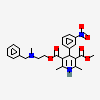
Nicardipine
- nicardipine
- 55985-32-5
- Nicardipino
- Nicardipinum
- Perpidine
- Create:2005-03-25
- Modify:2025-01-18
 Nicardipine Hydrochloride (has salt form).
Nicardipine Hydrochloride (has salt form).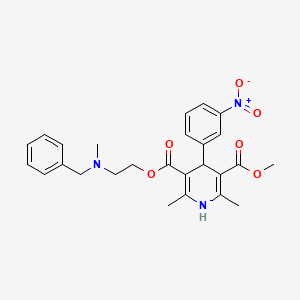
- Antagonil
- Cardene
- Cardene I.V.
- Cardene SR
- Dagan
- Flusemide
- Hydrochloride, Nicardipine
- LA, Nicardipine
- Lecibral
- Lincil
- Loxen
- Lucenfal
- Nicardipine
- Nicardipine Hydrochloride
- Nicardipine LA
- Nicardipino Ratiopharm
- Nicardipino Seid
- Perdipine
- Ridene
- Vasonase
- Y 93
- Y-93
- Y93
- nicardipine
- 55985-32-5
- Nicardipino
- Nicardipinum
- Perpidine
- Nicardipinum [INN-Latin]
- Nicardipino [INN-Spanish]
- Nicardipine (stn)
- (+/-)-Nicardipine
- CHEBI:7550
- EINECS 259-932-3
- Cardene
- Nicardipine (INN)
- BRN 0504321
- DTXSID6023363
- UNII-CZ5312222S
- YC-93 (free base)
- Cardene (TN)
- CZ5312222S
- DTXCID903363
- 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 2-(benzylmethylamino)ethyl methyl ester
- 3-(2-(benzyl(methyl)amino)ethyl) 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 5-O-[2-[benzyl(methyl)amino]ethyl] 3-O-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 2-(Benzylmethylamino)ethyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-(methyl(phenylmethyl)amino)ethyl ester
- NCGC00015747-03
- NICARDIPINE [INN]
- Nicardipinum (INN-Latin)
- Nicardipino (INN-Spanish)
- Nicardipine [INN:BAN]
- 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-[methyl(phenylmethyl)amino]ethyl ester
- Methyl 2-(benzyl-methyl-amino)ethyl2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 3,5-PYRIDINEDICARBOXYLIC ACID, 1,4-DIHYDRO-2,6-DIMETHYL-4-(3-NITROPHENYL)-, 3-METHYL 5-(2-(METHYL(PHENYLMETHYL)AMINO)ETHYL) ESTER
- 3-{2-[benzyl(methyl)amino]ethyl} 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- CAS-55985-32-5
- nicardipina
- nicardipineum
- rac-nicardipine
- racemic nicardipine
- (RS)-nicardipine
- (+-)-nicardipine
- (R,S)-nicardipine
- YC-93 free base
- Spectrum_001372
- NICARDIPINE [MI]
- Prestwick0_000383
- Prestwick1_000383
- Prestwick2_000383
- Prestwick3_000383
- Spectrum2_001415
- Spectrum3_001452
- Spectrum4_000422
- Spectrum5_001320
- NICARDIPINE [VANDF]
- CHEMBL1484
- CBiol_001802
- Lopac0_000809
- Oprea1_436998
- SCHEMBL34277
- BSPBio_000565
- BSPBio_001389
- BSPBio_002943
- KBioGR_000109
- KBioGR_000744
- KBioSS_000109
- KBioSS_001852
- NICARDIPINE [WHO-DD]
- BIDD:GT0621
- DivK1c_000540
- SPBio_001490
- SPBio_002486
- BPBio1_000623
- GTPL2559
- CHEMBL3302409
- KBio1_000540
- KBio2_000109
- KBio2_001852
- KBio2_002677
- KBio2_004420
- KBio2_005245
- KBio2_006988
- KBio3_000217
- KBio3_000218
- KBio3_002443
- C08CA04
- CHEBI:180905
- NINDS_000540
- Bio1_000088
- Bio1_000577
- Bio1_001066
- Bio2_000109
- Bio2_000589
- HMS1791F11
- HMS1989F11
- HMS2089C09
- HMS3886G17
- BCP21397
- EX-A4680
- Tox21_110211
- BDBM50101815
- s5255
- AKOS001637090
- AKOS040744847
- Tox21_110211_1
- CCG-204893
- CS-3685
- DB00622
- SDCCGSBI-0050786.P004
- IDI1_000540
- IDI1_033859
- NCGC00015747-02
- NCGC00015747-04
- NCGC00015747-05
- NCGC00015747-06
- NCGC00015747-07
- NCGC00015747-09
- NCGC00015747-11
- NCGC00015747-18
- NCGC00162262-01
- NCGC00162262-02
- NCGC00162262-03
- NCGC00162262-04
- 1ST10213
- AC-19947
- AC-36578
- AS-56335
- BN166182
- HY-12515
- methyl 2-[methyl(phenylmethyl)amino]ethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- PD033077
- PD156023
- SBI-0050786.P003
- DB-052833
- AB00514658
- NS00002168
- A12641
- C07264
- D08270
- EN300-708781
- AB00053604-03
- AB00053604_04
- AB00053604_05
- L000715
- Q729213
- BRD-A26711594-001-02-7
- BRD-A26711594-003-05-6
- BRD-A26711594-003-06-4
- BRD-A26711594-003-08-0
- BRD-A26711594-003-10-6
- 106664-28-2
- 2,6-dimethyl-3-methoxycarbonyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-5-[ 2-(N-benzyl-N-methylamino)ethoxycarbonyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine
- 2-(benzyl(methyl)amino)ethyl methyl (4RS)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 2-(Benzylmethylamino) ethyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
- 2-(BENZYLMETHYLAMINO)ETHYL METHYL 1,4-DIHYDRO-2,6-DIMETHYL-4-(M-NITROPHENYL)-3,5-PYRIDINEDICARBOXYLATE
- 2-(Benzylmethylamino)ethyl methyl 1.4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
- 2-(N-benzyl-N-methylamino)ethyl methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4(m-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 2-[benzyl(methyl)amino]ethyl methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- 3,5_Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-(methyl(phenylmethyl)amino)ethyl ester
- 3-(2-[Benzyl(methyl)amino]ethyl) 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate #
- 5-O-[2-[Benzyl(methyl)amino]ethyl] 3-O-methyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- O5-methyl O3-[2-(methyl-(phenylmethyl)amino)ethyl] 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
208.67 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
212.9 Ų [M+K]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
210.83 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
108.0218 100
162.0563 56.22
79.019 55.18
104.0507 49.70
224.0718 48.36
122.0247 100
108.0217 45.60
224.0717 31.75
95.0139 23.09
164.0717 21.72
480.213 999
166.1226 411
315.0974 272
148.112 155
359.1236 71
315.0973 999
148.112 549
166.1226 302
359.1237 245
91.0542 223
 Nicardipine Hydrochloride (has salt form)
Nicardipine Hydrochloride (has salt form)- Cytoplasm
- Membrane

P264, P270, P301+P317, P330, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 2 reports by companies from 1 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
