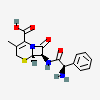
Cephalexin
- cephalexin
- Cefalexin
- 15686-71-2
- Keflex
- Cephacillin
- Create:2005-06-24
- Modify:2025-01-18
105879-42-3 (mono-hydrochloride, mono-hydrate)
105879-42-3 (mono-hydrochloride,mono-hydrate)
23325-78-2 (mono-hydrate)
38932-40-0 (mono-hydrochloride salt)
66905-57-5 (di-hydrate)
- 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-((aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-, (6R-(6alpha,7beta(R*)))-
- Cefalexin
- Cephalexin
- Cephalexin Dihydride
- Cephalexin Hemihydrate
- Cephalexin Hydrochloride
- Cephalexin Monohydrate
- Cephalexin Monohydrochloride
- Cephalexin Monohydrochloride, Monohydrate
- Cephalexin, (6R-(6alpha,7alpha(R*)))-Isomer
- Cephalexin, (6R-(6alpha,7beta(S*)))-Isomer
- Cephalexin, (6R-(6alpha,7beta))-Isomer
- Cephalexin, Monosodium Salt
- Cephalexin, Monosodium Salt, (6R-(6alpha,7beta))-Isomer
- Ceporexine
- Palitrex
- cephalexin
- Cefalexin
- 15686-71-2
- Keflex
- Cephacillin
- Ceporexin
- Cepexin
- Carnosporin
- Cefaleksin
- Cefalexina
- Cefalexine
- Cephalexine
- Cephalexinum
- Ceporexine
- Mamalexin
- Sinthecillin
- Uphalexin
- Alsporin
- Celexin
- Cepastar
- Ceporex
- Durantel
- Felexin
- Pyassan
- Keflet
- Alcephin
- Cefablan
- Cefalexinum
- Cefaloto
- Cephanasten
- Cefadin
- Ceforal
- Tepaxin
- Cefadina
- Cefaseptin
- Cephaxin
- Cophalexin
- Erocetin
- Factagard
- Inphalex
- Kefalospes
- Kekrinal
- Lafarine
- Lexibiotico
- Lopilexin
- Madlexin
- Mamlexin
- Medoxine
- Neolexina
- Ortisporina
- Sartosona
- Sencephalin
- Servispor
- Sialexin
- Sporicef
- Sporidex
- Tokiolexin
- Zozarine
- Alexin
- Cefadal
- Cefalin
- Cefovit
- Cephin
- Ibilex
- Ibrexin
- Kefolan
- Kidolex
- Larixin
- Lenocef
- Lonflex
- Neokef
- Oracef
- Oriphex
- Oroxin
- Ospexin
- Pectril
- Roceph
- Sanaxin
- Sepexin
- Syncle
- Synecl
- Voxxim
- Winlex
- Cefax
- Cepol
- Check
- Fexin
- Nufex
- Syncl
- Cephalexin anhydrous
- Ceporex Forte
- Cefa-iskia
- Ceporexin-E
- Durantel DS
- L-Keflex
- Cefalessina
- Ed A-Ceph
- Novolexin
- Palitrex
- Biocef
- Keforal
- Roceph Distab
- Cefalessina [DCIT]
- Panixine Disperdose
- Ceflax
- Cefalexine [INN-French]
- Cefalexinum [INN-Latin]
- Lilly 66873
- Cefalexina [INN-Spanish]
- Cefalexin anhydrous
- Anhydrous cephalexin
- Cerexin
- Optocef
- Taicelexin
- Cephalexin hydrate
- 7-(D-alpha-Aminophenylacetamido)desacetoxycephalosporanic acid
- CEFADROS
- CEPHAMASTEN
- EFALEXIN
- GARASIN
- IWALEXIN
- KEFLORIDINA
- ORACOCIN
- Cerexins
- CHEBI:3534
- HSDB 3022
- 7-beta-(D-alpha-Amino-alpha-phenylacetylamino)-3-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
- Anhydrous cefalexin
- EINECS 239-773-6
- Cefalexin [INN]
- Ceffanex
- UNII-5SFF1W6677
- BRN 0965503
- DTXSID9022780
- LILLY-66873
- 5SFF1W6677
- 7-(D-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-delta3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
- CEX
- NSC-758162
- SQ 20248
- CHEMBL1727
- DTXCID002780
- (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- NSC 758162
- (6R,7R)-7-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- NCGC00159522-02
- S-6437
- (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-(((2R)-aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-, (6R,7R)-
- 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(2R)-aminophenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, (6R,7R)-
- L-Cephalexin
- Cephalexin 1-hydrate
- CEPHALEXIN (USP-RS)
- 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-((aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-, (6R-(6alpha,7beta(R*)))-
- Cephalexin [USAN:BAN]
- (6R,7R)-7-[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- SMR000338536
- CEPHALEXIN (USP MONOGRAPH)
- S 6437
- CAS-15686-71-2
- Keflex (TN)
- 34632-04-7
- CEFALEXIN MONOHYDRATE (EP IMPURITY)
- CEFALEXIN MONOHYDRATE (EP MONOGRAPH)
- Amplex
- 7beta-((2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
- 7beta-[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3-methyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
- Cefalexin,(S)
- (6R,7R)-7-(((2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl)amino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-AMINO-2-PHENYLACETAMIDO)-3-METHYL-8-OXO-5-THIA-1-AZABICYCLO(4.2.0)OCT-2-ENE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID
