Lead(II) fluoride
PubChem CID
24549
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- Lead(II) fluoride
- difluorolead
- PbF2
- MFCD00011162
- Lead(+2) fluoride
Molecular Weight
245 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Dates
- Create:2005-03-27
- Modify:2024-12-06
Description
Lead(II) fluoride is a fluoride of lead. It is used in certain types of glass, in phosphors for television-tube screens, and as a catalyst for the manufacture of picoline. Lead is a heavy metal and stable element with the symbol Pb and the atomic number 82, existing in metallic, organic, and inorganic forms. It is mainly found in nature as the mineral galena (PbS), cerussite (PbCO3) or anglesite (PbSO4), usually in ore with zinc, silver, or copper. (L21, L401)
L21: Wikipedia. Lead poisoning. Last Updated 3 March 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_poisoning
L401: Wikipedia. Lead(II) fluoride. Last Updated 8 May 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead(II)_fluoride
Chemical Structure Depiction
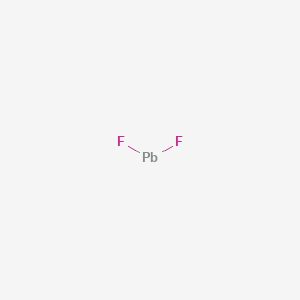
Conformer generation is disallowed since MMFF94s unsupported element
difluorolead
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/2FH.Pb/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
FPHIOHCCQGUGKU-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
F[Pb]F
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
F2Pb
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
106496-44-0, 1493800-25-1, 2098815-17-7
- lead fluoride
- lead fluoride (PbF2)
- lead fluoride (PbF3)
- lead(II) fluoride
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
245 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
2
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
245.97346 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
245.97346 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
0Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
3
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
2.8
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
10 to 30 grams for and adult human (lead salts). (T17)
T17: Baselt RC (2000). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 5th ed. Foster City, CA: Chemical Toxicology Institute.
Lead is absorbed following inhalation, oral, and dermal exposure. It is then distributed mainly to the bones and red blood cells. In the blood lead may be found bound to serum albumin or the metal-binding protein metallothionein. Organic lead is metabolized by cytochrome P-450 enzymes, whereas inorganic lead forms complexes with delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. Lead is excreted mainly in the urine and faeces. (L136)
L136: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp13.html
Lead(II) fluoride is used in certain types of glass, in phosphors for television-tube screens, and as a catalyst for the manufacture of picoline. (L401)
L401: Wikipedia. Lead(II) fluoride. Last Updated 8 May 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead(II)_fluoride
Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example, lead has been shown to competitively inhibit calcium's binding of calmodulin, interferring with neurotransmitter release. It exhibits similar competitive inhibition at the NMDA receptor and protein kinase C, which impairs brain microvascular formation and function, as well as alters the blood-brain barrier. Lead also affects the nervous system by impairing regulation of dopamine synthesis and blocking evoked release of acetylcholine. However, it's main mechanism of action occurs by inhibiting delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, an enzyme vital in the biosynthesis of heme, which is a necesssary cofactor of hemoglobin. (T4, A20, A22, L136)
A20: Gill KD, Gupta V, Sandhir R: Ca2+/calmodulin-mediated neurotransmitter release and neurobehavioural deficits following lead exposure. Cell Biochem Funct. 2003 Dec;21(4):345-53. PMID:14624473
A22: Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. PMID:10454514
L136: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp13.html
T4: Ellenhorn MJ and Barceloux DG (1988). Diagnosis and treatment of human poisoning. Medical Toxicology. New York, New York: Elsevier Science Publishing Company, Inc.
Carcinogen Classification
2A, probably carcinogenic to humans. (L135)
Lead is a neurotoxin and has been known to cause brain damage and reduced cognitive capacity, especially in children. Lead exposure can result in nephropathy, as well as blood disorders such as high blood pressure and anemia. Lead also exhibits reproductive toxicity and can results in miscarriages and reduced sperm production. (L21)
L21: Wikipedia. Lead poisoning. Last Updated 3 March 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_poisoning
Oral (L136) ; inhalation (L136) ; dermal (L136)
L136: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp13.html
Symptions of chronic lead poisoning include reduced cognitive abilities, nausea, abdominal pain, irritability, insomnia, metal taste in the mouth, excess lethargy or hyperactivity, chest pain, headache and, in extreme cases, seizures, comas, and death. There are also associated gastrointestinal problems, such as constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, poor appetite, weight loss, which are common in acute poisoning. (A2, L21)
A2: Needleman HL, Schell A, Bellinger D, Leviton A, Allred EN: The long-term effects of exposure to low doses of lead in childhood. An 11-year follow-up report. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 11;322(2):83-8. PMID:2294437
L21: Wikipedia. Lead poisoning. Last Updated 3 March 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_poisoning
LD50: 3031 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (T14)
T14: Lewis RJ (1996). Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 9th ed. Volumes 1-3. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Chronic Inhalation: 0.05 mg/m3 (L134)
L134: ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2001). Minimal Risk Levels (MRLs) for Hazardous Substances. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/mrls/
L21: Wikipedia. Lead poisoning. Last Updated 3 March 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_poisoning
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=FPHIOHCCQGUGKU-UHFFFAOYSA-L
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- SpectraBaseLEAD(II) FLUORIDEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/KS7Zzt9iMJyLEAD(II) FLUORIDEhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/JGlQ2vYdjBK
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)LICENSET3DB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (T3DB) and the original publication.http://www.t3db.ca/downloadsLead fluoridehttp://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D1327
- Wikidatalead(II) fluoridehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q419690
- Wikipedialead(II) fluoridehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead(II)_fluoride
- PubChemPFAS and Fluorinated Compounds in PubChemhttps://gitlab.com/uniluxembourg/lcsb/eci/pubchem-docs/-/raw/main/pfas-tree/PFAS_Tree.pdf?inline=false
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmllead fluoridehttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/67077765
- EPA Substance Registry ServicesEPA SRS List Classificationhttps://sor.epa.gov/sor_internet/registry/substreg/LandingPage.do
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 403413333https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/403413333
CONTENTS