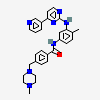
Imatinib
- Imatinib
- 152459-95-5
- STI571
- Imatinib (STI571)
- sti-571
- Create:2005-03-25
- Modify:2025-01-04
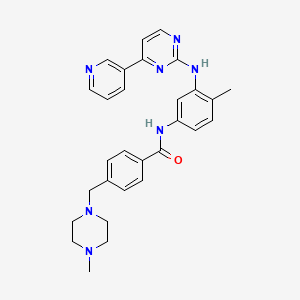
- alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-tolu-p-toluidide
- CGP 57148
- CGP-57148
- CGP57148
- CGP57148B
- Gleevec
- Glivec
- imatinib
- imatinib mesylate
- imatinib methanesulfonate
- Mesylate, Imatinib
- Methanesulfonate, Imatinib
- ST 1571
- ST1571
- STI 571
- STI-571
- STI571
- Imatinib
- 152459-95-5
- STI571
- Imatinib (STI571)
- sti-571
- Imatinib free base
- Glamox
- Cgp 57148
- N-(4-Methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
- STI 571
- CCRIS 9076
- UNII-BKJ8M8G5HI
- BKJ8M8G5HI
- Imatinib (INN)
- NSC-743414
- NSC-759854
- 4-(4-METHYL-PIPERAZIN-1-YLMETHYL)-N-[4-METHYL-3-(4-PYRIDIN-3-YL-PYRIMIDIN-2-YLAMINO)-PHENYL]-BENZAMIDE
- CHEBI:45783
- CGP-57148
- 152459-95-5 (free base)
- MFCD05662257
- CHEMBL941
- alpha-(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-tolu-p-toluidide
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
- 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
- DTXSID3037125
- NSC743414
- NSC 743414
- NSC 759854
- 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-N-{4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl}benzamide
- Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl)-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-N-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-
- N-(4-methyl-3-{[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)-4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]benzamide
- IMATINIB [INN]
- Imatinib [INN:BAN]
- alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-toluidide
- 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide
- 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-N-(4-methyl-3-{[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)benzamide
- STI
- BENZAMIDE, 4-((4-METHYL-1-PIPERAZINYL)METHYL)-N-(4-METHYL-3-((4-(3-PYRIDINYL)-2-PYRIMIDINYL)AMINOPHENYL)-
- Glamox (TN)
- SR-01000763561
- NCGC00159456-02
- ST1571
- ST 1571
- Imatinibum
- Imatinib base
- imatinib-CD3
- 1iep
- 1xbb
- Gleevec(TM)
- 4-((4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-N-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)benzamide
- 4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)benzamide
- 4-(4-METHYL-PIPERAZIN-1-YLMETHYL)-N-(4-METHYL-3-(4-PYRIDIN-3-YL-PYRIMIDIN-2-YLAMINO)-PHENYL)-BENZAMIDE
- 4-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-ylmethyl)-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]benzamide; CGP 57148; Genfatinib; Imatinib, Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-methyl]-N-{4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-amino]-phenyl)-benzamide
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-methyl]-N-{4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-amino]-phenyl}-benzamide
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[(4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide
- Imatinib (Gleevec)
- Imatinib, 21
- Imatinib (Standard)
- Imatinib, Free base
- Kinome_3724
- 112GI019
- IMATINIB [MI]
- IMATINIB [VANDF]
- IMATINIB [WHO-DD]
- Gleevec (TN) (Novartis)
- cid_5291
- SCHEMBL3827
- IMATINIB [EMA EPAR]
- STI-571; IMATINIB
- BIDD:GT0047
- GTPL5687
- DTXCID1017125
- BDBM13530
- EX-A063
- L01XE01
- BCPP000205
- HMS2089D03
- HMS3244P06
- HMS3244P10
- HMS3244P14
- HMS3656K04
- HMS3715P03
- Pharmakon1600-01502276
- BCP01542
- AC-524
- HY-15463R
- NSC759854
- NSC800772
- STK617705
- AKOS000280662
- BCP9000775
- CCG-101289
- CS-0964
- DB00619
- ES-0058
- NSC-800772
- PA-5291
- SB17306
- SDCCGSBI-0634386.P009
- MRF-0000449
- NCGC00159456-01
- NCGC00159456-03
- NCGC00159456-04
- NCGC00159456-05
- NCGC00159456-06
- NCGC00159456-07
- NCGC00159456-09
- NCGC00159456-16
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide methanesulfonate
- BI164570
- HY-15463
- N-(3-(4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-4-methylphenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
- N-(4-methyl-3-(4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide
- SY028029
- I0906
- NS00009172
- S2475
- SW197805-5
- D08066
- EN300-123057
- AB00698388-07
- AB00698388-10
- AB00698388-11
- AB00698388-12
- AB00698388-13
- AB00698388_15
- AB00698388_16
- Q177094
- Q-201231
- SR-01000763561-4
- SR-01000763561-6
- BRD-K92723993-001-06-7
- BRD-K92723993-001-12-5
- BRD-K92723993-066-02-9
- BRD-K92723993-066-04-5
- BRD-K92723993-066-22-7
- Z1546624232
- 1080014-82-9
- 4-(4-Me-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-N-[4-Me-3-(4-pyridin-3-yl-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-phenyl]-benzamide
- 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
