Fradiomycin sulfate
PubChem CID
71463900
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- NEOMYCIN SULFATE
- Fradiomycin sulfate
- 1405-10-3
- AKOS016010116
- (2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-5-amino-2-(aminomethyl)-6-{[(1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R)-4-{[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy}oxane-3,4-diol; sulfuric acid
Molecular Weight
712.7 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Parent Compound
Component Compounds
Dates
- Create:2013-05-31
- Modify:2025-01-18
Description
Neomycin Sulfate is the sulfate salt form of neomycin, a broad spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces fradiae with antibacterial activity. Neomycin is an antibiotic complex consisting of 3 components: the two isomeric components B and C are the active components, and neomycin A is the minor component. Neomycin irreversibly binds to the 16S rRNA and S12 protein of the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit. As a result, this agent interferes with the assembly of initiation complex between mRNA and the bacterial ribosome, thereby inhibiting the initiation of protein synthesis. In addition, neomycin induces misreading of the mRNA template and causes translational frameshift, thereby results in premature termination. This eventually leads to bacterial cell death.
Aminoglycoside antibiotic complex produced by Streptomyces fradiae. It is composed of neomycins A, B, and C, and acts by inhibiting translation during protein synthesis.
See also: Neomycin Sulfate (annotation moved to).
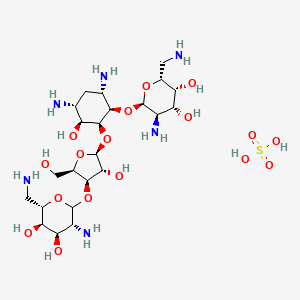
Chemical Structure Depiction
3D Conformer of Parent
(2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-5-amino-2-(aminomethyl)-6-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-[(2S,3R,4R,5R)-4-[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxyoxane-3,4-diol;sulfuric acid
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/C23H46N6O13.H2O4S/c24-2-7-13(32)15(34)10(28)21(37-7)40-18-6(27)1-5(26)12(31)20(18)42-23-17(36)19(9(4-30)39-23)41-22-11(29)16(35)14(33)8(3-25)38-22;1-5(2,3)4/h5-23,30-36H,1-4,24-29H2;(H2,1,2,3,4)/t5-,6+,7-,8+,9-,10-,11-,12+,13+,14+,15-,16-,17-,18-,19+,20+,21-,22?,23+;/m1./s1
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
OIXVKQDWLFHVGR-VTSVPHRWSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1N)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H](O2)CN)O)O)N)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O3)CO)OC4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O4)CN)O)O)N)O)O)N.OS(=O)(=O)O
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2024.12.12)
C23H48N6O17S
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
- Fradiomycin Sulfate
- Neomycin
- Neomycin Palmitate
- Neomycin Sulfate
- NEOMYCIN SULFATE
- Fradiomycin sulfate
- 1405-10-3
- AKOS016010116
- (2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-5-amino-2-(aminomethyl)-6-{[(1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R)-4-{[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy}oxane-3,4-diol; sulfuric acid
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
712.7 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
15
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
23
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
9
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
712.27966526 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
712.27966526 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
436 Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
47
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
953
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
18
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
2
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
Human drug -> Prescription; Discontinued; Active ingredient (NEOMYCIN SULFATE)
Active Ingredients (Neomycin Sulfate) -> FDA Greenbook
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Same Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Connectivity Count
Same Parent, Exact Count
Mixtures, Components, and Neutralized Forms Count
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
Same Count
Neomycin Sulfate (annotation moved to)
Drug and label
Active ingredient and drug
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)
Non-Proprietary Name
NEOMYCIN SULFATE
Pharmacological Classes
Aminoglycoside Antibacterial [EPC]; Aminoglycosides [CS]
Animal Drugs -> FDA Approved Animal Drug Products (Green Book) -> Active Ingredients
Human Drugs -> FDA Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations (Orange Book) -> Active Ingredients
New Zealand EPA Inventory of Chemical Status
Neomycin sulphate: Does not have an individual approval but may be used under an appropriate group standard
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/Neomycin sulfatehttps://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1405-10-3
- New Zealand Environmental Protection Authority (EPA)LICENSEThis work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International licence.https://www.epa.govt.nz/about-this-site/general-copyright-statement/
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- DailyMed
- Drugs@FDALICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linkingNEOMYCIN SULFATEhttps://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- FDA Approved Animal Drug Products (Green Book)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- FDA Orange BookLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuse
- NLM RxNorm TerminologyLICENSEThe RxNorm Terminology is created by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and is in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from NLM. Credit to the U.S. National Library of Medicine as the source is appreciated but not required. The full RxNorm dataset requires a free license.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/termsofservice.htmlneomycin sulfatehttps://rxnav.nlm.nih.gov/id/rxnorm/7300
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.htmlAnti-Bacterial Agentshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000900Protein Synthesis Inhibitorshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68011500
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- EPA Chemicals under the TSCAEPA TSCA Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory
CONTENTS

 CID 71463901
CID 71463901 CID 1118 (Sulfuric Acid)
CID 1118 (Sulfuric Acid)