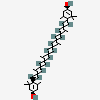
Lutein
- Lutein
- XANTHOPHYLL
- 127-40-2
- Bo-Xan
- Vegetable lutein
- Create:2004-09-16
- Modify:2025-01-04
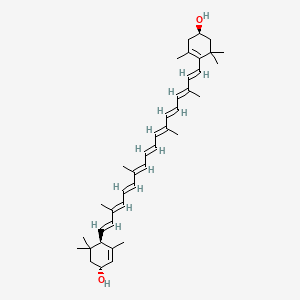
- beta,epsilon-Carotene-3, 3'-Diol, (3R,3'R,6'S)-
- beta,epsilon-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3S,3'R,6'S)-
- gamma Lutein
- Lutein
- Lutein F
- Lutein G
- Lutein, gamma
- Lutein
- XANTHOPHYLL
- 127-40-2
- Bo-Xan
- Vegetable lutein
- all-trans-Lutein
- Vegetable luteol
- trans-Lutein
- Lutein ester
- Xantofyl
- all-trans-(+)-Xanthophyll
- FloraGLO
- FloraGLO Lutein
- Lutein A
- beta,epsilon-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)-
- Lutein, all-trans-
- all-trans-Xanthophyll
- Lutamax
- E 161b
- Oro Glo 7
- Xanthophyll, all-trans-(+)-
- Leutein
- Lutein from tagetes erecta
- OS 24
- UNII-X72A60C9MT
- (3R,3'R,6'R)-Lutein
- INS NO.161B(I)
- X72A60C9MT
- DTXSID8046749
- CHEBI:28838
- INS-161B(I)
- beta,epsilon-Carotene-3,3'-diol
- Xanthophyll (~80%)
- E 161
- EINECS 204-840-0
- E-161B
- E-161B(I)
- NSC 59193
- NSC-59193
- (1R)-4-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-[(1R,4R)-4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-yl]-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl]-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol
- DTXCID6026749
- (3R,3'R,6'R)-beta,epsilon-carotene-3,3'-diol
- .beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol
- .beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)-
- A1LXP
- LUTEIN (USP-RS)
- LUTEIN [USP-RS]
- LUTEIN (MART.)
- LUTEIN [MART.]
- NSC59193
- gamma Lutein
- Lutein, gamma
- (3R,3'R,6R)-4,5-didehydro-5,6-dihydro-beta,beta-carotene-3,3'-diol
- 180580-60-3
- (1R,4R)-4-((1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-((4R)-4-HYDROXY-2,6,6-TRIMETHYL-1-CYCLOHEXEN-1-YL)-3,7,12,16-TETRAMETHYL-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-OCTADECANONAEN-1-YL)-3,5,5-TRIMETHYL-2-CYCLOHEXEN-1-OL
- (1R,4R)-4-((1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-((R)-4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaen-1-yl)-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-enol
- Leutin
- Noon for Kids
- Lutein; Xantofyl
- (3R,3'R,6S)-4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-BETA,BETA-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOL
- NCGC00167965-01
- Lutein (Standard)
- ()-Lutein
- MFCD08435941
- Lutein (Xanthophyll)
- Lutein - 5%
- Xanthophyll, tech grade
- LEUTEIN [VANDF]
- LUTEIN [VANDF]
- e-carotene-3,3'-diol
- Lutein - 10%
- Lutein - 20%
- LUTEIN [DSC]
- LUTEIN [FCC]
- XANTHOPHYLL [MI]
- Xanthophyll, from marigold
- XANTOFYL [WHO-DD]
- Lutein, analytical standard
- SCHEMBL19342
- 3,3'-Dihydroxy-alpha-carotene
- CHEMBL173929
- (invertedexclamationmarkA)-Lutein
- BCBcMAP01_000190
- GTPL13099
- HY-N6947R
- HMS3886I13
- HY-N6947
- (3R,3'R)-dihydroxy-alpha-carotene
- Tox21_112594
- ( inverted exclamation markA)-Lutein
- BBL101804
- LMPR01070274
- s5103
- STL555601
- AKOS008901394
- 1ST1576
- CCG-270087
- DB00137
- SMP1_000317
- AS-63011
- CAS-127-40-2
- XL176941
- XL176947
- XL176948
- CS-0015250
- NS00019507
- C08601
- BRD-K16742848-001-01-8
- BRD-K16742848-001-02-6
- Q63409232
- 4',5'-Didehydro-6'-hydro-.beta.-carotene-3,3'-diol #
- AB972DAC-E626-49F1-898D-598AF7729FD0
- (3R,3'R,6R)-4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-beta,beta-CAROTIN-3,3'-DIOL
- Lutein, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
- (3R,3'R,6R)-4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-.BETA.,.BETA.-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOL
- (3R,3'R,6R)-4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-.BETA.,.BETA.-CAROTIN-3,3'-DIOL
- .BETA.,.BETA.-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOL, 4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-, (3R,3'R,6R)-
- beta,beta-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOL, 4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-, (3R,3'R,6R)-
- 4-(18-(4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohex-2-enyl)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-octadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl)-3,5,5-trimethyl-cyclohex-3-en-1-ol
338.26 100
568.427 92.04
476.364 61.63
569.43 57.28
145.101 40.73
568.427 100
338.26 95.83
476.365 91.33
