Tacrolimus monohydrate
- TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE
- Tacrolimus hydrate
- 109581-93-3
- Prograf
- Protopic
- Create:2005-06-24
- Modify:2025-01-18
 Tacrolimus (annotation moved to).
Tacrolimus (annotation moved to).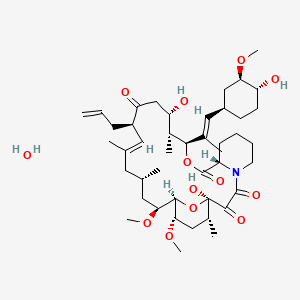
- Anhydrous Tacrolimus
- Anhydrous, Tacrolimus
- FK 506
- FK-506
- FK506
- FR 900506
- FR-900506
- FR900506
- Prograf
- Prograft
- Tacrolimus
- Tacrolimus Anhydrous
- Tacrolimus, Anhydrous
- TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE
- Tacrolimus hydrate
- 109581-93-3
- Prograf
- Protopic
- Tsukubaenolide hydrate
- FK-506 monohydrate
- Tacrolimus (monohydrate)
- LCP-Tacro
- WM0HAQ4WNM
- Tacrolimus [USAN]
- UNII-WM0HAQ4WNM
- FK 506
- MFCD11045918
- FR900506
- (1R,9S,12S,13R,14S,17R,18E,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-1,14-dihydroxy-12-[(E)-1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl]-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-17-prop-2-enyl-11,28-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[22.3.1.04,9]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetrone;hydrate
- Prograf (TN)
- NSC-758659
- FR 900506
- TACROLIMUS [USP-RS]
- CHEBI:61057
- (-)-(3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,19-dihydroxy-3-{(1E)-1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl}-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-3H-15,19-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone monohydrate
- (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,19-dihydroxy-3-{(1E)-1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl}-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-3H-15,19-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone--water (1/1)
- TACROLIMUS [USP MONOGRAPH]
- NSC 758659
- TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- Tacrolimus [USAN:INN:BAN]
- Protopic (TN)
- Tacrolimus (USP/INN)
- TACROLIMUS [VANDF]
- Tacrolimus hydrate (JP18)
- SCHEMBL317005
- TACROLIMUS [EMA EPAR]
- CHEMBL3989887
- TACROLIMUS [ORANGE BOOK]
- TACROLIMUS HYDRATE [JAN]
- NWJQLQGQZSIBAF-MLAUYUEBSA-N
- GLXC-02501
- HY-13756AR
- TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE [MI]
- EX-A2657
- Tacrolimus (monohydrate) (Standard)
- HY-13756A
- AKOS015994743
- KS-1245
- TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE [WHO-DD]
- AC-32477
- FK-506 monohydrate, >=98% (HPLC)
- D00107
- EN300-220769
- EN300-21682061
- Q-101412
- Q27130595
- Tacrolimus, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
- Tacrolimus, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
- Tacrolimus for system suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (-)-(3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-8-allyl-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-Hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-((E)-2-((1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylvinyl)-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone)monohydrate
- (-)-(3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-8-Allyl-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[(E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylvinyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone monohydrate
- (1R,9S,12S,13R,14S,17R,18E,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-1,14-dihydroxy-12-[(1E)-1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl]-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-17-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-11,28-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[22.3.1.0,4,9]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetrone hydrate
- (1R,9S,12S,13R,14S,17R,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-1,14-dihydroxy-12-{1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl}-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-17-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-11,28-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[22.3.1.0,4,9]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetrone hydrate
- 15,19-Epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[(1E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propen-1-yl)-, hydrate (1:1), (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-
 Tacrolimus (annotation moved to)
Tacrolimus (annotation moved to)
P264, P270, P301+P316, P321, P330, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 115 reports by companies from 9 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory.
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation
Limited data indicate that amounts of systemically administered tacrolimus are low in breastmilk and probably do not adversely affect the breastfed infant. United States and European experts and guidelines consider tacrolimus to be probably safe to use during breastfeeding. Exclusively breastfed infants should be monitored if this drug is used during lactation, possibly including measurement of serum levels to rule out toxicity if there is a concern.
Topical tacrolimus presents a low risk to the nursing infant because it is poorly absorbed after topical application and peak blood concentrations are less than 2 mcg/L in most patients. Ensure that the infant's skin does not come into direct contact with the areas of skin that have been treated. Current guidelines allow topical tacrolimus to be applied to the nipples just after nursing, with the nipples cleaned gently before nursing. Only water-miscible cream or gel products should be applied to the breast or nipple because ointments may expose the infant to high levels of mineral paraffins via licking, so pimecrolimus cream may be preferable to tacrolimus ointment for nipple application.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants
One infant was exclusively breastfed during maternal tacrolimus therapy throughout gestation to at least 2.5 months of age at which time the infant was developing normally physically and neurologically. An ultrasound examination of the infant's thymus was normal.
