Piperaquine
PubChem CID
122262
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- piperaquine
- 4085-31-8
- Piperaquine phosphate
- Piperaquinoline
- 1,3-Bis(4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)propane
Molecular Weight
535.5 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Dates
- Create:2005-08-08
- Modify:2025-01-18
Description
Piperaquine is an aminoquinoline that is 1,3-di(piperazin-1-yl)propane in which the nitrogen at position 4 of each of the piperazine moieties is replaced by a 7-chloroquinolin-4-yl group. It has a role as an antimalarial. It is a N-arylpiperazine, an organochlorine compound and an aminoquinoline.
Piperaquine is an antimalarial agent first synthesized in the 1960's and used throughout China. Its use declined in the 1980's as piperaquine resistant strains of *Plasmodium falciparum* appeared and artemisinin derivatives became available. It has come back into use in combination with the artemisinin derivative [DB11638] as part of the combination product Eurartesim. Eurartesim was first authorized for market by the European Medicines Agency in October 2011.
PIPERAQUINE is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of III (across all indications) and has 7 investigational indications.
Chemical Structure Depiction
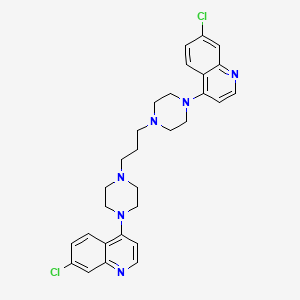
7-chloro-4-[4-[3-[4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]quinoline
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/C29H32Cl2N6/c30-22-2-4-24-26(20-22)32-8-6-28(24)36-16-12-34(13-17-36)10-1-11-35-14-18-37(19-15-35)29-7-9-33-27-21-23(31)3-5-25(27)29/h2-9,20-21H,1,10-19H2
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
UCRHFBCYFMIWHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C1CN(CCN1CCCN2CCN(CC2)C3=C4C=CC(=CC4=NC=C3)Cl)C5=C6C=CC(=CC6=NC=C5)Cl
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
C29H32Cl2N6
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
83764-65-2
- 1,3-bis(1-(7-chloro-4'-quinolyl)-4'-piperazinyl)propane
- piperaquine
- piperaquine phosphate
- piperaquine phosphate (1:1)
- piperaquine phosphate (1:4) anhydrous
- piperaquine tetraphosphate anhydrous
- piperaquine tetraphosphate tetrahydrate
- quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-)
- quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-, phosphate (1:1)
- quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-, phosphate (1:4)
- quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-, phosphate, hydrate (1:4:4)
- piperaquine
- 4085-31-8
- Piperaquine phosphate
- Piperaquinoline
- 1,3-Bis(4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)propane
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis[7-chloro-
- 7-chloro-4-[4-[3-[4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]quinoline
- UNII-A0HV2Q956Y
- BRN 0905079
- A0HV2Q956Y
- 4,4'-(propane-1,3-diyldipiperazine-4,1-diyl)bis(7-chloroquinoline)
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-
- PIPERAQUINE [WHO-DD]
- CHEBI:91231
- DTXSID00193825
- Piperaquine-d6
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(trimethylenedi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-
- 5-23-03-00072 (Beilstein Handbook Reference)
- 1,3-bis[4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propane
- 7-chloro-4-(4-{3-[4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl}piperazin-1-yl)quinoline
- 7-chloro-4-(4-(3-(4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)piperazin-1-yl)quinoline
- piperaquine-phosphate
- 1261394-71-1
- 1,3-bis(1-(7-chloro-4'-quinolyl)-4'-piperazinyl)propane
- QUINOLINE, 4,4'-(1,3-PROPANEDIYLDI-4,1-PIPERAZINEDIYL)BIS(7-CHLORO-, PHOSPHATE (1:4)
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-)
- SCHEMBL131649
- CHEMBL303933
- GTPL10025
- DTXCID40116316
- BCP09615
- HY-B1896
- BDBM50519563
- AKOS015896173
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis(7-chloro-(9CI)
- DB13941
- SB19150
- NCGC00344515-02
- CS-0013957
- NS00002457
- G78383
- AA-504/36954029
- Q7197338
- BRD-K27382019-418-01-9
- 1,3-bis[4-(7-chloroquinoline-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propane
- 4,4'-(1,3-Propanediydi-4,1-piper-azinediyl)bis[7-chloroquinoline]
- Quinoline, 4,4'-(1,3-Propanediyldi-4,1-Piperazinediyl)Bis(7-Chloro)-
- 7-chloro-4-(4-{3-[4-(7-chloro-4-quinolinyl)-1-piperazinyl]propyl}-1-piperazinyl)quinoline
- 7-chloro-4-[4-[3-[4-(7-chloro-4-quinolyl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]quinoline
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
535.5 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
XLogP3-AA
Property Value
5.6
Reference
Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
6
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
6
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
534.2065504 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
534.2065504 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
38.7 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
37
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
655
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
Pharmaceuticals -> Listed in ZINC15
S55 | ZINC15PHARMA | Pharmaceuticals from ZINC15 | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3247749
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Same Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Exact Count
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
PubMed Count
For the treatment of uncomplicated *Plasmodium falciparum* infection in adults, children, and infants aged 6 months and up weighing over 5 kg. Used in combination with [DB11638].
