Rifalazil
PubChem CID
135431094
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- Rifalazil
- 129791-92-0
- Benzoxazinorifamycin
- KRM-1648
- Krm 1648
Molecular Weight
941.1 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Dates
- Create:2019-01-15
- Modify:2025-01-18
Description
Rifalazil is a phenoxazine.
Rifalazil is a derivative of the antibiotic rifamycin. It is being investigated by ActivBiotics for the treatment of various bacterial infections.
RIFALAZIL is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of III (across all indications) and has 2 investigational indications.
Chemical Structure Depiction
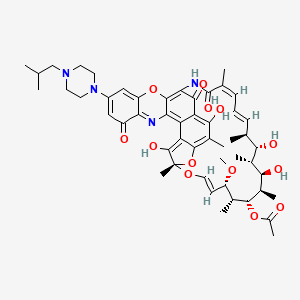
Conformer generation is disallowed since too many atoms
[(7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,6,15,17-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-30-[4-(2-methylpropyl)piperazin-1-yl]-23,32,37-trioxo-8,27,38-trioxa-24,34-diazahexacyclo[23.11.1.14,7.05,36.026,35.028,33]octatriaconta-1,3,5,9,19,21,25,28,30,33,35-undecaen-13-yl] acetate
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
InChI=1S/C51H64N4O13/c1-24(2)23-54-16-18-55(19-17-54)32-21-33(57)39-35(22-32)67-48-40(52-39)36-37-44(60)30(8)47-38(36)49(62)51(10,68-47)65-20-15-34(64-11)27(5)46(66-31(9)56)29(7)43(59)28(6)42(58)25(3)13-12-14-26(4)50(63)53-41(48)45(37)61/h12-15,20-22,24-25,27-29,34,42-43,46,58-60,62H,16-19,23H2,1-11H3,(H,53,63)/b13-12+,20-15+,26-14-/t25-,27+,28+,29+,34-,42-,43+,46+,51-/m0/s1
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
IXSVOCGZBUJEPI-HTQYORAHSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
C[C@H]1/C=C/C=C(\C(=O)NC2=C3C(=C4C(=C(C(=C5C4=C([C@](O5)(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)O)C)O)C2=O)N=C6C(=CC(=CC6=O)N7CCN(CC7)CC(C)C)O3)/C
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
C51H64N4O13
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
188910-97-6
- 3'-hydroxy-5'-(4-isobutylpiperazinyl)benzoxazinorifamycin
- ABI 1648
- ABI-1648
- ABI1648
- benzoxazinorifamycin
- KRM 1648
- KRM-1648
- rifalazil
- Rifalazil
- 129791-92-0
- Benzoxazinorifamycin
- KRM-1648
- Krm 1648
- S1976TE8QK
- [(7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,6,15,17-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-30-[4-(2-methylpropyl)piperazin-1-yl]-23,32,37-trioxo-8,27,38-trioxa-24,34-diazahexacyclo[23.11.1.14,7.05,36.026,35.028,33]octatriaconta-1,3,5,9,19,21,25,28,30,33,35-undecaen-13-yl] acetate
- 3'-Hydroxy-5'-(4-isobutylpiperazinyl)benzoxazinorifamycin
- (2S,16Z,18E,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26R,27S,28E)-5,12,21,23,25-Pentahydroxy-10-(4-isobutyl-1-piperazinyl)-27-methoxy-2,4,16,20,22,24,26-heptamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca(1,11,13)trienimino)-6H-benzofuro(4,5-a)phenoxazine-1(2H),6,15-trione 25-acetate
- 3'-hydroxy-5'-(4-isobutyl-1-piperazinyl)benzoxazinorifamycin
- (7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,15,17,32-Tetrahydroxy-30-(4-isobutyl-1-piperazinyl)-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23,37-trioxo-8,27,38-trioxa-24,34-diazahexacyclo[23.11;.1.14,7.05,36.026,35.028,33]octatriaconta-1(36),2,4,9,19,21,25,28,30,32,34-undecaen-13-yl acetate
- Rifamycin viii, 1',4-didehydro-1-deoxy-1,4-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-5'-(4-(2-methylpropyl)-1-piperazinyl)-1-oxo-
- Rifalazil [USAN:INN]
- Rifalazilo
- [tetrahydroxy-(4-isobutylpiperazin-1-yl)-methoxy-heptamethyl-trioxo-[?]yl] acetate
- ABI 1648
- Rifamycin VIII, 1',4-didehydro-1-deoxy-1,4-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-5'-[4-(2-methylpropyl)-1-piperazinyl]-1-oxo-
- RLZ
- RIFALAZIL [INN]
- RIFALAZIL [MI]
- Rifalazil (USAN/INN)
- RIFALAZIL [USAN]
- KRM-1648 and Yokuinin
- UNII-S1976TE8QK
- SCHEMBL76007
- CHEMBL236297
- KRM-1648 & MBST
- ABI1648
- CHEBI:188526
- ABI-1648
- BDBM50491559
- KRM-1648 & Mao-Bushi-Saishin-To
- DB04934
- PA-1648
- HY-105099
- CS-0024983
- D02550
- G12816
- KRM-1648 & Scretory leukocyte protease inhibitor
- Q7333206
- (2S,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26R,27S)-5,12,21,23-Tetrahydroxy-10-(4-isobutylpiperazin-1-yl)-27-methoxy-2,4,16,20,22,24,26-heptamethyl-1,6,15-trioxo-1,2-dihydro-6H-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)[1]benzofuro[4,5-a]phenoxazin-25-yl acetate
- 1',4-DIDEHYDRO-1-DEOXY-1,4-DIHYDRO-3'-HYDROXY-5'-(4-(2-METHYLPROPYL)-1-PIPERAZINYL)-1-OXORIFAMYCIN VIII