IMAP assessments - 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-[methyl(phenylmethyl)amino]ethyl ester: Environment tier I assessment
IMAP assessments - 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-[methyl(phenylmethyl)amino]ethyl ester: Human health tier I assessment
Nicardipine has not been associated with significant increases in rates of elevations in serum aminotransferase or alkaline phosphatase levels, even with chronic long term therapy. Cases of idiosyncratic liver injury have not been published, although a single instance of marked serum enzyme elevations without jaundice has been reported with the use of intravenous nicardipine. Large trials of nicardipine have not mentioned liver injury, serum aminotransferase elevations or discontinuation of drug because of hepatic adverse events. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice due to nicardipine must be rare, if it occurs at all.
Likelihood Score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
The reason why some calcium channel blockers are known to cause idiosyncratic liver injury while others such as nicardipine do not, is unknown.
Drug Class: Cardiovascular Agents, Calcium Channel Blockers
Other Drugs in the Subclass, Calcium Channel Blockers: Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Felodipine, Isradipine, Nifedipine, Nimodipine, Nisoldipine, Verapamil
M Chen, V Vijay, Q Shi, Z Liu, H Fang, W Tong. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Drug Discovery Today, 16(15-16):697-703, 2011. PMID:21624500 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.05.007
M Chen, A Suzuki, S Thakkar, K Yu, C Hu, W Tong. DILIrank: the largest reference drug list ranked by the risk for developing drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21(4): 648-653. PMID:26948801 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.015
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Because of the low levels of nicardipine in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. No special precautions are required.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=ZBBHBTPTTSWHBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=LLJIPIVXTNFKEG-UHFFFAOYSA-O
- Avoid grapefruit products.
- Take with or without food. The absorption is unaffected by food.
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-[methyl(phenylmethyl)amino]ethyl esterhttps://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusNicardipine [INN:BAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0055985325ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_useNicardipinehttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00622
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-notice2-(benzylmethylamino)ethyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylatehttps://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.054.4662-(benzylmethylamino)ethyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate (EC: 259-932-3)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/47790
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingNicardipinehttp://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014760HMDB0014760_msms_2228744https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014760#spectra
- CCSbaseCCSbase Classificationhttps://ccsbase.net/
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- LiverTox
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloadsNICARDIPINEhttps://www.dgidb.org/drugs/rxcui:7396
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) DatasetLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NicardipineNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-lawNicardipinehttp://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.keg
- MassBank Europe
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- SpectraBaseNicardipinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/FElLR6gLknhNicardipinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/2hjvCiIlDCANicardipinehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/Dw7Uy3dbwgDNICARDIPINE;2,6-DIMETHYL-3-METHOXYCARBONYL-5-(N-METHYL-N-PHENYLMETHYL)-AMINOETHOXYCARBONYL-4-(3-NITROPHENYL)-1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/LjoOrUsJkV7NICARDIPINE;2,6-DIMETHYL-3-METHOXYCARBONYL-5-(N-METHYL-N-PHENYLMETHYL)-AMINOETHOXYCARBONYL-4-(3-NITROPHENYL)-1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/63O4I5pAwsh
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmlnicardipinehttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/7396
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policiesnicardipinehttps://www.pharmgkb.org/chemical/PA450620
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/aboutnicardipinehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/NPG251WB2WCQ
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidatanicardipinehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q729213
- WikipediaCholine theophyllinatehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Choline_theophyllinateNicardipinehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicardipine
- Wiley
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlNicardipinehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68009529Calcium Channel Blockershttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68002121Antihypertensive Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000959Vasodilator Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68014665
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 388479250https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/388479250SID 470933245https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/470933245
- NCBI