Piperaquine inhibits the P. Falciparum parasite's haem detoxification pathway.
Antimalarials
Agents used in the treatment of malaria. They are usually classified on the basis of their action against plasmodia at different stages in their life cycle in the human. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p1585) (See all compounds classified as Antimalarials.)
Absorption
Piperaquine is slowly absorbed and exhibits multiple peaks in its plasma concentration curve suggestive of enterohepatic recycling occurring alongside the absorption process. Due to this complication there is no discreet value for bioavailability but piperaquine is highly absorbed into systemic circulation. When taken with food, Cmax increases by 217% and mean exposure increases by 177%. Tmax is not affected by food and remains around 5 h. Piperaquine has been observed to accumulate more in females to a degree of 30-50% more than males. It also collects in red blood cells similar to [DB11638].
Route of Elimination
Piperaquine is mainly excreted in the feces with a negligible amount in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
Piperaquine is thought to distribute into a central compartment with an apparent volume of 26.7 L/kg, and two peripheral compartments with apparent volumes of 76.8 L/kg and 617 L/kg. These combine for a total volume of distribution of 720.5 L/kg.
Clearance
The mean apparent total clearance has been observed to be 1.12 L/h/kg in adult malaria patients.
Piperaquine undergoes N-dealkylation, separating its aliphatic bridge from one of the nitrogen-containing rings. The resulting aldehyde is then oxidized to a carboxylic acid to form metabolite 1 (M1). The same nitrogen-containing rings can also undergo hydroxylation at one of two sites to form M3 or M4. M2 is formed via N-oxidation of one of the nitrogens in the quinoline groups at either side of the molecule. M5 results when both of these nitrogens are oxidized. M1 and M2 are the major metabolism products. Each of these metabolites were observed in the urine.
The terminal elimination half-life was observed to be 576h or 24 days. This is thought to be due to the extensive distribution of piperaquine.
The mechanism of piperaquine inhibition of the haem detoxification pathway is unknown but is expected to be similar to that of [DB00608].
Piperaquine's binding to plasma proteins is considered to be virtually complete. It has been measured to be >99% in humans, rats, and dogs.
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=UCRHFBCYFMIWHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/Quinoline, 4,4′-(1,3-propanediyldi-4,1-piperazinediyl)bis[7-chloro-https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=4085-31-8
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_usePiperaquinehttps://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB13941
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- ChEBI
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)LICENSEThe data used in DGIdb is all open access and where possible made available as raw data dumps in the downloads section.http://www.dgidb.org/downloadsPIPERAQUINEhttps://www.dgidb.org/drugs/ncit:C87634
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingpiperaquinehttp://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0256572
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- Metabolomics Workbench
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/PiperaquineNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- Therapeutic Target Database (TTD)
- PharmGKBLICENSEPharmGKB data are subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareALike 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/).https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/policies
- PharosLICENSEData accessed from Pharos and TCRD is publicly available from the primary sources listed above. Please respect their individual licenses regarding proper use and redistribution.https://pharos.nih.gov/aboutPiperaquinehttps://pharos.nih.gov/ligands/XZWZZFX4VFLM
- SpectraBasePIPERAQUINE;1,3-BIS-[4-(7-CHLOROQUINOLYL-4)-PIPERAZINYL-1]-PROPANEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/DeGkcT1PkEJ
- Springer Nature
- Wikidatapiperaquinehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7197338
- WikipediaPiperaquinehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piperaquine
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlpiperaquinehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/67034759Antimalarialshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000962
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 390986859https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/390986859
- NCBI
CONTENTS