- 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3- pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
- 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide
- benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-
- Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]- (9CI)
- N-[4-Methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidyl]amino]phenyl]-4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]benzamide
394.1664 100
222.0913 38.99
379.1429 26.32
99.0916 20.19
264.1131 19.30
378.1351 100
247.0866 83.08
222.0914 80.98
264.1131 33.12
131.0603 31.68
494.2664 999
495.2694 316
496.2708 51
394.1661 7
494.2663 999
495.2695 335
394.1658 129
496.2714 53
217.1322 39
Imatinib Mesylate (has salt form)
IKT-001Pro (is active moiety of)
- Cytoplasm
- Membrane
Use (kg; approx.) in Germany (2009): >1000
Use (kg; exact) in Germany (2009): 1300
Consumption (g per capita; approx.) in Germany (2009): 0.0122
Consumption (g per capita; exact) in Germany (2009): 0.0159
Excretion rate: 0.25
Calculated removal (%): 5.8


H302 (10%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral]
H315 (20%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation]
H319 (20%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H335 (10%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation]
H341 (70%): Suspected of causing genetic defects [Warning Germ cell mutagenicity]
H351 (70%): Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity]
H360 (70%): May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity]
H361 (10%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity]
H362 (70%): May cause harm to breast-fed children [Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation]
P203, P260, P261, P263, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P318, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 10 reports by companies from 4 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Skin Irrit. 2 (20%)
Eye Irrit. 2A (20%)
STOT SE 3 (10%)
Muta. 2 (70%)
Carc. 2 (70%)
Repr. 1B (70%)
Repr. 2 (10%)
Imatinib therapy is associated with three forms of acute liver injury: transient and usually asymptomatic elevations in serum enzymes during treatment, clinically apparent acute hepatitis, and reactivation of an underlying chronic hepatitis B.
Elevations in serum aminotransferase levels are common during imatinib therapy, but ALT levels above 5 times the upper limit of the normal range occur in only 2% to 4% of patients treated for 6 months or more. In addition, mild elevations in serum bilirubin can occur. These abnormalities are usually mild, asymptomatic, and resolve despite continuing therapy. Nevertheless, dose adjustment or temporary discontinuation and restarting at a lower dose may be needed and is recommended if levels are markedly elevated (ALT or AST persistently >5 times ULN or bilirubin >3 times ULN).
In addition, imatinib has been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice. The time to onset has varied from 6 days to as long as several years after starting treatment, the usual latency being 2 to 6 months (Cases 1 and 2). The pattern of serum enzyme elevations is typically hepatocellular, although cholestatic and mixed forms of hepatitis have also been reported. The injury can be severe and instances of acute liver failure and death have been reported as well as severe hepatitis resulting in a posthepatitic cirrhosis. Immunoallergic features (rash, fever and eosinophilia) are not common, but some patients develop low levels of autoantibodies and instances of chronic hepatitis on long term imatinib have been reported. More importantly, many instances of an apparent clinical response to prednisone therapy have been described. Recurrence of injury is common with reexposure, but concurrent prednisone therapy may blunt or prevent the recurrence of liver injury and, in some instances, has allowed for continued, long term therapy despite a previous bout of clinically apparent liver injury on imatinib.
Finally, there have been several instances of reactivation of chronic hepatitis B during imatinib therapy in patients with inactive hepatitis B or the HBsAg carrier state (Case 3). The clinical presentation is generally with an acute hepatitis like syndrome with marked elevations in serum ALT and minimal changes in alkaline phosphatase levels. Typically, hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA is present in serum in increasing levels early in the course of reactivation which rapidly falls to pretreatment levels with recovery. Patients may also test positive for IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (IgM anti-HBc). Reactivation of hepatitis B due to imatinib can be severe and fatal instances have been reported.
