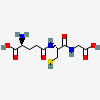
Glutathione
- glutathione
- 70-18-8
- L-Glutathione
- L-Glutathione reduced
- Glutathion
- Create:2005-06-08
- Modify:2024-12-28
 Glutathione sodium (is active moiety of); Glutathione; nonapeptide-1 (component of) ... View More ...
Glutathione sodium (is active moiety of); Glutathione; nonapeptide-1 (component of) ... View More ...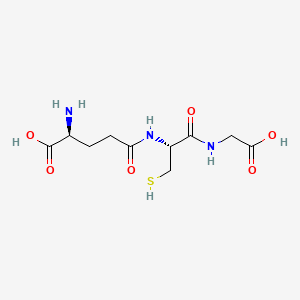

- gamma L Glu L Cys Gly
- gamma L Glutamyl L Cysteinylglycine
- gamma-L-Glu-L-Cys-Gly
- gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-Cysteinylglycine
- Glutathione
- Glutathione, Reduced
- Reduced Glutathione
- glutathione
- 70-18-8
- L-Glutathione
- L-Glutathione reduced
- Glutathion
- Isethion
- Tathion
- Glutathione-SH
- Glutinal
- Tathione
- reduced glutathione
- Deltathione
- Neuthion
- Copren
- Glutide
- Triptide
- Ledac
- Glutatione
- Glutatiol
- GSH
- Panaron
- Glutathione SH
- L-Glutatione
- Glutathione (reduced)
- glutathione reduced
- Agifutol S
- L-Glutathione, reduced
- L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- Glutathione [JAN]
- 5-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- Glutham
- gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine
- Reduced l-glutathione
- CCRIS 2094
- gamma-L-Glutamylcysteinylglycine
- glutathione red
- Aec glutathione
- Glycine, L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-
- red. glutathione
- Bakezyme RX
- UNII-GAN16C9B8O
- (S)-2-Amino-5-(((R)-1-((carboxymethyl)amino)-3-mercapto-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoic acid
- EINECS 200-725-4
- GAN16C9B8O
- gamma-Glutamylcysteinylglycine
- NSC 400639
- L-Glutathione reduce
- (2S)-2-amino-5-[[(2R)-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxo-3-sulfanylpropan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid
- DTXSID6023101
- CHEBI:16856
- N-(N-gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine
- N-(N-L-gamma-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine
- glycine, N-(N-L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)-
- Glutathione (Reduced type)
- L-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- L-Glutathione (reduced form)
- (2S)-2-amino-4-{[(1R)-1-[(carboxymethyl)carbamoyl]-2-sulfanylethyl]carbamoyl}butanoic acid
- DTXCID903101
- BenzenaMine, 2-[(4-Methoxyphenyl)Methoxy]-
- 106272-20-2
- 95687-20-0
- GLUTATHIONE (II)
- GLUTATHIONE [II]
- MFCD00065939
- GLUTATHIONE (MART.)
- GLUTATHIONE [MART.]