- MFCD00056877
- Cefalexin (JP18)
- Cephalexin (Standard)
- Cephalexin (Cefalexin)
- CEFALEXIN [JAN]
- CEPHALEXIN [MI]
- Prestwick0_000358
- Prestwick1_000358
- Prestwick2_000358
- Prestwick3_000358
- CEPHALEXIN [HSDB]
- Epitope ID:117132
- CEFALEXIN [WHO-DD]
- SCHEMBL2961
- 7-(D-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-delta (sup 3)-cephem-4- carboxylic acid
- BSPBio_000455
- (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-en-2-carbonsaeure
- MLS000759527
- MLS001424036
- SPBio_002376
- BPBio1_000501
- GTPL4832
- HY-B0200R
- BCPP000289
- HMS2051A04
- HY-B0200
- Tox21_111740
- BDBM50139896
- AKOS004119846
- Tox21_111740_1
- BCP9000509
- CCG-100831
- CS-2137
- DB00567
- NC00081
- 7-(D-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-delta (sup 3)-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
- NCGC00159522-03
- NCGC00159522-05
- (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenyl-acetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-8-oxo-, D-
- DS-11971
- NS00098606
- Cefalexin, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard
- C-2660
- C06895
- D00263
- H10995
- Cefalexin 1000 microg/mL in Acetonitrile:Water
- Cephalexin, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only
- Q411417
- Q-200819
- BRD-K90733503-001-05-3
- BRD-K90733503-001-06-1
- BRD-K90733503-001-07-9
- BRD-K90733503-002-03-6
- Cefalexin, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard
- Z1880962282
- Cephalexin monohydrate, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only
- 7-(D-alpha-amino-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-3-cepheme-4-carboxylic acid
- Cephalexin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
- 7-(D-.ALPHA.-AMINO-.ALPHA.-PHENYLACETAMIDO)-3-METHYL-3-CEPHEM-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID
- 7-(D-alpha-AMINO-alpha-PHENYLACETAMIDO)-3-METHYL-3-CEPHEM-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID
- (6R,7R)-7-((2R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetylamino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenyl-acetylamino)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
- 5-THIA-1-AZABICYCLO(4.2.0)OCT-2-ENE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID, 7-((AMINOPHENYLACETYL)AMINO)-3-METHYL-8-OXO-,(6R-(6.ALPHA.,7.BETA.(R*)))-
182.19 Ų [M+K]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
182.91 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
163.36 Ų [M+H-H2O]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
178.02 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
183.1 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with Waters Major Mix]
186.9 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with Waters Major Mix]
158.0278 100
174.0556 56.16
192.0481 19.21
106.0663 11.66
175.0587 9.36
158.0278 100
174.0556 56.16
192.0481 19.21
106.0663 11.66
175.0587 9.36
158.0278 999
174.0556 561
192.0481 191
106.0663 116
175.0587 93
158.0278 100
174.0556 56.16
192.0481 19.21
106.0663 11.66
175.0587 9.36
189.066025 100
173.072189 91.61
142.032211 59.55
268.109863 54.77
109.075684 44.98
189.066055 100
135.055939 14.35
166.033615 10.92
268.109741 10.69
173.048538 9.91
- Extracellular
- Membrane
Use (kg; approx.) in Germany (2009): >1000
Use (kg; exact) in Germany (2009): 2020
Use (kg) in USA (2002): 148000
Consumption (g per capita; approx.) in Germany (2009): 0.0122
Consumption (g per capita; exact) in Germany (2009): 0.0247
Consumption (g per capita) in the USA (2002): 0.525
Excretion rate: 0.8
Calculated removal (%): 22


H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin]
H334 (100%): May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled [Danger Sensitization, respiratory]
P233, P260, P261, P271, P272, P280, P284, P302+P352, P304+P340, P321, P333+P317, P342+P316, P362+P364, P403, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 75 reports by companies from 5 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Skin Sens. 1 (100%)
Resp. Sens. 1 (100%)
IMAP assessments - 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, [6R-[6.alpha.,7.beta.(R*)]]-: Human health tier I assessment
