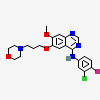
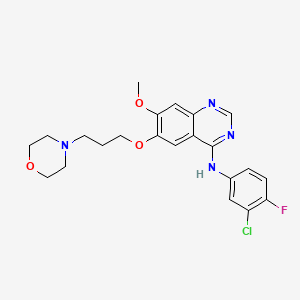
Gefitinib
- Gefitinib
- 184475-35-2
- Iressa
- ZD1839
- Irressat
- Create:2005-03-26
- Modify:2025-01-18
- gefitinib
- Iressa
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy)-4-quinazolinamide
- ZD 1839
- ZD1839
- Gefitinib
- 184475-35-2
- Iressa
- ZD1839
- Irressat
- N-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
- gefitinib (zd1839)
- ZD 1839
- ZD-1839
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy]quinazolin-4-amine
- gefitinibum
- CCRIS 9011
- UNII-S65743JHBS
- Gefitinib (GMP)
- MFCD04307832
- NSC-759856
- N-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
- S65743JHBS
- DTXSID8041034
- CHEBI:49668
- 4-(3'-Chloro-4'-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-4-quinazolinamine
- CHEMBL939
- DTXCID6021034
- NSC715055
- NSC 759856
- Gefitinib [USAN]
- NCGC00159455-02
- GEFITINIB (MART.)
- GEFITINIB [MART.]
- 3-Chloro-4-Fluoro-N-[(4z)-7-Methoxy-6-(3-Morpholin-4-Ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4(1h)-Ylidene]aniline
- C22H24ClFN4O3
- GEFITINIB (EP MONOGRAPH)
- GEFITINIB [EP MONOGRAPH]
- Iressa(TM)
- IRE
- Iressa (TN)
- CAS-184475-35-2
- SR-00000000262
- Gefitinib [USAN:INN:BAN]
- Gefitini; Iressa
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy)-4-quinazolinamine
- Gefitinib (Standard)
- Iressa (AstraZeneca)
- nchembio866-comp14
- Kinome_3321
- Kinome_3322
- GEFITINIB [INN]
- GEFITINIB [JAN]
- GEFITINIB [MI]
- GEFITINIB [VANDF]
- Gefitinib (ZD1839)?
- GEFITINIB [WHO-DD]
- SCHEMBL7866
- Gefitinib,ZD-1839,Iressa
- GEFITINIB [EMA EPAR]
- KBioSS_002241
- MLS003899193
- CU-00000000396-1
- BDBM5447
- cid_123631
- GTPL4941
- Gefitinib (JP18/USAN/INN)
- GEFITINIB [ORANGE BOOK]
- Gefitinib, >=98% (HPLC)
- L01XE02
- BCPP000221
- HMS2089B19
- HMS3244M21
- HMS3244M22
- HMS3244N21
- HMS3295A21
- HMS3413H08
- HMS3654A07
- HMS3677H08
- HMS3714A05
- HMS3748E17
- Pharmakon1600-01502274
- BCP01365
- Tox21_111683
- HY-50895G
- HY-50895R
- NSC759856
- NSC800105
- s1025
- STK621310
- AKOS000280752
- Tox21_111683_1
- AB20814
- AC-1556
- BCP9000718
- CCG-220642
- CS-0124
- DB00317
- KS-1204
- NSC-715055
- NSC-800105
- SDCCGSBI-0634411.P005
- 4-[(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline
- 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-4-morpholin)propoxy)-
- 6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxyquinazolin-4-amine
- N-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
- NCGC00159455-03
- NCGC00159455-04
- NCGC00159455-05
- NCGC00159455-06
- NCGC00159455-08
- NCGC00159455-09
- NCGC00159455-14
- BCB03_000781
- BG164498
- HY-50895
- SMR002204119
- SY002154
- CS-0622782
- G0546
- NS00006312
- SW199108-4
- D01977
- EN300-123024
- G-4408
- K00240
- AB01273954-01
- AB01273954-02
- AB01273954-03
- AB01273954_04
- Q417824
- Q-201149
- SR-00000000262-2
- SR-00000000262-3
- BRD-K64052750-001-16-7
- BRD-K64052750-001-17-5
- BRD-K64052750-001-22-5
- BRD-K64052750-001-23-3
- Gefitinib, EuropePharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- Z1546610485
- 4-(3'-chloro-4'-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-quinazoline
- Gefitinib for system suitability, EuropePharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (3-CHLORO-4-FLUORO-PHENYL)-[7-METHOXY-6-(3-MORPHOLIN-4-YL-PROPOXY)-QUINAZOLIN-4-YL]-AMINE
447.158752 78368
128.107681 53380
449.157135 20488
448.160553 15956
100.075844 6184
224.084763 100
225.08284 49.24
224.584457 41.83
318.043671 33.78
225.582962 15.18
224.084763 100
225.082840 49.24
224.584457 41.83
318.043671 33.78
225.582962 15.18
447.158752 100
128.107681 68.11
449.157135 26.14
448.160553 20.36
100.075844 7.89
128.1073107857281 100
100.07668958423722 21.66
447.16546232653366 3.72
320.05668253121223 0.47
70.0657200849362 0.30
317.0351911060067 100
445.14427574574825 68.93
302.01876124713664 53.78
316.0438860314912 16.14
274.01660519474035 7.19
Gefitinib is approved to treat:
• Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has metastasized (spread to other parts of the body). It is used as first-line treatment in patients whose tumors have certain EGFRgenemutations.
