Grossman's sealer
PubChem CID
5152822
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- Grossman's sealer
- Kitol,90%(MixtureofDiastereomers)
- 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester, polymer with butyl 2-propenoate, ethenylbenzene, formaldehyde, 2-hydroxyethyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, methyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, methyl 2-propenoate, oxiranylmethyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, 2-propenenitrile a
Molecular Weight
98.08 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Dates
- Create:2005-09-26
- Modify:2025-01-18
See also:  Sulfuric Acid (preferred); Phenolsulfonic acid; sulfuric acid (component of) ... View More ...
Sulfuric Acid (preferred); Phenolsulfonic acid; sulfuric acid (component of) ... View More ...
 Sulfuric Acid (preferred); Phenolsulfonic acid; sulfuric acid (component of) ... View More ...
Sulfuric Acid (preferred); Phenolsulfonic acid; sulfuric acid (component of) ... View More ...Chemical Structure Depiction
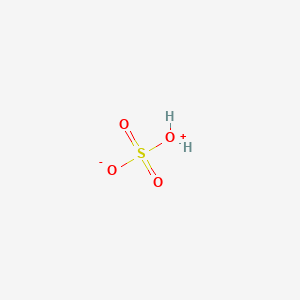
InChI=1S/H2O4S/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H2,1,2,3,4)
Computed by InChI 1.0.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
[OH2+]S(=O)(=O)[O-]
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
H2O4S
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
14808-79-8
Grossman's sealer
- Grossman's sealer
- Kitol,90%(MixtureofDiastereomers)
- 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester, polymer with butyl 2-propenoate, ethenylbenzene, formaldehyde, 2-hydroxyethyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, methyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, methyl 2-propenoate, oxiranylmethyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, 2-propenenitrile a
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
98.08 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
XLogP3-AA
Property Value
-1.5
Reference
Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.6.11 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
3
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.6.11 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.6.11 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
97.96737971 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
97.96737971 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
66.6 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.6.11 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
5
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
76
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.6.11 (PubChem release 2019.06.18)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2010.01.29)
Solid
Spectra ID
Instrument Type
GC-EI-TOF
Ionization Mode
positive
Top 5 Peaks
147.0 100
148.0 15.52
227.0 12.11
149.0 7.91
131.0 4.90
Notes
instrument=Leco Pegasus IV
Spectra ID
Instrument Type
Linear Ion Trap
Ionization Mode
negative
Top 5 Peaks
860.166685 0.94
879.500019 0.70
781.226922 0.69
720.416681 0.68
659.666679 0.66
Notes
instrument=Thermo Finnigan LTQ
Spectra ID
Instrument Type
Linear Ion Trap
Ionization Mode
negative
Top 5 Peaks
232.884933 100
312.890789 54.93
266.861087 3.20
330.903205 2.70
250.87025 2.25
Notes
instrument=Thermo Finnigan LTQ
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
Same Count
Sulfuric Acid (preferred)
- Copper; nitric acid; potassium alum; sulfuric acid; tin (component of)
- Phenolsulfonic acid; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Bellis perennis whole; glechoma hederacea flowering top; goldenseal; gratiola officinalis whole; lachesis muta venom; lytta vesicatoria; silver nitrate; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Arsenic trioxide; chamaelirium luteum root; goldenseal; lemna minor whole; magnesium fluoride; silicon dioxide; sulfuric acid; wood creosote (component of)
- Asafetida; capsicum; cola nut; lachesis muta venom; potassium dichromate; ranunculus bulbosus; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid; zinc (component of)
- Chionanthus virginicus root bark; corn silk; lactic acid, DL-; onion; phosphorus; sulfuric acid; syzygium cumini fruit; zinc sulfate heptahydrate (component of)
- Conium maculatum flowering top; delphinium staphisagria seed; lytta vesicatoria; nasturtium officinale whole; ononis spinosa whole; selenium; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Aconitum napellus; black cohosh; lachesis muta venom; melissa officinalis; platinum; sanguinaria canadensis root; sepia officinalis juice; sulfuric acid; valerian (component of)
- Arnica montana whole; bellis perennis whole; erigeron canadensis whole; hamamelis virginiana root bark/stem bark; phosphorus; rhododendron tomentosum leafy twig; sulfuric acid (component of)
- American ginseng; anemone pulsatilla; angelica archangelica root; black cohosh; goldenseal; juniperus sabina leafy twig; lachesis muta venom; sepia officinalis juice; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Activated charcoal; ammonium carbonate; antimony arsenate; antimony potassium tartrate; arsenic trioxide; bromine; chlorine; lobelia inflata whole; potassium carbonate; sulfuric acid; tin (component of)
