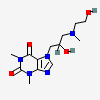
Xanthinol
- Xanthinol
- 2530-97-4
- xantinol
- UNII-TN1B5910V2
- 7-[2-hydroxy-3-[2-hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]propyl]-1,3-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione
- Create:2005-03-26
- Modify:2024-12-27
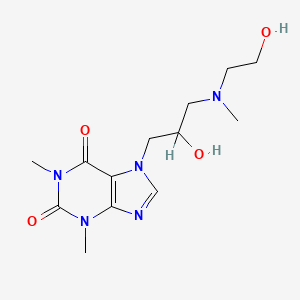
- Xanthinol
- 2530-97-4
- xantinol
- UNII-TN1B5910V2
- 7-[2-hydroxy-3-[2-hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]propyl]-1,3-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione
- TN1B5910V2
- 7-(2-Hydroxy-3-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylamino)propyl)theophylline
- 7-{2-hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino]propyl}-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
- DTXSID1048255
- Theophylline, 7-(2-hydroxy-3-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylamino)propyl)-
- Xavin
- Jupal
- 7-(2-hydroxy-3-((2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino)propyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione
- 7-{2-hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino]propyl}-1,3-dimethyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione
- 7-(2-hydroxy-3-((2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino)propyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione
- SCHEMBL121656
- CHEMBL1624126
- DTXCID6028230
- CHEBI:94314
- STL581678
- AKOS026751462
- DB09092
- NS00008286
- EN300-18568176
- Q8042975
- 7-(2-Hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino]propyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione #
312.16785 100
132.10197 71.53
237.09862 65.45
114.09274 64.67
219.08842 37.70
312.16602 100
132.10188 30.83
114.09158 26.75
237.09792 24.15
219.08739 13.62
312.16785 100
132.10197 71.53
237.09862 65.45
114.09274 64.67
219.08842 37.70
IMAP assessments - 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-7-[2-hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)methylamino]propyl]-1,3-dimethyl-: Environment tier I assessment
IMAP assessments - 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-7-[2-hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)methylamino]propyl]-1,3-dimethyl-: Human health tier I assessment
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=DSFGXPJYDCSWTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-7-[2-hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)methylamino]propyl]-1,3-dimethyl-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEBI7-[2-hydroxy-3-[2-hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]propyl]-1,3-dimethylpurine-2,6-dionehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:94314
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0259919_msms_2231996https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0259919#spectra
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-lawTheophylline, 7-(2-hydroxy-3-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylamino)propyl)-http://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm
- SpectraBase7-(2-Hydroxy-3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino]propyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dionehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/Ga4ZLRHDf4X
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/XANTINOL NICOTINATENORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidata
- WikipediaTriethylene glycol dinitratehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triethylene_glycol_dinitrate
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 394686256https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/394686256