2254742-23-7
Use (kg; approx.) in Germany (2009): >50
Consumption (g per capita; approx.) in Germany (2009): 0.000611
Calculated removal (%): 92.1

P264, P270, P301+P317, P330, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 50 reports by companies from 1 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
M Chen, V Vijay, Q Shi, Z Liu, H Fang, W Tong. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Drug Discovery Today, 16(15-16):697-703, 2011. PMID:21624500 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.05.007
M Chen, A Suzuki, S Thakkar, K Yu, C Hu, W Tong. DILIrank: the largest reference drug list ranked by the risk for developing drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21(4): 648-653. PMID:26948801 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.015
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=YTGJWQPHMWSCST-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Take at the same time every day. Take each dose at the same time every day.
- Take on an empty stomach. Take tiopronin at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating food.
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusTiopronin [INN:DCF:JAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0001953022ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- DTP/NCILICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeTiopronin (EC: 217-778-4)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/122724
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloads
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- DailyMed
- Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) DatasetLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citing
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegAnimal drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08331.keg
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-law(2-Mercaptopropionylamino)acetic acidhttp://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/TIOPRONINNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- SpectraBaseN-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/Gpwn0D9x3aN-(2-MERCAPTOPROPIONYL)GLYCINEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/5N8VaDShFLmN-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/u95NQGRxwcN-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/J9ywN7E7q4S
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Wikidata
- WikipediaN-Acetylneuraminic acidhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/N-Acetylneuraminic_acid
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.html
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 403399091https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/403399091
- NCBI