- Alcohol; beta vulgaris whole; capsicum; chelidonium majus whole; lycopodium clavatum spore; quercus robur nut; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sucrose; sulfuric acid; taraxacum officinale; trifolium pratense flower (component of)
- Arnica montana; bellis perennis; calcium fluoride; calendula officinalis flowering top; comfrey root; ferrum phosphoricum; hypericum perforatum; ledum palustre twig; sodium sulfate; sulfuric acid; toxicodendron pubescens leaf (component of)
- Amyl nitrite; black cohosh; caulophyllum thalictroides root; gelsemium sempervirens root; iron; lachesis muta venom; oyster shell calcium carbonate, crude; pulsatilla vulgaris whole; sanguinaria canadensis root; sepia officinalis juice; sulfur; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Aconitum napellus; echinacea purpurea; ferric ferrocyanide; gelsemium sempervirens root; hops; lead; passiflora incarnata flowering top; phosphorus; quinine; sepia officinalis juice; silver nitrate; strychnos ignatii seed; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid (component of)
- Arnica montana whole; bellis perennis whole; calcium fluoride; calendula officinalis flowering top; comfrey root; ferrosoferric phosphate; hypericum perforatum whole; rhododendron tomentosum leafy twig; sodium sulfate; sulfuric acid; toxicodendron pubescens leaf (component of)
- Arnica montana; bellis perennis; calcium fluoride; calendula officinalis flowering top; comfrey root; ferrosoferric phosphate; hypericum perforatum; ledum palustre twig; ruta graveolens flowering top; sodium sulfate; sulfuric acid; toxicodendron pubescens leaf (component of)
- Acetone; arsenic trioxide; benzene; berberis vulgaris root bark; cadmium sulfide; carbon dioxide; chlorine; hydrofluoric acid; kerosene; lead; melatonin; mercurius solubilis; nitrous oxide; ozone; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid; tin; toluene; uranyl nitrate hexahydrate (component of)
- Antimony trisulfide; arctium lappa root; arnica montana root; euphrasia stricta; formic acid; graphite; histamine dihydrochloride; ledum palustre twig; lycopodium clavatum spore; pine tar; selenium; strychnos ignatii seed; sulfur; sulfuric acid; tellurium; thuja occidentalis leafy twig (component of)
- Acetone; activated charcoal; aniline; benzene; benzo(A)pyrene; carbon tetrachloride; ether; kerosene; lead; lead chloride; magnesium sulfate heptahydrate; methyl alcohol; phenol; phenolphthalein; phosphorus; picric acid; pine tar; sulfonmethane; sulfuric acid; trichloroethylene; turpentine oil; vanadium (component of)
- Acetaldehyde; ammonium carbonate; benzene; berberis vulgaris root bark; camphor (natural); carbon tetrachloride; chloroform; cysteine; ether; formaldehyde solution; kerosene; lachesis muta venom; lead; naphthalene; oyster shell calcium carbonate, crude; paraffin; phenol; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid; taraxacum officinale; wood creosote (component of)
- Alcohol, X-ray exposed (1000 rad); allylthiourea; ammonium carbonate; barium chloride dihydrate; caulophyllum thalictroides root; chaste tree; conium maculatum flowering top; estrone; graphite; hyoscyamus niger; juniperus sabina leafy twig; saw palmetto; selenium; sepia officinalis juice; sodium borate; sodium carbonate; sulfuric acid; sus scrofa fallopian tube; sus scrofa hypothalamus; sus scrofa uterus; thyroid, porcine (component of)
- Arctium lappa root; arsenic trioxide; asarum canadense root; berberis vulgaris root bark; butylbenzene; carbon disulfide; chlorine; glycyrrhiza glabra; iridium; kerosene; lycopodium clavatum spore; nitric acid; phenol; phosphorus; phytolacca americana root; pork liver; selenium; sorbitol; stillingia sylvatica root; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid; sus scrofa adrenal gland; sus scrofa thyroid; trifolium pratense flower (component of)
- Arsenic trioxide; bromine; cadmium sulfate; cinchona officinalis bark; coffea arabica seed, roasted; conium maculatum flowering top; gelsemium sempervirens root; glycyrrhiza glabra; goldenseal; hydrogen; iodine; kerosene; lachesis muta venom; mercurius solubilis; nitric acid; phosphoric acid; phosphorus; phytolacca americana root; pulsatilla vulgaris whole; silicon dioxide; strychnos nux-vomica seed; sulfuric acid; taraxacum officinale (component of)
Placenta
- Cytoplasm
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Extracellular
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- 17-Beta Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase III Deficiency
- Androgen and Estrogen Metabolism
- Aromatase deficiency
- Fabry disease
- Gaucher Disease
- Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy
- Krabbe disease
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD)
- Starch and sucrose metabolism
- Sulfite oxidase deficiency
- Total 11 pathways, visit the HMDB page for details
CSL No
Reactants/Reagents
Warning Message
Warning- Incorrect concentrations of sodium bromide with concentrated sulfuric acid can cause bromine gas to be released
GHS Category
Corrosive,Toxic
Reaction Class
CSL00040 Bromination BROMINE
Reference Source
User-Reported
Modified Date
5/24/18
Create Date
11/5/17
CSL No
Reactants/Reagents
Warning Message
Hydrogen azide is generated which is very explosive. Concentration on a rotary evaporator may lead to an explosion.
