Naldemedine
- NALDEMEDINE
- 916072-89-4
- UNII-03KSI6WLXH
- 03KSI6WLXH
- naldemedina
- Create:2011-12-27
- Modify:2025-01-25
 Naldemedine Tosylate (active moiety of).
Naldemedine Tosylate (active moiety of).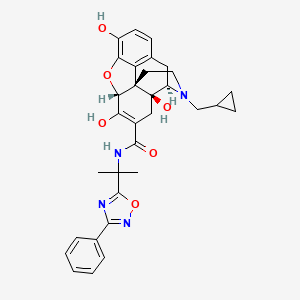
- 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5alpha-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-(2-(3-phenyl- 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl)morphinan-7-carboxamide
- naldemedine
- S-297995
- Symproic
- NALDEMEDINE
- 916072-89-4
- UNII-03KSI6WLXH
- 03KSI6WLXH
- naldemedina
- S-297995
- Naldemedine [USAN:INN]
- S 297995
- S-297,995
- (4R,4aS,7aR,12bS)-3-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4a,7,9-trihydroxy-N-[2-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]-1,2,4,5,7a,13-hexahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-6-carboxamide
- Morphinan-7-carboxamide, 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3,6,14- trihydroxy-N-(1-methyl-1-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)ethyl)-,(5alpha)-
- compound 9k (PMID: 30446313)
- compound 9k [PMID: 30446313]
- 17-(CYCLOPROPYLMETHYL)-6,7-DIDEHYDRO-4,5A-EPOXY-3,6,14-TRIHYDROXY-N-(2-(3-PHENYL-1,2,4-OXADIAZOL-5-YL)PROPAN-2-YL)MORPHINAN-7-CARBOXAMIDE
- 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5alpha-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-(2-(3-phenyl- 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl)morphinan-7-carboxamide
- Naldemedine [USAN]
- naldemedinum
- Nalmedine; (5alpha)-17-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-[1-methyl-1-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)ethyl]-Morphinan-7-carboxamide;
- NALDEMEDINE [MI]
- NALDEMEDINE [INN]
- Naldemedine (USAN/INN)
- NALDEMEDINE [WHO-DD]
- GTPL9150
- SCHEMBL9880572
- CHEMBL2105755
- A06AH05
- DTXSID501030350
- EX-A10201A
- BDBM50503604
- AKOS032945757
- DB11691
- DA-67333
- HY-19627
- CS-0016072
- NS00073301
- D10188
- EN300-20605629
- Q6960846
- (1S,5R,13R,17S)-4-(cyclopropylmethyl)-10,14,17-trihydroxy-N-[2-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]-12-oxa-4-azapentacyclo[9.6.1.0^{1,13}.0^{5,17}.0^{7,18}]octadeca-7(18),8,10,14-tetraene-15-carboxamide
- Morphinan-7-carboxamide, 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-(1-methyl-1-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)ethyl)-,(5alpha)-
 Naldemedine Tosylate (active moiety of)
Naldemedine Tosylate (active moiety of)Therapy with naldemedine has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations or to clinically apparent liver injury. In preregistration studies, liver test abnormalities arose in less than 1% of treated patients but were transient, mild and not associated with symptoms. There were no reported cases of liver injury with jaundice or symptoms. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been no published reports of hepatotoxicity attributed to naldemedine.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=AXQACEQYCPKDMV-RZAWKFBISA-N
- Avoid St. John's Wort. This herb induces CYP3A metabolism and may reduce serum levels of naldemedine.
- Take with or without food.
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/(5α)-17-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-[1-methyl-1-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)ethyl]morphinan-7-carboxamidehttps://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=916072-89-4
- ChemIDplusNaldemedine [USAN:INN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0916072894ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_useNaldemedinehttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11691
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloadsNALDEMEDINEhttps://www.dgidb.org/drugs/rxcui:1876597
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGYLICENSEThe Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL) https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/. Its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/about.jsp#licenseGuide to Pharmacology Target Classificationhttps://www.guidetopharmacology.org/targets.jsp
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- FDA Pharm ClassesLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingFDA Pharmacological Classificationhttps://www.fda.gov/ForIndustry/DataStandards/StructuredProductLabeling/ucm162549.htm
- LiverTox
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)LICENSEInformation on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) website is subject to a disclaimer and copyright and limited reproduction notices.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/legal-noticeRizmoic (EMEA/H/C/004256)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/rizmoicNaldemedine (P/0379/2021)https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/paediatric-investigation-plans/emea-001893-pip01-15-m02
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.kegTarget-based classification of drugshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08310.keg
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmlnaldemedinehttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/1876597
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NaldemedineNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/aboutnaldemedinehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/QAFW35N3FPPK
- Springer Nature
- Wikidatanaldemedinehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q6960846
- WikipediaNaldemedinehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naldemedine
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlnaldemedinehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2020343
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 402764346https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/402764346

