Dimethylarsinate
PubChem CID
167250
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- Dimethylarsinate
- Cacodylate Ion
- Cacodylate
- 15132-04-4
- Arsinic acid, dimethyl-, ion(1-)
Molecular Weight
136.99 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Parent Compound
Dates
- Create:2004-09-16
- Modify:2025-01-11
Description
Dimethylarsinate is the arsenic oxoanion that is the conjugate base of dimethylarsinic acid. It is functionally related to an arsinate. It is a conjugate base of a dimethylarsinic acid.
Cacodylic acid is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2AsO2H. Derivatives of cacodylic acid, cacodylates, were frequently used as herbicides. For example, Agent Blue, one of the chemicals used during the Vietnam War, is a mixture of cacodylic acid and sodium cacodylate. Sodium cacodylate is frequently used as a buffering agent in the preparation and fixation of biological samples for transmission electron microscopy. Cacodylic acid is highly toxic by ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. Once thought to be a byproduct of inorganic arsenic detoxification, it is now believed to have serious health consequences of its own. It has been shown to be teratogenic in rodents, most often causing cleft palate but also fetal fatality at high doses. It has been shown to be genotoxic in human cells, causing apoptosis and also decreased DNA production and shorter DNA strands. While not itself a strong carcinogen, cacodylic acid does promote tumors in the presence of carcinogens in organs such as the kidneys and liver. (Wikipedia).
An arsenical that has been used as a dermatologic agent and as an herbicide.
Chemical Structure Depiction
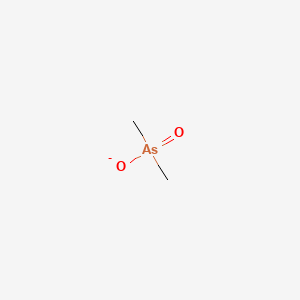
Conformer generation is disallowed since MMFF94s unsupported element
dimethylarsinate
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/C2H7AsO2/c1-3(2,4)5/h1-2H3,(H,4,5)/p-1
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
OGGXGZAMXPVRFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C[As](=O)(C)[O-]
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
C2H6AsO2-
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
- Acid, Cacodylic
- Acid, Dimethylarsinic
- Cacodylate
- Cacodylic Acid
- Dimethylarsinate
- Dimethylarsinic Acid
- Dimethylarsinate
- Cacodylate Ion
- Cacodylate
- 15132-04-4
- Arsinic acid, dimethyl-, ion(1-)
- Bolate
- Bolls
- Acid, Cacodylic
- Dimethylarsonic Acid
- Cacodylate ions
- Cacodylic acid, free acid
- Kakodylat
- DMAV
- Me2AsO2(-)
- BDBM92451
- CHEBI:16223
- DTXSID60164758
- OGGXGZAMXPVRFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
- [As(CH3)2O2](-)
- Scotts Spot Grass and Weed Control
- Scotts Stop Weeds After They Start
- Q27098592
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
136.99 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
2
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
136.958374 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
136.958374 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
40.1 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
5
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
-1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
53.8
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Same Parent, Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Exact Count
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
Same Count
Herbicides
Pesticides used to destroy unwanted vegetation, especially various types of weeds, grasses (POACEAE), and woody plants. Some plants develop HERBICIDE RESISTANCE. (See all compounds classified as Herbicides.)
Arsenic and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine. (L2)
L2: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp2.html
Dimethylarsinic acid is used as an herbicide and pesticide. (L180)
L180: Wikipedia. Cacodylic acid. Last Updated 22 January 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cacodylic_acid
Arsenic and its metabolites disrupt ATP production through different mechanisms. At the level of the citric acid cycle, arsenic inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase and uncouples the oxidative phosphorylation by competing with phosphate. This leads to inhibition of energy-linked reduction of NAD+, mitochondrial respiration, and ATP synthesis. Hydrogen peroxide production is increased, leading to oxidative stress due to the formation of reactive oxygen species. Arsenic's carginogenicity is influenced by the arsenical binding of tubulin, which results in aneuploidy, polyploidy and mitotic arrests. The binding of other arsenic protein targets may also cause altered DNA repair enzyme activity, altered DNA methylation patterns and cell proliferation. (T1, A17)
A17: Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID:18164070
T1: Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Carcinogen Classification
2B, possibly carcinogenic to humans. (L135)
L20: Wikipedia. Arsenic toxicity. Last Updated 22 February 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic_toxicity
T1: Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Oral (L2) ; inhalation (L2); dermal (L2)
L2: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp2.html
Exposure to lower levels of arsenic can cause nausea and vomiting, decreased production of red and white blood cells, abnormal heart rhythm, damage to blood vessels, and a sensation of “pins and needles” in hands and feet. Breathing high levels of inorganic arsenic can provoque sore throat or irritated lungs. Arsenic also affects the brain, causing neurological disturbances such as headaches, confusion, and drowsiness. (A1)
A1: Croal LR, Gralnick JA, Malasarn D, Newman DK: The genetics of geochemistry. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:175-202. PMID:15568975
LD50: 644 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (T14)
LD50: 720 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Rat) (T32)
T14: Lewis RJ (1996). Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 9th ed. Volumes 1-3. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
T32: Verschueren K (1983). Handbook of Environmental Data of Organic Chemicals. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.
L20: Wikipedia. Arsenic toxicity. Last Updated 22 February 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic_toxicity
- BindingDBLICENSEAll data curated by BindingDB staff are provided under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/us/).https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/info.jsp
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)Cacodylate Ionhttps://idrblab.net/ttd/data/drug/details/D09TVP
- Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)LICENSET3DB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (T3DB) and the original publication.http://www.t3db.ca/downloadsDimethylarsinatehttp://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D0075
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusArsinic acid, dimethyl-, ion(1-)https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0015132044ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- EPA DSSToxArsinic acid, dimethyl-, ion(1-)https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60164758CompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- ChEBIDimethylarsinatehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:16223
- Crystallography Open Database (COD)LICENSEAll data in the COD and the database itself are dedicated to the public domain and licensed under the CC0 License. Users of the data should acknowledge the original authors of the structural data.https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/DimethylarsinateNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe)
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB)LICENSEData files contained in the PDB archive (ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org) are free of all copyright restrictions and made fully and freely available for both non-commercial and commercial use. Users of the data should attribute the original authors of that structural data.https://www.rcsb.org/pages/policies
- Rhea - Annotated Reactions DatabaseLICENSERhea has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). This means that you are free to copy, distribute, display and make commercial use of the database in all legislations, provided you credit (cite) Rhea.https://www.rhea-db.org/help/license-disclaimer
- SpectraBaseArsinic acid, anionhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/BgJf50XgLHc
- Wikidatadimethylarsinate ionhttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q27098592
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlCacodylic Acidhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68002101
- PubChem
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
CONTENTS
 CID 2513 (Cacodylic Acid)
CID 2513 (Cacodylic Acid)