Gefitinib is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.
- Extracellular
- Membrane




H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral]
H315 (73.4%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation]
H318 (72.2%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H351 (73.4%): Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity]
H361 (39.2%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity]
H361f (36.7%): Suspected of damaging fertility [Warning Reproductive toxicity]
H373 (73.4%): May causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure]
H400 (22.8%): Very toxic to aquatic life [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard]
H411 (72.2%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard]
P203, P260, P264, P264+P265, P270, P273, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P305+P354+P338, P317, P318, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P362+P364, P391, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 79 reports by companies from 14 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Acute Tox. 4 (100%)
Skin Irrit. 2 (73.4%)
Eye Dam. 1 (72.2%)
Carc. 2 (73.4%)
Repr. 2 (39.2%)
Repr. 2 (36.7%)
STOT RE 2 (73.4%)
Aquatic Acute 1 (22.8%)
Aquatic Chronic 2 (72.2%)
In large early clinical trials, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occurred in 9% to 13% of patients treated with standard doses of gefitinib, and 2% to 4% of patients had to stop therapy because of elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal. Serum enzyme elevations typically arise after 4 to 12 weeks of treatment with a hepatocellular pattern. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features have not been described, but rash is common in patients receiving gefitinib. Most cases of liver injury due to gefitinib in the literature have been minimally or not symptomatic, and the injury resolved within 1 to 2 months of stopping the drug. Restarting therapy was usually but not always followed by rapid recurrence of serum enzyme elevations, and corticosteroid therapy did not appear to prevent this recurrence. In some instances, lower doses were tolerated with minimal or no ALT elevations. Periodic monitoring of liver tests during therapy is recommended. Despite the frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations during gefitinib therapy, cases of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice are rare. Cases of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity have been reported to the sponsor and monitoring of liver tests during therapy is recommended.
Likelihood score: B (likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
M Chen, V Vijay, Q Shi, Z Liu, H Fang, W Tong. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Drug Discovery Today, 16(15-16):697-703, 2011. PMID:21624500 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.05.007
M Chen, A Suzuki, S Thakkar, K Yu, C Hu, W Tong. DILIrank: the largest reference drug list ranked by the risk for developing drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21(4): 648-653. PMID:26948801 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.015
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
No information is available on the clinical use of gefitinib during breastfeeding. Because gefitinib is 90% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 48 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during gefitinib therapy.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=XGALLCVXEZPNRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Exercise caution with grapefruit products. Grapefruit is an inhibitor of CYP3A4, the enzyme primarily responsible for metabolizing gefitinib. Coadministration with grapefruit products may decrease gefitinib metabolism and increase plasma concentrations.
- Take with or without food.
- BindingDBLICENSEAll data curated by BindingDB staff are provided under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/us/).https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/info.jsp
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloads
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusGefitinib [USAN:INN:BAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0184475352ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DTP/NCILICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeN-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy]quinazolin-4-aminehttps://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.171.043N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy]quinazolin-4-amine (EC: 643-034-7)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/175956
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0014462_msms_374198https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014462#spectra
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- LiverTox
- LOTUS - the natural products occurrence databaseLICENSEThe code for LOTUS is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.https://lotus.nprod.net/LOTUS Treehttps://lotus.naturalproducts.net/
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Crystallography Open Database (COD)LICENSEAll data in the COD and the database itself are dedicated to the public domain and licensed under the CC0 License. Users of the data should acknowledge the original authors of the structural data.https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
- The Cambridge Structural Database
- DailyMed
- Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) DatasetLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)LICENSEInformation on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) website is subject to a disclaimer and copyright and limited reproduction notices.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/legal-noticeGefitinib Mylan (EMEA/H/C/004826)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/gefitinib-mylanIressa (EMEA/H/C/001016)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/iressa
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/Gefitinib | IressaNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- WHO Model Lists of Essential MedicinesLICENSEPermission from WHO is not required for the use of WHO materials issued under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Intergovernmental Organization (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO) license.https://www.who.int/about/policies/publishing/copyright
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-law
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.kegDrugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeiahttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08311.keg
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NCI Cancer Drugs
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/about
- Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe)
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB)LICENSEData files contained in the PDB archive (ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org) are free of all copyright restrictions and made fully and freely available for both non-commercial and commercial use. Users of the data should attribute the original authors of that structural data.https://www.rcsb.org/pages/policies
- SpectraBase
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidata
- Wikipedia
- Wiley
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAntineoplastic Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000970Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitorshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2103139
- PubChemPFAS and Fluorinated Compounds in PubChemhttps://gitlab.com/uniluxembourg/lcsb/eci/pubchem-docs/-/raw/main/pfas-tree/PFAS_Tree.pdf?inline=false
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 389147678https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/389147678
- NCBI