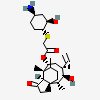Lefamulin
- Lefamulin [INN]
- Lefamulin [USAN:INN]
- UNII-21904A5386
- (+)-LEFAMULIN
- 21904A5386
- Create:2012-08-19
- Modify:2025-01-18
 Lefamulin Acetate (active moiety of).
Lefamulin Acetate (active moiety of).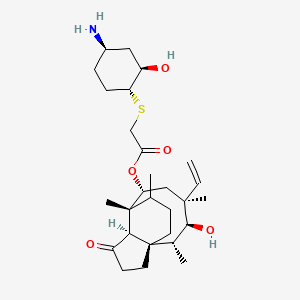
- BC-3781
- lefamulin
- Xenleta
- Lefamulin [INN]
- Lefamulin [USAN:INN]
- UNII-21904A5386
- (+)-LEFAMULIN
- 21904A5386
- BC-3781
- lefamulina
- lefamuline
- Acetic acid, 2-(((1R,2R,4R)-4-amino-2-hydroxycyclohexyl)thio)-, (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3ah-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester
- lefamulinum
- BC3781
- compound 7 (PMID: 24874438)
- LEFAMULIN [MI]
- LEFAMULIN [USAN]
- LEFAMULIN [WHO-DD]
- SCHEMBL1083688
- J01XX12
- DB12825
- EN300-33419804
- (1S,2R,3S,4S,6R,7R,8R)-4-ethenyl-3-hydroxy-2,4,7,14-tetramethyl-9-oxotricyclo[5.4.3.0,1,8]tetradecan-6-yl 2-{[(1R,2R,4R)-4-amino-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]sulfanyl}acetate
- 2743429-93-6
 Lefamulin Acetate (active moiety of)
Lefamulin Acetate (active moiety of)



H302 (50%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral]
H315 (50%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation]
H317 (50%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin]
H318 (50%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H330 (50%): Fatal if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation]
H411 (50%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard]
P260, P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P284, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P354+P338, P316, P317, P320, P321, P330, P332+P317, P333+P317, P362+P364, P391, P403+P233, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 2 reports by companies from 2 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Acute Tox. 4 (50%)
Skin Irrit. 2 (50%)
Skin Sens. 1B (50%)
Eye Dam. 1 (50%)
Acute Tox. 2 (50%)
Aquatic Chronic 2 (50%)
Serum ALT, AST and GGT elevations above 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 1.2% to 3.5% of patients treated with lefamulin (n=641), but rates and severity of serum enzyme elevations were similar to those in comparator arms (moxifloxacin: n=641). These enzymes elevations were usually mild-to-moderate in severity, self-limited in duration and not accompanied by symptoms or jaundice. Instances of clinically apparent liver injury attributable to lefamulin have not been reported but this antibiotic has had limited general use.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
No information is available on the use of lefamulin during breastfeeding. The manufacturer recommends that mothers should avoid breastfeeding during treatment and for 2 days after the final dose. An alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=KPVIXBKIJXZQJX-CSOZIWFHSA-N
- Exercise caution with grapefruit products. Grapefruit inhibits CYP3A, which may increase the serum concentration of lefamulin.
- Exercise caution with St. John's Wort. This herb induces the CYP3A metabolism of lefamulin and may reduce its serum concentration.
- Take on an empty stomach. This drug should be taken at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
- Take with a full glass of water. The tablet should be swallowed whole with water.
- ChemIDplusLefamulin [USAN:INN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1061337516ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeAcet i c ac id, 2- [ [ (1R,2R,4R) -4-amino-2-hydroxycyclohexyl ] thio] -, (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl esterhttps://chem.echa.europa.eu/100.246.378Acet i c ac id, 2- [ [ (1R,2R,4R) -4-amino-2-hydroxycyclohexyl ] thio] -, (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester (EC: 813-124-2)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/252226
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- LiverTox
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)LICENSEInformation on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) website is subject to a disclaimer and copyright and limited reproduction notices.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/legal-notice
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- WikipediaEstradiol stearatehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiol_stearate
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAnti-Bacterial Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000900
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 392900296https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/392900296