Triclofos
PubChem CID
5563
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- triclofos
- 306-52-5
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphate
- Trichlophos
- Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphate
Molecular Weight
229.38 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Dates
- Create:2005-03-25
- Modify:2025-01-11
Description
Triclofos is a monoalkyl phosphate.
TRICLOFOS is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV that was first approved in 1982.
Chemical Structure Depiction
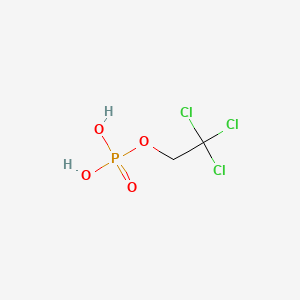
2,2,2-trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphate
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/C2H4Cl3O4P/c3-2(4,5)1-9-10(6,7)8/h1H2,(H2,6,7,8)
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
YYQRGCZGSFRBAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C(C(Cl)(Cl)Cl)OP(=O)(O)O
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
C2H4Cl3O4P
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
306-52-5
7246-20-0 (mono-hydrochloride salt)
8060-81-9, 857522-20-4
857522-20-4
- 2,2,2-trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphate, sodium salt
- 2,2,2-trichloroethyl phosphate
- monosodium trichloroethyl phosphate
- triclofos
- triclofos, monosodium salt
- triclofos
- 306-52-5
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphate
- Trichlophos
- Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphate
- Trichloryl
- Triclofoso [DCIT]
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethanol dihydrogen phosphate
- TRI-BETA-CHLOROETHYLPHOSPHATE
- CHEBI:9695
- Triclofos (INN)
- J712EO9048
- TRICLOFOS [INN]
- Triclofosa
- Triclofoso
- Triclofosum
- Triclofos [INN:BAN]
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethyl phosphate
- Trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphate
- Triclofosum [INN-Latin]
- Triclofosa [INN-Spanish]
- Trichloroethanol 1-phosphate
- Trichloroethanol-1-phosphate
- HSDB 3276
- EINECS 206-185-6
- BRN 1841552
- Phosphoric acid, 2,2,2-trichloroethyl ester
- UNII-J712EO9048
- 2,2,2-Trichloroethanol, dihydrogen phosphate
- (2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)phosphonic acid
- TRICLOFOS [MI]
- TRICLOFOS [HSDB]
- TRICLOFOS [WHO-DD]
- Neguvon [veterinary] (TN)
- SCHEMBL125854
- CHEMBL1201317
- DTXSID9023700
- YYQRGCZGSFRBAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- MFCD00242992
- DB06753
- SY299205
- DB-234103
- HY-148149
- CS-0613731
- NS00022027
- C07165
- D08634
- G78139
- EN300-7653367
- Q15305564
- InChI=1/C2H4Cl3O4P/c3-2(4,5)1-9-10(6,7)8/h1H2,(H2,6,7,8
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
229.38 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
XLogP3-AA
Property Value
0.3
Reference
Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
2
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
4
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
2
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
227.891279 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
227.891279 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
66.8 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
10
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
147
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
WHITE OR ALMOST WHITE POWDER
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
SALINE
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
SOL IN WATER /MONOSODIUM/
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1519
1 g in 250 ml alcohol; almost insol in ether
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
STABLE IN LIGHT, UNSTABLE IN HEAT ABOVE ROOM TEMP /MONOSODIUM/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
1D NMR Spectra
HYGROSCOPIC IN AIR
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Same Parent, Exact Count
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
Hypnotics and Sedatives
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
A HYPNOTIC AGENT SUGGESTED FOR INSOMNIA CHARACTERIZED BY DIFFICULTY IN FALLING ASLEEP, NOCTURNAL AWAKENING, & EARLY MORNING AWAKENING. /TRICLOFOS SODIUM/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
A DOSE OF TRICLOFOS SODIUM OF 1.5 G WILL YIELD BLOOD LEVEL OF TRICHLOROETHANOL APPROX EQUAL TO THAT FROM 900 MG OF CHLORAL HYDRATE. /TRICLOFOS SODIUM/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 363
In a study involving seven healthy subjects stabilized on warfarin, triclofos considerably incr the hypoprothrombinemic response initially, with a gradual diminution of this effect after the first week....patients receiving chronic oral anticoagulant therapy who are started on triclofos are only at risk of hemorrhage during the first two weeks of combined therapy.