IMAP assessments - 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, [6R-[6.alpha.,7.beta.(R*)]]-: Environment tier I assessment
M Chen, V Vijay, Q Shi, Z Liu, H Fang, W Tong. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Drug Discovery Today, 16(15-16):697-703, 2011. PMID:21624500 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.05.007
M Chen, A Suzuki, S Thakkar, K Yu, C Hu, W Tong. DILIrank: the largest reference drug list ranked by the risk for developing drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21(4): 648-653. PMID:26948801 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.015
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Limited information indicates that maternal cephalexin produces low levels in milk that are usually not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Cephalexin is an alternative for the treatment of mastitis. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. A rare case of a severe allergic reaction occurred in an infant previously exposed to intravenous cefazolin whose mother began taking cephalexin while breastfeeding. Cephalexin is acceptable in nursing mothers.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
In a prospective follow-up study, 7 nursing mothers reported taking cephalexin (dosage not specified). Two mothers reported diarrhea in their infants. No rashes or candidiasis were reported among the exposed infants.
A prospective, controlled study asked mothers who called an information service about adverse reactions experience by their breastfed infants. One of 11 cephalexin-exposed infants reportedly developed diarrhea during maternal cephalexin therapy.
A woman received intravenous cephalothin 1 g every 6 hours for 3 days. Her breastfed infant had a green liquid stool, severe diarrhea, discomfort and crying. The mother's drug regimen was then changed to oral cephalexin 500 mg plus oral probenecid 500 mg 4 times daily for another 16 days. The infant continued to have diarrhea during this time. The authors rated the diarrhea as probably related to cephalexin in milk.
A 4-month-old infant was treated with intravenous cefazolin for a urinary tract infection. Nine days after being discharged and cefazolin discontinuation, the infant developed a blistering rash over most of the body that was diagnosed as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). The infant was being breastfed (extent unspecified) by his mother who had begun cephalexin 2 days prior to the onset of symptoms. A lymphocyte transformation test performed 4 weeks after treatment for TEN was completed found sensitization to both cefazolin and cephalexin. The infant's reaction was probably caused by cephalexin in breastmilk after initial sensitization and subsequent cross-reaction to cefazolin.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◈ What is cephalexin?
Cephalexin is an antibiotic medication that has been used to treat infections such as Staphylococcus aureus (Staph) and Escherichia coli (E. coli). Some brand names for cephalexin are Keflex® and Keftab®.Sometimes when people find out they are pregnant, they think about changing how they take their medication, or stopping their medication altogether. However, it is important to talk with your healthcare providers before making any changes to how you take your medication. Your healthcare providers can talk with you about the benefits of treating your condition and the risks of untreated illness during pregnancy.Having certain infections (such as a Staph or E. coli infection )during pregnancy can increase the chance for pregnancy-related problems or infections in a newborn baby. MotherToBaby has fact sheets on Staph and E. coli infections here: https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/staphylococcus-aureus-pregnancy/ and https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/e-coli-pregnancy/.
◈ I take cephalexin. Can it make it harder for me to get pregnant?
Studies have not been done in humans to see if cephalexin can make it harder to get pregnant. In animal studies, cephalexin did not affect fertility (ability to get pregnant).