- 2,7-(Epoxy[1,11,13]pentadecatrienoimino)-6H-benzofuro[4,5-a]phenoxazine-1,6,15(2H)-trione, 25-(acetyloxy)-5,12,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,16,20,22,24,26-heptamethyl-10-[4-(2-methylpropyl)-1-piperazinyl]-, (2S,16Z,18E,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26R,27S,28E)-
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
941.1 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
XLogP3-AA
Property Value
3.3
Reference
Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
5
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
16
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
6
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
940.44698811 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
940.44698811 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
226 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
68
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
2510
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
9
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
3
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.05.07)
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Same Connectivity Count
Same Isotope Count
Same Parent, Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Isotope Count
Same Parent, Exact Count
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
PubMed Count
Investigated for use/treatment in atherosclerosis, bacterial infection, and peripheral vascular disease.
Rifalazil represents a new generation of ansamycins that contain a unique four-ring structure. Originally rifalazil was developed as a therapeutic agent to replace rifampin as part of a multiple drug regimen in the treatment of tuberculosis. As a result of its superior antimicrobial activity and high intracellular levels, rifalazil has potential to treat indications caused by the intracellular pathogen, Chlamydia trachomatis, which causes non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis, often leading to pelvic inflammatory disease. Rifalazil also has potential to treat the related microorganism, Chlamydia pneumoniae, which may be involved in chronic inflammatory processes thought to be partly responsible for atherosclerosis. Due to its favourable antimicrobial spectrum and other positive attributes, rifalazil may also prove valuable in the treatment of gastric ulcer disease, caused by Helicobacter pylori, and antibiotic-associated colitis, the result of toxin production following the growth of Clostridium difficile in the colon. The potential value of rifalazil in the treatment of these indications will be assessed in human clinical trials.
Antibiotics, Antitubercular
Substances obtained from various species of microorganisms that are, alone or in combination with other agents, of use in treating various forms of tuberculosis; most of these agents are merely bacteriostatic, induce resistance in the organisms, and may be toxic. (See all compounds classified as Antibiotics, Antitubercular.)
Leprostatic Agents
Substances that suppress Mycobacterium leprae, ameliorate the clinical manifestations of leprosy, and/or reduce the incidence and severity of leprous reactions. (See all compounds classified as Leprostatic Agents.)
The major metabolites of rifalazil in human are 25-deacetyl-benzoxazinorifamycin and 32-hydroxy-benzoxazinorifamycin. The enzyme responsible for the benzoxazinorifamycin-25-deacetylation is a B-esterase while the enzyme responsible for the benzoxazinorifamycin-32-hydroxylation is CYP3A4.
The potent antimycobacterial activity of rifalazil is due to inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase.
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusRifalazil [USAN:INN]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0129791920ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEBI
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlAntiinfectiveshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08307.keg
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- WikipediaIguratimodhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iguratimod
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAntibiotics, Antitubercularhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000904Leprostatic Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68007917
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
CONTENTS