Hansten, P.D. Drug Interactions. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1979., p. 59
IT IS CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH MARKED RENAL OR HEPATIC IMPAIRMENT. TRICLOFOS SODIUM MAY BE HABIT FORMING AND IS SUBJECT TO SAME WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, AND DRUG INTERACTIONS AS CHLORAL HYDRATE... EXCEPT FOR SINGLE DOSE TO INDUCE SLEEP DURING ECG, DRUG CANNOT BE RECOMMENDED IN CHILDREN UNDER 12 YR OF AGE. /TRICLOFOS SODIUM/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
In patients on chronic oral anticoagulant therapy who require sedative-hypnotics...use drugs which...do not interact such as flurazepam (dalmane) or diazepam (valium). If triclofos is used, the patient should be monitored closely during the first two weeks of triclofos therapy.
Hansten, P.D. Drug Interactions. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1979., p. 59
HYDROLYSIS KINETICS WAS STUDIED AT PH 0-7.8, TEMP 80.1-98.4 °F & IONIC STRENGTH 0.02-1.50. VARIOUS MECHANISTIC POSSIBILITIES FOR THE DIFFERENT NATURES OF TRICLOFOS SODIUM AT THE VARYING RANGES OF PH, TEMPERATURE AND IONIC STRENGTH ARE DISCUSSED. /TRICLOFOS SODIUM MONOPHOSPHATE ESTER/
MCRAE JD, TADROS LM; J PHARM SCI 67 (MAY): 630-5 (1978)
After 6 hr, 4.6% of 15 mg/kg and 22 mg/kg dose of triclofos sodium given orally to seven healthy people, was recovered in the urine.
Sellers EM et al; J Clin Pharmacol 18 (Oct): 457-61 (1978)
...IS RAPIDLY DEPHOSPHORYLATED, PRINCIPALLY IN GUT, TO TRICHLOROETHANOL... TRICLOFOS SODIUM PRODUCES A PEAK TRICHLOROETHANOL LEVEL IN 1 HR... /TRICLOFOS SODIUM/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
METABOLISM OF CHLORAL HYDRATE AND TRICLOFOS SODIUM WAS COMPARED IN SEVEN HEALTHY PEOPLE WHO INGESTED 15 MG/KG & 22.5 MG/KG. TRICHLOROETHANOL WAS PRODUCED. AFTER 6 HR 4.6% OF TRICLOFOS SODIUM WAS RECOVERED IN URINE AS TRICHLOROETHANOL & TRICHLOROACETIC ACID.
SELLERS EM ET AL; J CLIN PHARMACOL 18 (OCT): 457-61 (1978)
...IT HAS A HALF-LIFE OF APPROXIMATELY 8 HR. /TRICLOFOS SODIUM/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
MEDICATION
HEMS ET AL, BRIT MED J 1, 1834 (1962).
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1519
Chloral is reduced with sodium borohydride and the resulting trichloroethanol is esterified with polyphosphoric acid to give the dihydrogen phosphate. The ester is then reacted with an equimolar quantity of sodium hydroxide. /Triclofos sodium/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
Syrup: 500 mg/5 ml
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 351
Tablets: 750 mg; liquid: 100 mg/ml
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1019
EPA TSCA Commercial Activity Status
Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphate: ACTIVE
SRP: At the time of review, criteria for land treatment or burial (sanitary landfill) disposal practices are subject to significant revision. Prior to implementing land disposal of waste residue (including waste sludge), consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices.
Chemical Assessment
IMAP assessments - Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphate: Environment tier I assessment
IMAP assessments - Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphate: Human health tier I assessment
BLALOCK CC; DRUG EVALUATION DATA: TRICLOFOS SODIUM; DRUG INTEL CLIN PHARM 7 (MAR): 126-8 (1973). MONOGRAPH ON TRICLOFOS SODIUM INCLUDING CHEMISTRY, MECHANISM OF ACTION, TOXICOLOGY, BIOPHARMACEUTICS, MFR CLAIMS, SIDE EFFECTS & ADVERSE REACTIONS, DRUG INTERACTIONS, DOSAGE & ADMIN & COST IS PRESENTED.
...TRICLOFOS.../IS/ SLOWLY HYDROLYZED IN STOMACH TO YIELD CHLORAL HYDRATE AND .../IT HAS/ BEEN SHOWN TO DECR WARFARIN HALF-LIFE BY INCR AMT OF UNBOUND WARFARIN AVAILABLE FOR METABOLISM.