- GLUTATHIONE (USP-RS)
- GLUTATHIONE [USP-RS]
- [Glu(-Cys)]n-Gly
- GLUTATHIONE (EP MONOGRAPH)
- GLUTATHIONE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- C10H17N3O6S
- NSC400639
- N5-((R)-1-((carboxymethyl)amino)-3-mercapto-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-L-glutamine
- CAS-70-18-8
- (S)-2-Amino-5-((R)-1-(carboxymethylamino)-3-mercapto-1-oxopropan-2-ylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Glutathione, Reduced
- Glutathione; l-gamma-Glutamyl-l-cysteinylglycine
- SR-05000002567
- Glutathione [BAN:JAN]
- L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine
- L-Glutathione reduced form
- phytochelatins
- ReadiSorb
- 1lbk
- NSC-400639
- NCGC00094976-01
- gamma-Glu-Cys-Gly
- Tathion (TN)
- Glutathione (JP18)
- Spectrum_000419
- 1oe7
- 1oe8
- 1r4w
- C(N-.gamma.Glu-)G
- GLUTATHIONE, L-
- Glycine, L-.gamma.-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-
- GLUTATHIONE [MI]
- Reduced Glutathione,(S)
- Spectrum2_001500
- Spectrum3_000946
- Spectrum4_001056
- Spectrum5_000940
- ?-Glutamylcysteinylglycine
- Glutathione, Reduced Form
- bmse000185
- bmse000952
- bmse000956
- GLUTATHIONE [VANDF]
- Cys(N-.gamma.Glu-)-Gly
- SCHEMBL9167
- CHEMBL1543
- GLUTATHIONE [WHO-DD]
- KBioGR_001352
- KBioSS_000899
- MLS001333069
- DivK1c_000075
- SPECTRUM1502248
- SPBio_001519
- gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine
- GTPL6737
- ?-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- L-?-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine
- L-Glutathione reduced, 97.0%
- CHEBI:60836
- HMS500D17
- KBio1_000075
- KBio2_000899
- KBio2_003467
- KBio2_006035
- KBio3_002012
- (gamma-Glutamylcysteine)n-glycine
- L-g-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine
- NINDS_000075
- HMS1921N22
- Pharmakon1600-01502248
- HARUTO HANGOVER DEFENCEPATCH
- HY-D0187
- L-Glutathione reduced, >=98.0%
- Tox21_111371
- BDBM50422268
- CCG-38876
- NSC758199
- s4606
- AKOS015999135
- Tox21_111371_1
- CS-7948
- DB00143
- NSC-758199
- SDCCGMLS-0066687.P001
- .gamma.-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine
- IDI1_000075
- N-(N-L-?-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine
- Pharm Biol 11: 539 (1968)
- SMP1_000247
- NCGC00264046-02
- DS-14675
- GSH;gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine
- SMR000857220
- SBI-0051743.P002
- L-Glutathione reduced, BioXtra, >=98.0%
- G0074
- Glycine, N-(N-L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)
- N-(N-L-.gamma.-Glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine
- C00051
- C02471
- D00014
- EN300-311690
- G-3980
- P19615
- AB00443568_03
- Glutathione 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile:Water
- Q116907
- SR-05000002567-1
- SR-05000002567-2
- BRD-K69346723-001-04-8
- L-Glutathione reduced, Vetec(TM) reagent grade, >=98%
- Z2183947556
- Glutathione, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- Glutathione, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
- Glutathione, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
- L-Glutathione reduced, cell culture tested, BioReagent, >=98.0%, powder
- (2S)-2-AMINO-4-{[(1R)-1-[(CARBOXYMETHYL)CARBAMOYL]-2-SULFANYLETHYL]CARBAMOYLBUTANOIC ACID
- glutathione; l-glutathione reduced; 5-l-glutamyl-l-cysteinylglycine; gamma-l-glutamyl-l-cysteinylglycine; gsh
161.18 Ų [M+H-H2O]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
163.44 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
164.59 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
166.87 Ų [M+K]+ [CCS Type: TW; Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
164.24 Ų [M-H]- [CCS Type: DT; Method: stepped-field]
168.23 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT; Method: stepped-field]
167 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT; Method: single field calibrated with ESI Low Concentration Tuning Mix (Agilent)]
