Cisplatin
- Cisplatina
- Citoplatino
- Cysplatyna
- Metaplatin
- Plastistil
- Create:2004-09-16
- Modify:2025-01-11
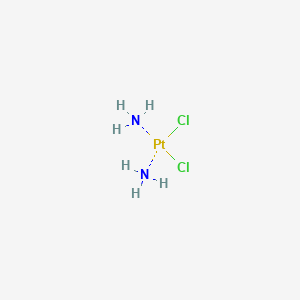
- Biocisplatinum
- cis Diamminedichloroplatinum
- cis Platinum
- cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum
- cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
- cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II)
- cis-Platinum
- Cisplatin
- Diamminodichloride, Platinum
- Dichlorodiammineplatinum
- NSC-119875
- Platidiam
- Platino
- Platinol
- Platinum Diamminodichloride
- Cisplatina
- Citoplatino
- Cysplatyna
- Metaplatin
- Plastistil
- Platinoxan
- Abiplatin
- Blastolem
- Citosin
- Platiran
- Platistin
- Platosin
- Placis
- cis Platinum
- Platiblastin-S
- Cisplatin?
- Dichlorodiammineplatinum
- CIS-PLATINUM II
- Platinol-AQ VHA Plus
- diammine(dichloro)platinum
- Lopac-P-4394
- Platinum diamminodichloride
- Diamminodichloride, Platinum
- Cis-diammine-dichloroplatinum
- Cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum
- Cis-platinous Diamine Dichloride
- Cis-dichloroammine Platinum (II)
- L01XA01
- Platinum, Diaminedichloro-, cis-
- Cis-diamminedichloro Platinum (II)
- Cis-platinum II Diamine Dichloride
- Tox21_500918
- NCGC00015812-01
- NCGC00094229-01
- NCGC00094229-02
- NCGC00162292-01
- NCGC00162292-02
- NCGC00162292-05
- NCGC00178241-13
- NCGC00261603-01
- BC164315
Cisplatin is approved to be used alone or with other drugs to treat:
• Bladder cancer. It is used alone in patients with advanced cancer that cannot be treated with other therapies, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
• Ovarian cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. It is used with other drugs in patients who have already had surgery or radiation therapy. It is used alone in patients whose cancer has not gotten better with standard chemotherapy and who have not received previous cisplatin.
• Testicular cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. It is used with other drugs in patients who have already had surgery or radiation therapy.
Cisplatin is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.
15-16 L/h/m^2 [total body clearance, 7-hour infusion of 100 mg/m^2]
62 mL/min/m^2 [renal clearance, 2-hour infusion of 100 mg/m^2]
50 mL/min/m^2 [renal clearance, 6- to 7-hour infusion of 100 mg/m^2] The renal clearance of free (ultrafilterable) platinum also exceeds the glomerular filtration rate indicating that cisplatin or other platinum-containing molecules are actively secreted by the kidneys. The renal clearance of free platinum is nonlinear and variable and is dependent on dose, urine flow rate, and individual variability in the extent of active secretion and possible tubular reabsorption.




H300+H310 (21.4%): Fatal if swallowed or in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, oral; acute toxicity, dermal]
H300 (99%): Fatal if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral]
H310 (23.3%): Fatal in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal]
H317 (39.8%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin]
H318 (58.3%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H319 (39.8%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H334 (40.8%): May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled [Danger Sensitization, respiratory]
H335 (11.7%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation]
H340 (38.8%): May cause genetic defects [Danger Germ cell mutagenicity]
H350 (91.3%): May cause cancer [Danger Carcinogenicity]
H360 (36.9%): May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity]
P203, P233, P260, P261, P262, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P272, P280, P284, P301+P316, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P305+P354+P338, P316, P317, P318, P319, P321, P330, P333+P317, P337+P317, P342+P316, P361+P364, P362+P364, P403, P403+P233, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 103 reports by companies from 18 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Acute Tox. 2 (99%)
Acute Tox. 2 (23.3%)
Skin Sens. 1 (39.8%)
Eye Dam. 1 (58.3%)
Eye Irrit. 2 (39.8%)
Resp. Sens. 1 (40.8%)
STOT SE 3 (11.7%)
Muta. 1B (38.8%)
Carc. 1B (91.3%)
Repr. 1B (36.9%)
Hazard Traits - Carcinogenicity
Authoritative List - IARC Carcinogens - 2A; NTP RoC - reasonable; Prop 65
Report - regardless of intended function of ingredient in the product
The platinum compounds generally are not considered to be hepatotoxic, but cisplatin has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations during therapy. These elevations are usually mild, self-limited and asymptomatic, rarely requiring dose modification. There have been only rare case reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to cisplatin. In one instance, steatosis and necrosis (steatohepatitis) was found by liver biopsy in a patient who developed liver enzyme elevations 4 weeks after starting a regimen of cisplatin. In another instance, hepatocellular liver injury was described. The number of cases of liver injury attributed to cisplatin have been too few to characterize the liver injury clinically. Autoimmune and immunoallergic features have not been described and cases have all been self-limited. Cisplatin is usually given in combination with other antineoplastic agents and adverse events that occur with these combinations cannot always be attributed to cisplatin. In this regard, individual case reports of reactivation of hepatitis B, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and severe hyperammonemic coma (without liver injury) have been described after chemotherapeutic regimens that include cisplatin and other platinum coordination complexes such as carboplatin and oxaliplatin.
Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Volume 26: (1981) Some Antineoplastic and Immunosuppressive Agents
Volume Sup 7: Overall Evaluations of Carcinogenicity: An Updating of IARC Monographs Volumes 1 to 42, 1987; 440 pages; ISBN 92-832-1411-0 (out of print)
IARC Carcinogen - Class 2: International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies chemicals as probable (2a), or possible (2b) human carcinogens.
NTP Carcinogen - Reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
- California Safe Cosmetics Program (CSCP) Product Database
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/Platinum, diamminedichloro-https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=26035-31-4
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticecisplatin (EC: 239-733-8)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/52479
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- LiverTox
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- NCI Investigational Drugs
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- WHO Model Lists of Essential MedicinesLICENSEPermission from WHO is not required for the use of WHO materials issued under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Intergovernmental Organization (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO) license.https://www.who.int/about/policies/publishing/copyright
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational DiseasesLICENSECopyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission.https://haz-map.com/AboutCisplatinhttps://haz-map.com/Agents/1877
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)LICENSEMaterials made available by IARC/WHO enjoy copyright protection under the Berne Convention for the Protection of Literature and Artistic Works, under other international conventions, and under national laws on copyright and neighbouring rights. IARC exercises copyright over its Materials to make sure that they are used in accordance with the Agency's principles. All rights are reserved.https://publications.iarc.fr/Terms-Of-Use
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.html
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NCI Cancer Drugs
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe)
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Wikidata
- Wikipedia
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAntineoplastic Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000970Cross-Linking Reagentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68003432Radiation-Sensitizing Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68011838
- PubChem
 CID 222 (Ammonia)
CID 222 (Ammonia) CID 2770 (Platinum(II) chloride)
CID 2770 (Platinum(II) chloride)