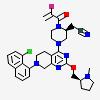
Adagrasib
- MRTX849
- Adagrasib
- 2326521-71-3
- MRTX-849
- KRAZATI
- Create:2019-07-20
- Modify:2025-01-04
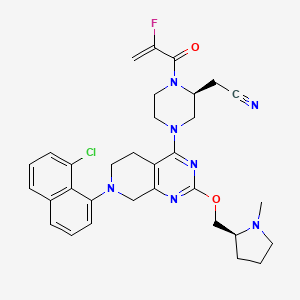
- 2-((S)-4-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido(3,4-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoroacryloyl)piperazin-2-yl)acetonitrile
- 2-Piperazineacetonitrile, 4-(7-(8-chloro-1-naphthalenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-(((2S)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methoxy)pyrido(3,4-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoro-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-, (2S)-
- adagrasib
- MRTX-849
- MRTX849
- MRTX849
- Adagrasib
- 2326521-71-3
- MRTX-849
- KRAZATI
- Kras G12C inhibitor MRTX849
- 8EOO6HQF8Y
- Adagrasib [USAN]
- UNII-8EOO6HQF8Y
- 2-((S)-4-(7-(8-Chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoroacryloyl)piperazin-2-yl)acetonitrile
- 2-[(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-[[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy]-6,8-dihydro-5H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl]acetonitrile
- 2-Piperazineacetonitrile, 4-[7-(8-chloro-1-naphthalenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-[[(2S)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]methoxy]pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoro-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-, (2S)-
- 2-Piperazineacetonitrile, 4-(7-(8-chloro-1-naphthalenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-(((2S)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methoxy)pyrido(3,4-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoro-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-, (2S)-
- MFCD32263433
- compound 20 (PMID: 32250617)
- compound 20 [PMID: 32250617]
- 2-[(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-{[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-5H,6H,7H,8H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl]acetonitrile
- 2-((S)-4-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido(3,4-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoroacryloyl)piperazin-2-yl)acetonitrile
- 2-[(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-{[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-5H,6H,8H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl]acetonitrile
- Krazati (TN)
- ADAGRASIB [INN]
- Adagrasib (USAN/INN)
- Adagrasib (MRTX849)
- MRTX849(Adagrasib)?
- ADAGRASIB [WHO-DD]
- MRTX 849
- CHEMBL4594350
- SCHEMBL20974691
- GTPL10888
- DTXSID801336759
- BCP31538
- EX-A3258
- MRTX-849; MRTX 849
- BDBM50539763
- NSC831453
- WHO 11519
- AKOS037648997
- AT23561
- NSC-831453
- AC-35659
- BM177692
- BS-16211
- HY-130149
- CS-0105265
- D12301
- EN300-26953032
- Z4145344023
- ((2S)-4-(7-(8-CHLORONAPHTHALEN-1-YL)-2-(((2S)-1- METHYLPYRROLIDIN-2-YL)METHOXY)-5,6,7,8- TETRAHYDROPYRIDO(3,4-D)PYRIMIDIN-4-YL)-1-(2-FLUOROPROP2-ENOYL)PIPERAZIN-2-YL)ACETONITRILE
- ((2S)-4-(7-(8-CHLORONAPHTHALEN-1-YL)-2-(((2S)-1-METHYLPYRROLIDIN-2-YL)METHOXY)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDROPYRIDO(3,4-D)PYRIMIDIN-4-YL)-1-(2-FLUOROPROP2-ENOYL)PIPERAZIN-2-YL)ACETONITRILE
Adagrasib is approved to treat adults with cancer that has spread and has an abnormal KRAS gene, including:
• non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It is used in patients who have received at least one other systemic therapy
• colorectal cancer. It is used with cetuximab in patients who have received chemotherapy that included a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan hydrochloride
These uses are approved under FDA’s Accelerated Approval Program. As a condition of approval, a confirmatory trial(s) must show that adagrasib provides a clinical benefit in these patients.Adagrasib is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.

H302 (66.7%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral]
H315 (66.7%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation]
H319 (66.7%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
H335 (66.7%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation]
P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, and P501
(The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.)
Aggregated GHS information provided per 3 reports by companies from 2 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies.
Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria per 1 of 3 reports by companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website.
There is 1 notification provided by 2 of 3 reports by companies with hazard statement code(s).
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
Acute Tox. 4 (66.7%)
Skin Irrit. 2 (66.7%)
Eye Irrit. 2A (66.7%)
STOT SE 3 (66.7%)
In the prelicensure clinical trials of adagrasib in patients with solid tumors harboring KRAS G12C mutations, liver test abnormalities were frequent although usually self-limited and mild. Some degree of ALT elevations arose in 28% to 46% of adagrasib treated patients and elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were seen in 5% to 7%. In these trials that enrolled approximately 366 patients, adagrasib was discontinued early due to increased AST or ALT in 8% of patients. In addition, a small proportion of patients developed clinically apparent hepatotoxicity requiring adagrasib discontinuation. The liver test abnormalities had a median onset of 3 weeks after initiation of therapy. While serum aminotransferase elevations were occasionally quite high (5 to 20 times ULN), there were no accompanying elevations in serum bilirubin and no patient developed clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. The product label for adagrasib recommends monitoring for routine liver tests before, at 3 week intervals during the first 3 months of therapy, and thereafter as clinically indicated.
Likelihood score: D (possible but infrequent cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=PEMUGDMSUDYLHU-ZEQRLZLVSA-N
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- Chemical Probes Portal
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloads
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-notice2-[(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-{[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-5H,6H,7H,8H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl]acetonitrilehttps://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.329.9282-[(2S)-4-[7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-{[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-5H,6H,7H,8H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-(2-fluoroprop-2-enoyl)piperazin-2-yl]acetonitrile (EC: 870-640-0)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/318082
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- LiverTox
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)LICENSEInformation on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) website is subject to a disclaimer and copyright and limited reproduction notices.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/legal-notice
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlUSP drug classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08302.kegAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.keg
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NCI Cancer Drugs
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.html
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/about2-((S)-4-(7-(8-Chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-(2-fluoroacryloyl)piperazin-2-yl)acetonitrilehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/J66TKZAG9PRG
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Wikidata
- Wikipedia3-Aminoacetanilidehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3-Aminoacetanilide
- PubChemPFAS and Fluorinated Compounds in PubChemhttps://gitlab.com/uniluxembourg/lcsb/eci/pubchem-docs/-/raw/main/pfas-tree/PFAS_Tree.pdf?inline=false
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAntineoplastic Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000970
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 397275154https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/397275154