GHS Category
Explosive
Functional Group
AZIDE
Reference Source
ACS Safety Letters
Modified Date
7/8/18
Create Date
2/20/18
CSL No
Reactants/Reagents
Warning Message
Chemical & Engineering News (14 Mar 1994) Vol. 72, No. 11, pp. 4. Peter G. Urben pointed out that "eschewing halogenated solvents will not eliminate azide explosions" (C&EN, Dec. 13, 1993, page 4). And if we stop reading his letter at this point, he is correct; however, the remainder of the statement and the letter are either incorrect or inappropriate to the facts we described (C&EN, April 19, 1993, page 4). We cannot speak to the specifics of the explosion described by Victor J. Hruby, Lakmal Boteju, and Guigen Li (C&EN, Oct. 11, 1993, page 2), but in our case, we used a catalytic amount of sulfuric acid and a large excess of sodium azide. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with methylene chloride. After drying and filtering the organic layer, we concentrated it on a rotary evaporator. The explosion took place after all the solvent had been removed and the flask was being detached from the steam tube. The detonation occurred in the flask; the evaporator was destroyed by the conclusive force of the explosion. We again point to the articles by A. Hassner et al. [Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 25, 479 (1986), and J. Org. Chem., 55, 2304 (1990)] describing the synthesis and explosive potential of polyazidomethanes. We believe strongly that diazidomethane and not hydrogen azide was the culprit in our explosion and that Urben should not attempt to change our conclusion. Our intent is to warn our colleagues of the dangers of producing this explosive chemical. We reiterate that because of this incident we no longer permit any chemical reactions with azide to be performed in the presence of a halogenated solvent in our laboratories.
GHS Category
Explosive
Functional Group
AZIDE
Reaction Scale
Not Available
Reaction Class
Azide
DOI Link
ACS letters
Reference Source
ACS Safety Letters
Modified Date
2/28/18
Create Date
2/23/18
CSL No
Reactants/Reagents
Warning Message
Upon drying the powder product was being scraped from a sintered glass funnel to complete the neutralization of the hemiacid salt when an explosion occurred. Subsequent testing determined that the peroxide dimer of acetone was the most likely cause of the explosion. This material is reported to be both shock and friction sensitive and known to sublime at room temperature.
GHS Category
Explosive
Reference Source
ACS Safety Letters
Modified Date
7/8/18
Create Date
2/27/18
CSL No
Reactants/Reagents
Warning Message
Abstract: Piranha solution is a dangerous and useful substance used throughout academia and industry. However, there is little peer-reviewed work on its safe use, and institutional protocols are limited in their applicability beyond their institute of origin. Here, we review institutional safety protocols for Piranha use to develop a consensus on the best safe practices and try to fill any gaps and resolve any ambiguities with reference to the related safety literature.
GHS Category
Explosive,Oxidizer
Reaction Scale
Not Available
Reaction Class
Oxidation
Additional Information
Substance ID information came from CAS Common Chemistry: https://commonchemistry.cas.org/
Reference Source
Literature Reference
Modified Date
10/15/2022
Create Date
07/28/2022
Disease
References
Disease
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency
References
PubMed: 10102915, 8051926, 27289259, 12872846
MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de)
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0001448_cms_31783https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001448#spectra
- SpectraBaseAcide sulfuriquehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/LuuyWBVr1GTAcide sulfuriquehttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/Glrc3G2lZuHSULFURIC_ACID-CONC.https://spectrabase.com/spectrum/hnQRzMo0TY
- Pistoia Alliance Chemical Safety LibraryBROMINE + SULFURIC ACID + SODIUM BROMIDEhttps://safescience.cas.org/
- Wikidatasulfuric acidhttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q4118Sulfur tetroxidehttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q72509244
- PubChem
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlGrossman's sealerhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/67045432
- LOTUS - the natural products occurrence databaseLICENSEThe code for LOTUS is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.https://lotus.nprod.net/LOTUS Treehttps://lotus.naturalproducts.net/
CONTENTS