The National Transplantation Pregnancy Registry reported data gathered from 1991 to 2011 on mothers who breastfed their infants following organ transplantation. A total of 68 mothers with transplants (mostly kidney or liver) used tacrolimus while breastfeeding a total of 83 infants. Duration of nursing ranged from 1 week to 1.5 years and follow-up of the children ranged from weeks to 16 years. There were no reports of problems in any of the infants or children. As of December 2013, a total of 92 mothers had breastfed 125 infants for as long as 26 months with no apparent adverse effects in infants.
The breastfed infants of six women who took tacrolimus during pregnancy for organ transplantation were breastfed (4 exclusive, 2 partial) for 45 to 180 days and followed for periods of 2 to 30 months. The mothers' mean daily tacrolimus dosage during breastfeeding was 9.6 mg daily (range 4.5 to 15 mg daily). Four mothers were also taking azathioprine 100 to 150 mg daily, one was taking diltiazem, and one was taking prednisolone 15 mg and aspirin 75 mg daily. None of the infants had any clear tacrolimus-related side effects, although one had transient thrombocytosis that resolved despite continued breastfeeding. Developmental milestones were normal and no pattern of infections was noted.
Two mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus were reported who took tacrolimus 3 mg daily during pregnancy and lactation as well as prednisolone 30 or 40 mg daily. Three years after birth, both children were healthy. The durations of lactation were not stated.
In a case series of women who had liver transplants over a 25-year period, one woman breastfed (extent not stated) her infant while taking tacrolimus. No neonatal complications were noted.
A mother with a liver transplant was maintained on belatacept 10 mg/kg monthly, slow-release tacrolimus (Envarsus and Veloxis) 2 mg daily, azathioprine 25 mg daily, and prednisone 2.5 mg daily. She breastfed her infant for a year (extent not stated). The infant’s growth and cognitive milestones were normal.
An Australian case series reported 3 women with heart transplants who had a total of 5 infants, all of whom were breastfed (extent not stated) during maternal tacrolimus therapy. Daily dosages ranged from 3 to 13 mg daily. No adverse infant effects were reported up to the times of discharge.
A woman with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to etanercept took sarilumab 200 mg every two weeks during pregnancy until 37 weeks of gestation. She was also taking prednisolone 10 mg and tacrolimus 3 mg daily. She delivered a healthy infant at 38 weeks of gestation and breastfed her infant. Prednisolone was continued postpartum, tacrolimus was restarted at 7 days postpartum, and sarilumab was restarted at 28 days postpartum. The mother continued to breastfeed until 6 months postpartum. The infant was vaccinated with multiple live vaccines after reaching six months old, including the Bacille-Calmette-Guerin vaccine, with no adverse effects.
A woman with a heart transplant took tacrolimus alone throughout pregnancy and postpartum while breastfeeding her infant (extent not stated) for one year. The child had normal weight gain, normal motor development, and no signs of metabolic disorders or significant infections. The age of the infant at evaluation was not stated.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
A study in renal transplant patients who were on a tacrolimus-based immunosuppression regimen found that women’s median serum prolactin levels were 14.4 mcg/L compared with women who were not taking tacrolimus (17.6 mcg/L). The difference was statistically significant. Median serum testosterone levels (0.121 vs 0.137 mcg/L) and serum cortisol levels (82.5 vs 105 mg/L) were also significantly lower in the tacrolimus group. The reduced prolactin may be caused by inhibition of the transcription of the human prolactin gene. Not all studies have found a reduction in serum prolactin with tacrolimus. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=NWJQLQGQZSIBAF-MLAUYUEBSA-N
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/Tacrolimus hydratehttps://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=109581-93-3
- ChemIDplusTacrolimus [USAN:INN:BAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0109581933ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-notice15,19-Epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-C)-(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21- (4H,23H)-tetrone, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a -hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl)-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8- (2-propenyl)-, monohydrate,(3S-(3R*,(E(1S*,3S*,4S*)),4S*,5R*,8S*, 9E,12R*,14R*,15S*,16R*,18S*,19S*,26aR*))-https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.162.52915,19-Epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-C)-(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21- (4H,23H)-tetrone, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a -hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl)-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8- (2-propenyl)-, monohydrate,(3S-(3R*,(E(1S*,3S*,4S*)),4S*,5R*,8S*, 9E,12R*,14R*,15S*,16R*,18S*,19S*,26aR*))- (EC: 634-559-2)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/167350
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEBITacrolimus hydratehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:61057
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlTherapeutic category of drugs in Japanhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08301.kegUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.kegDrugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeiahttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08311.keg
- Metabolomics WorkbenchTacrolimus hydratehttps://www.metabolomicsworkbench.org/data/StructureData.php?RegNo=61427
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- Springer Nature
- Wikidatatacrolimus hydratehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q27130595
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlCalcineurin Inhibitorshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68065095Immunosuppressive Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68007166
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 389236457https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/389236457
 CID 962 (Water)
CID 962 (Water)