167.8 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT; Method: single field calibrated with ESI Low Concentration Tuning Mix (Agilent)]
164.8 Ų [M+Na-2H]- [CCS Type: DT; Method: single field calibrated with ESI Low Concentration Tuning Mix (Agilent)]
162.1 Ų [M-H]- [CCS Type: DT; Method: single field calibrated with ESI Low Concentration Tuning Mix (Agilent)]
162.8 Ų [M-H]-
164.8 Ų [M-2H+Na]-
167.1 Ų [M+Na]+
167.9 Ų [M+H]+
156.0 100
147.0 19.42
157.0 13.81
230.0 5.91
158.0 4.90
156.0 100
147.0 19.72
157.0 13.91
230.0 6.41
258.0 4.90
129.998 100
307.967 91.15
76.063 41.37
84.066 31.86
299.297 30.09
84.081 100
76.056 66
129.99 25
161.848 14.58
115.928 11.75
76.0228 100
84.0451 89.52
58.996 45.35
116.016 16.24
56.0505 10.78
76.0228 100
162.0215 47.33
84.0449 33.41
116.0164 24.01
130.0497 20.23
306 100
143 15.96
306 100
305 3.28
Glutathione sodium (is active moiety of)
- Glutathione; nonapeptide-1 (component of)
- Ascorbic acid; collagen, soluble, fish skin; glutathione (component of)
- Chamomile; glutathione; sanguinaria canadensis root; sodium sulfate (component of)
- Beta vulgaris; chelidonium majus; glutathione; lycopodium clavatum spore; petroselinum crispum; peumus boldus leaf; phosphorus; pork liver; silybum marianum seed; strychnos nux-vomica seed; taraxacum officinale (component of)
- Arctium lappa root; chelidonium majus whole; glutathione; lycopodium clavatum spore; milk thistle; petroselinum crispum whole; peumus boldus leaf; phosphorus; pork liver; strychnos nux-vomica seed; taraxacum officinale (component of)
- Arctostaphylos uva-ursi leaf; chondrodendron tomentosum root; echinacea angustifolia whole; glutathione; lycopodium clavatum spore; lytta vesicatoria; petroselinum crispum whole; pork kidney; solidago virgaurea flowering top (component of)
- alpha-TOCOPHEROL; ASCORBIC ACID; BETA CAROTENE; CHOLECALCIFEROL; CYANOCOBALAMIN; CYCLOASTRAGENOL; GLUTATHIONE; HERRING SPERM DNA; OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS; PANTOTHENIC ACID; RIBOFLAVIN; SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE RNA; SUS SCROFA PITUITARY GLAND, POSTERIOR; THIAMINE (component of)
- Arctostaphylos uva-ursi leaf; berberis vulgaris root bark; bryonia alba root; eutrochium purpureum root; glutathione; hydrangea arborescens root; mercuric chloride; petroselinum crispum; pork kidney; rubia tinctorum root; solidago virgaurea flowering top (component of)
- alpha-TOCOPHEROL; APPLE CIDER VINEGAR; ARSENIC TRIOXIDE; ASCORBIC ACID; ASCORBYL PALMITATE; ASTRAGALUS PROPINQUUS ROOT; BIANCAEA DECAPETALA ROOT BARK; BRYONIA ALBA ROOT; CITRUS PARADISI SEED; CURCUMIN; CURDLAN; DRIMIA MARITIMA BULB; GARLIC; GLUTATHIONE; MAITAKE; OLEA EUROPAEA LEAF; OREGANO; POTASSIUM CARBONATE; PYRIDOXINE; RUMEX CRISPUS ROOT; ZINC PICOLINATE (component of)
- alpha-KETOGLUTARIC ACID; alpha-LIPOIC ACID; alpha-TOCOPHEROL; gamma-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID; ACETALDEHYDE; ALFALFA; ASCORBYL PALMITATE; BARLEY; COBALT; CYSTEINE; FUCUS VESICULOSUS; GLUTATHIONE; IRON; MAGNESIUM FLUORIDE; MANGANESE GLUCONATE; METHIONINE; N,N-DIMETHYLGLYCINE; NASTURTIUM OFFICINALE; ORYZA SATIVA WHOLE; QUERCETIN; RAPHANUS SATIVUS; SELENIUM; SODIUM SELENITE; UBIDECARENONE; WHEAT; ZINC; ZINC PICOLINATE (component of)
- All Tissues
- Placenta
- Cytoplasm
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Extracellular
- Mitochondria
- 2-Hydroxyglutric Aciduria (D And L Form)
- 4-Hydroxybutyric Aciduria/Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency
- 5-oxoprolinase deficiency
- 5-Oxoprolinuria
- Acetaminophen Action Pathway
- Acetaminophen Metabolism Pathway
- Acetylsalicylic Acid Action Pathway
- Antipyrine Action Pathway
- Antrafenine Action Pathway
- Arachidonic Acid Metabolism
- Total 63 pathways, visit the HMDB page for details

P203, P280, P318, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 57 reports by companies from 4 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory.
Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria per 47 of 57 reports by companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website.
There are 3 notifications provided by 10 of 57 reports by companies with hazard statement code(s).
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=RWSXRVCMGQZWBV-WDSKDSINSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)Glycine, N-(N-L-.gamma.-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/Glycine, N-(N-L-.gamma.-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-inventory/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusGlutathione [BAN:JAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000070188ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_useGlutathionehttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00143
- DTP/NCILICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- EPA Chemicals under the TSCAGlycine, L-.gamma.-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tscaEPA TSCA Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeGlutathione (EC: 200-725-4)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/42985
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingGlutathionehttp://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000125HMDB0000125_cms_30368https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000125#spectra
- New Zealand Environmental Protection Authority (EPA)LICENSEThis work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International licence.https://www.epa.govt.nz/about-this-site/general-copyright-statement/
- BindingDBLICENSEAll data curated by BindingDB staff are provided under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/us/).https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/info.jsp
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)LICENSET3DB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (T3DB) and the original publication.http://www.t3db.ca/downloadsGlutathionehttp://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D4352
- CCSbaseCCSbase Classificationhttps://ccsbase.net/
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/GlutathioneNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- ChEBI
- E. coli Metabolome Database (ECMDB)
- LOTUS - the natural products occurrence databaseLICENSEThe code for LOTUS is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.https://lotus.nprod.net/Glutathionehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q116907LOTUS Treehttps://lotus.naturalproducts.net/
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- DailyMed
- ECI Group, LCSB, University of Luxembourgglutathione
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- West Coast Metabolomics Center-UC DavisGlutathione
- EPA Chemical and Products Database (CPDat)EPA CPDat Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/chemical-and-products-database-cpdat
- Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational DiseasesLICENSECopyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission.https://haz-map.com/AboutGlutathionehttps://haz-map.com/Agents/14425
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- SpectraBaseGlutathione, 5TMShttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/H2mE9HWF58KGlutathione, 5TMShttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/rOlmj5Zyagglutathionehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/3ZaCLT2wrf3L-Glutathione, reducedhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/66eXnVBd18eGLUTATHIONE(GSH PH:6.98)https://spectrabase.com/spectrum/EZjnbt4ujFYL-Glutathione, reducedhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/JzmKy9bkhm4Glutathione (reduced)https://spectrabase.com/spectrum/IpJYY4xRu0CL-Glutathione reducedhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/HlnpTm9VL6gGlutathione (reduced)https://spectrabase.com/spectrum/5NPOXBRB6YoGLUTATHIONEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/I8Cf5tq4oahL-Glutathione reducedhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/LrjmYCNATQY
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-lawL-Glutathione, reducedhttp://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#license
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlCompounds with biological roleshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08001.kegTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegDrugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeiahttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08311.kegAnimal drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08331.keg
- MarkerDBLICENSEThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.https://markerdb.ca/Glutathionehttps://markerdb.ca/chemicals/77
- Metabolomics Workbench
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmlglutathionehttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/4890
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policiesglutathionehttps://www.pharmgkb.org/chemical/PA449780
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/aboutglutathionehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/82VDMK4PDWYL
- Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe)
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB)LICENSEData files contained in the PDB archive (ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org) are free of all copyright restrictions and made fully and freely available for both non-commercial and commercial use. Users of the data should attribute the original authors of that structural data.https://www.rcsb.org/pages/policies
- Springer Nature
- The Cambridge Structural Database
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Wikidataglutathionehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q116907
- WikipediaGlutathionehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutathione
- Wiley
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlGlutathionehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68005978
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 403032690https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/403032690
- NCBI