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 274
...TRICLOFOS /IS/...METABOLIZED TO YIELD TRICHLOROETHANOL /WHICH/ WILL INTERACT WITH ALCOHOL.
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 20
It is proposed that a metabolite of triclofos (trichloroacetic acid) displaces warfarin from plasma protein binding.
Hansten, P.D. Drug Interactions. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1979., p. 59
PRETERM INFANT WITH ACCIDENTAL TRICLOFOS SODIUM POISONING DEVELOPED DEEP COMA, SEVERE HYPOTHERMIA, HYPOTENSION & LACK OF PRIMITIVE & DEEP TENDON REFLEXES.
SHAHAR E ET AL; CLIN PEDIATR (PHILA) 18 (11): 706-7 (1979)
THIRTY PT COMPLAINING OF INSOMNIA WERE STUDIED IN DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL WITH CROSSOVER OF FINORGAL, NITRAZEPAM & TRICLOFOS SODIUM. FINORGAL PRODUCED SIMILAR RESULTS TO TRICLOFOS SODIUM. SIDE-EFFECTS WERE NOT SERIOUS. NO DRUG TOXICITY DEVELOPED OVER THREE WK PERIOD OF TREATMENT.
BAIOTTI G; J INT MED RES 7 (5): 383-6 (1979)
Triclofos's production and use as a medicinal drug may result in its release to the environment. If released to the atmosphere, triclofos will exist in both the vapor phase and particulate phase based on an estimated vapor pressure of 2.13X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C. It will degrade in the vapor phase by reaction with hydroxyl radicals with a half-life of 10 days. Particulate phase triclofos may be removed physically from air by wet and dry deposition. In soil, triclofos is expected to have moderate mobility; some leaching may be possible as triclofos should be fairly water soluble. Hydrolysis of triclofos in soil may be an important fate process, particularly under alkaline soil conditions. In water, hydrolysis may be a major fate process for triclofos, particularly if the water is alkaline. An estimated Henry's Law constant of 5.64X10-7 atm-cu/mole indicates that this compound will not volatilize from water surfaces. Triclofos is not expected to bioconcentrate in aquatic organisms. (SRC)
Triclofos's production and use as a medicinal drug may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams(1).
(1) Budavari S et al; The Merck Index-Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., p 1519 (1989)
TERRESTRIAL FATE: An estimated Koc of 352(1,2,SRC) indicates that triclofos will have moderate mobility in soil(3). Under alkaline soil conditions, hydrolysis of triclofos may be rapid and will be expected to be a major fate process for this compound; the rate of hydrolysis in neutral or slightly acid soil environments should be slower(4). Triclofos is not expected to volatilize from soil surfaces based on an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.41X10-13 atm-cu m/mole(5).
(1) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical Property Estimation Methods. Washington DC: Amer Chem Soc pp. 4-9 (1990)
(2) Meylan WM, Howard PH; J Pharm Sci 84: 83-92 (1995)
(3) Swann RL et al; Res Rev 85: 23 (1983)
(4) Mabey W, Mill T; J Phys Chem Ref Data 7: 383-415 (1978)
(5) Meylan W, Howard PH; Environ Toxicol Chem 10: 1283-93 (1991)
AQUATIC FATE: Hydrolysis of triclofos, particularly in alkaline waters, will be a major fate process for this compound; in neutral or slightly acidic water, triclofos will hydrolyze less rapidly(1). Triclofos is not expected to volatilize from water surfaces based on an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.41X10-13 atm-cu/mole(2). If released to an aquatic environment, triclofos is not expected to bioconcentrate with an estimated BCF value of 25(3,4,SRC).
(1) Mabey W, Mill T; J Phys Chem Ref Data 7: 383-415 (1978)
(2) Meylan W, Howard PH; Environ Toxicol Chem 10: 1283-93 (1991)
(3) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical Property Estimation Methods Washington, DC: Amer Chem Soc p. 5-4 (1990)
(4) Meylan WM, Howard PH; J Pharm Sci 84: 83-92 (1995)
ATMOSPHERIC FATE: Based on an estimated vapor pressure of 2.13X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C(1,SRC), triclofos can exist in both the vapor phase and particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere(2,SRC). It will degrade fairly rapidly in the vapor phase by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals with an estimated half-life of 10 days(3,SRC). Particulate phase triclofos may be removed physically from air by wet and dry deposition(SRC).