Likelihood score: B (likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury as well as reactivation of hepatitis B).
M Chen, V Vijay, Q Shi, Z Liu, H Fang, W Tong. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Drug Discovery Today, 16(15-16):697-703, 2011. PMID:21624500 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.05.007
M Chen, A Suzuki, S Thakkar, K Yu, C Hu, W Tong. DILIrank: the largest reference drug list ranked by the risk for developing drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21(4): 648-653. PMID:26948801 DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.015
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Limited information indicates that maternal doses of imatinib up to 400 mg daily produce low levels of the drug and its active metabolite in milk. Although a few breastfed infants apparently experienced no adverse effects during maternal use of imatinib, no long-term data are available. Until more data are available, imatinib should be used only with careful monitoring during breastfeeding. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, the manufacturer and some authors recommend that breastfeeding be discontinued during imatinib therapy and for 1 month after therapy.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
A woman receiving oral imatinib 400 mg daily for chronic myeloid leukemia breastfed her infant. No adverse effects were noted in the infant during the first 2 months of nursing.
One woman with chronic myelogenous leukemia received imatinib 400 mg daily throughout pregnancy and during breastfeeding (extent not stated) for nearly 6 months postpartum. Her infant reportedly grew and developed normally.
A woman with chronic myeloid leukemia received imatinib 400 mg daily starting at week 8 of pregnancy and continuing throughout 8 months of breastfeeding (extent not stated). The infant was healthy, but an atrial septal defect was repaired at 30 months of age. It was thought to be unrelated to imatinib therapy.
A pregnant woman with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia was started on imatinib 400 mg daily during pregnancy. After delivery, her preterm infant was fed colostrum until the middle of the fifth day postpartum when exclusive formula feeding was instituted. The infant was treated for apnea of prematurity and discharged on day 25 of life. No adverse effects on growth or development were noted during the first year of life.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=KTUFNOKKBVMGRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Avoid grapefruit products. Grapefruit inhibits CYP3A4 metabolism, which can increase serum levels of imatinib.
- Exercise caution with St. John's Wort. This herb induces CYP3A4 metabolism, which may reduce the serum concentration of imatinib.
- Take with a full glass of water. Taking imatinib with water may reduce gastric irritation.
- Take with food. Food reduces gastric irritation.
- BindingDBLICENSEAll data curated by BindingDB staff are provided under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/us/).https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/info.jsp4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamidehttps://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/chemsearch/marvin/MolStructure.jsp?monomerid=13530
- Chemical Probes Portal
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jspImatinib Mesylatehttps://ctdbase.org/detail.go?type=chem&acc=D000068877
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloads
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DTP/NCILICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeBenzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-https://chem.echa.europa.eu/100.122.739Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]- (EC: 604-855-6)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/82124
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0014757_msms_2227214https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014757#spectra
- CCSbaseCCSbase Classificationhttps://ccsbase.net/
- ChEBI
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- LiverTox
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/IMATINIBNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) DatasetLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)LICENSEInformation on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) website is subject to a disclaimer and copyright and limited reproduction notices.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/legal-noticeGlivec (EMEA/H/C/000406)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/glivecImatinib Koanaa (EMEA/H/C/005595)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-koanaaImatinib Teva (EMEA/H/C/002585)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-tevaImatinib Accord (EMEA/H/C/002681)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-accordImatinib Actavis (EMEA/H/C/002594)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-actavisImatinib medac (EMEA/H/C/002692)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-medacImatinib Teva B.V. (EMEA/H/C/004748)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/imatinib-teva-bv
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- WHO Model Lists of Essential MedicinesLICENSEPermission from WHO is not required for the use of WHO materials issued under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Intergovernmental Organization (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO) license.https://www.who.int/about/policies/publishing/copyright
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-law
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.keg
- MassBank Europe
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/about
- Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe)
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB)LICENSEData files contained in the PDB archive (ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org) are free of all copyright restrictions and made fully and freely available for both non-commercial and commercial use. Users of the data should attribute the original authors of that structural data.https://www.rcsb.org/pages/policies
- SpectraBase
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidata
- Wikipedia
- Wiley
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlImatinib Mesylatehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2009892Antineoplastic Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000970Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitorshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2103139
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 403715570https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/403715570
- NCBI