◈ Does taking cephalexin increase the chance of miscarriage?
Miscarriage is common and can occur in any pregnancy for many different reasons. In a study of 262 people who took cephalexin during pregnancy, there was no increase in miscarriages compared to a similar group of people who did not take cephalexin.
◈ Does taking cephalexin increase the chance of birth defects?
Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. Information on the use of cephalexin in pregnancy is limited. In a study of 262 people who took cephalexin during pregnancy, there was no increased chance for birth defects above the background risk.
◈ Does taking cephalexin in pregnancy increase the chance of other pregnancy-related problems?
Studies have not been done to see if cephalexin increases the chance for pregnancy-related problems such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth).
◈ Does taking cephalexin in pregnancy affect future behavior or learning for the child?
Studies have not been done to see if cephalexin can cause behavior or learning issues for the child.
◈ Breastfeeding while taking cephalexin:
Cephalexin gets into breast milk in small amounts. In reports of 20 babies exposed to cephalexin through breast milk, 4 had diarrhea. There is one report of a baby getting a rash after being breastfed, due to a sensitivity to cephalexin. If you suspect the baby has any symptoms (such as diarrhea or rash), contact the child’s healthcare provider. Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about all your breastfeeding questions.
◈ If a male takes cephalexin, could it affect fertility or increase the chance of birth defects?
Studies have not been done to see if cephalexin could affect male fertility (ability to get partner pregnant) or increase the chance of birth defects above the background risk. Some infections, such as Staph or E.coli, might affect male fertility. In general, exposures that fathers or sperm donors have are unlikely to increase risks to a pregnancy. For more information, please see the MotherToBaby fact sheet Paternal Exposures at https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/paternal-exposures-pregnancy/.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=ZAIPMKNFIOOWCQ-UEKVPHQBSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, [6R-[6.alpha.,7.beta.(R*)]]-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusCephalexin [USAN:BAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0015686712ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_useCephalexinhttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00567
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeCephalexin hydratehttps://echa.europa.euCefalexin (EC: 239-773-6)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/122324Cephalexin hydrate (EC: 998-943-4)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/386006
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingCEPHALEXIN ANHYDROUShttps://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/5SFF1W6677
- Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0014707_msms_440789https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014707#spectra
- New Zealand Environmental Protection Authority (EPA)LICENSEThis work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International licence.https://www.epa.govt.nz/about-this-site/general-copyright-statement/5-Thia-1-azabicyclo4.2.0oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-(2R)-aminophenylacetylamino-3-methyl-8-oxo-, (6R,7R)-https://www.epa.govt.nz/industry-areas/hazardous-substances/guidance-for-importers-and-manufacturers/hazardous-substances-databases/
- CCSbaseCCSbase Classificationhttps://ccsbase.net/
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/CefalexinNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingCEPHALEXIN ANHYDROUShttps://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/browse-drug-classes.cfmFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- LOTUS - the natural products occurrence databaseLICENSEThe code for LOTUS is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.https://lotus.nprod.net/LOTUS Treehttps://lotus.naturalproducts.net/
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licenceCEPHALEXIN ANHYDROUShttps://platform.opentargets.org/drug/CHEMBL1727
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloadsCEPHALEXIN ANHYDROUShttps://www.dgidb.org/drugs/rxcui:1299782
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- DailyMed
- Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) DatasetLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Mother To Baby Fact SheetsLICENSECopyright by OTIS. This work is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/about/copyright/
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingPANIXINE DISPERDOSEhttps://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/
- WHO Model Lists of Essential MedicinesLICENSEPermission from WHO is not required for the use of WHO materials issued under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Intergovernmental Organization (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO) license.https://www.who.int/about/policies/publishing/copyright
- EPA Chemical and Products Database (CPDat)EPA CPDat Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/chemical-and-products-database-cpdat
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Approved Animal Drug Products (Green Book)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegAntiinfectiveshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08307.kegDrugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeiahttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08311.keg
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- MassBank Europe
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmlcephalexinhttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/2231cephalexin anhydroushttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/1299782
- NMRShiftDB
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- SpectraBase
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidatacephalexinhttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q411417
- Wikipedia
- Wiley
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAnti-Bacterial Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000900
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 404007949https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/404007949
- NCBI