(1) Lyman WJ; in Environmental Exposure From Chemicals Vol I, Neely WB, Blau Ge (eds), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p 31 (1985)
(2) Bidleman TF; Environ Sci Technol 22: 361-367 (1988)
(3) Meylan WM, Howard PH; Chemosphere 26: 2293-2299 (1993)
The rate constant for the vapor phase reaction of triclofos with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals has been estimated as 1.58X10-12 cu-cm/molecule-sec at 25 °C(1). This corresponds to an atmospheric half-life of about 10 days at an atmospheric concentration of 5X10+5 hydroxyl radicals per cu cm(1,SRC). Hydrolysis of triclofos is expected to be rapid. Hydrolysis of phosphate esters is generally promoted by alkaline conditions as the phosphate ester undergoes second order nucleophilic reactions involving cleavage of the O-P bond due to hydroxide ions(2). A half-life of 852 years has been reported for methyl phosphate in water at 25 °C and at a pH 4.17(3); the reaction rate was 2.57X10-11 1/sec(3). The three chlorines on the ethyl will act as electron withdrawing groups and will promote hydrolysis by OH-(2). In addition, monoalkyl phosphates, which exist as mono and dianions at common environmental pH's, are generally more susceptible to hydrolysis than the di- or triesters. Thus under alkaline conditions triclofos may hydrolyze fairly rapidly(2,SRC).
(1) Meylan WM, Howard PH; Chemosphere 26: 2293-2299 (1993)
(2) Mabey W, Mill T; J Phys Chem Ref Data 7: 383-415 (1978)
(3) Midwest Research Institute; MRI 4309-L. Kansas City, MO. Midwest Res. Inst. 279 p. (1977)
Based on an estimated log Kow of 1.13(1), the BCF of triclofos is estimated as 4.2 from a regression-derived equation(2,SRC). This BCF value indicates that bioconcentration is not an important fate process for triclofos(SRC).
(1) Meylan WM, Howard PH; J Pharm Sci 84: 83-92 (1995)
(2) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical Property Estimation Methods Washington, DC: Amer Chem Soc p. 5-4 (1990)
Using a regression-derived equation(1) and an estimated log Kow of 1.13(2), the Koc for triclofos was estimated as 98(SRC). According to a suggested classification scheme, this Koc value suggests that triclofos will have moderate mobility in soil(3). As triclofos should be fairly water soluble, leaching of this compound may occur under certain environmental conditions(SRC).
(1) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical Property Estimation Methods. Washington DC: Amer Chem Soc pp. 4-9 (1990)
(2) Meylan WM, Howard PH; J Pharm Sci 84: 83-92 (1995)
(3) Swann RL et al; Res Rev 85: 23 (1983)
The Henry's Law constant for triclofos is estimated as 1.41X10-13 atm-cu m/mole(1,SRC). This value indicates that triclofos is essentially non-volatile from water surfaces(2).
(1) Meylan WM, Howard PH; Environ Toxicol Chem 10: 1283-93 (1991)
(2) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical Property Estimation Methods. Washington DC: Amer Chem Soc p. 15-15 to 15-29 (1990)
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=YYQRGCZGSFRBAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS)Ethanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphatehttps://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-assessments/
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/Trichloroethyl phosphatehttps://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=306-52-5
- ChemIDplusTriclofos [INN:BAN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000306525ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- EPA Chemicals under the TSCAEthanol, 2,2,2-trichloro-, dihydrogen phosphatehttps://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tscaEPA TSCA Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-notice
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
- ChEBI
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citing
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classificationhttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08303.keg
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- NMRShiftDB
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/about
- SpectraBase2,2,2-Trichloroethyl dihydrogen phosphatehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/D72StvSOlgg
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) ClassificationLICENSEUse of all or parts of the material requires reference to the WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Copying and distribution for commercial purposes is not allowed. Changing or manipulating the material is not allowed.https://www.whocc.no/copyright_disclaimer/
- Wikidata
- Wikipedia
- Wiley
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.html
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- EPA Substance Registry ServicesEPA SRS List Classificationhttps://sor.epa.gov/sor_internet/registry/substreg/LandingPage.do
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 403030147https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/403030147
- NCBI
CONTENTS