569.43 58.71
145.101 48.34
463 100
533 100
551 100
568.4209 99.96
105.0856 66.10
119.0823 62.01
145.0845 54.54
91.0674 54.23
550.0000 91.63
568.0000 55.48
551.0000 40.46
569.0000 24.43
552.0000 11.34
- Calendula Officinalis Flower (part of)
- Corn (part of)
- Chicken; lutein (component of)
- Adipose Tissue
- Adrenal Gland
- Epidermis
- Eye Lens
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Neuron
- Ovary
- Placenta
- Retina
- Spleen
- Testis
- Extracellular
- Membrane
Not Classified
Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 134 of 141 companies (only 5% companies provided GHS information). For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website.
Aggregated GHS information provided per 141 reports by companies from 4 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory.
Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria per 134 of 141 reports by companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website.
There are 2 notifications provided by 7 of 141 reports by companies with hazard statement code(s).
Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown.
PubMed: 12067838, 22279428, 16452910
Lorena Ivona ŞTEFAN, Alina NICOLESCU, Simona POPA, Maria MOŢA, Eugenia KOVACS and Calin DELEANU. 1H-NMR URINE METABOLIC PROFILING IN TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS. Rev. Roum. Chim., 2010, 55(11-12), 1033-1037
Metabolomics reveals determinants of weight loss during lifestyle intervention in obese children
Patents are available for this chemical structure:
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/result.jsf?inchikey=KBPHJBAIARWVSC-RGZFRNHPSA-N
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme (AICIS).beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)-https://services.industrialchemicals.gov.au/search-inventory/
- EU Food Improvement Agents
- CAS Common ChemistryLICENSEThe data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- ChemIDplusChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- DrugBankLICENSECreative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode)https://www.drugbank.ca/legal/terms_of_use
- EPA Chemicals under the TSCA.beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)-https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tscaEPA TSCA Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory
- EPA DSSToxCompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)LICENSEUse of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-noticeβ,ε-carotene-3,3'-diolhttps://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.004.401β,ε-carotene-3,3'-diol (EC: 204-840-0)https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/79663
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)LICENSEHMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications.http://www.hmdb.ca/citingHMDB0003233_msms_2226526https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0003233#spectra
- New Zealand Environmental Protection Authority (EPA)LICENSEThis work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International licence.https://www.epa.govt.nz/about-this-site/general-copyright-statement/.beta.,.epsilon.-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R,6'R)-https://www.epa.govt.nz/industry-areas/hazardous-substances/guidance-for-importers-and-manufacturers/hazardous-substances-databases/
- ChEBI
- LOTUS - the natural products occurrence databaseLICENSEThe code for LOTUS is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.https://lotus.nprod.net/LOTUS Treehttps://lotus.naturalproducts.net/
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt)LICENSEUnless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source.https://www.cancer.gov/policies/copyright-reuseNCI Thesaurushttps://ncit.nci.nih.gov
- Open TargetsLICENSEDatasets generated by the Open Targets Platform are freely available for download.https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/licence
- ChEMBLLICENSEAccess to the web interface of ChEMBL is made under the EBI's Terms of Use (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.html). The ChEMBL data is made available on a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/).http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Information/termsofuse.htmlChEMBL Protein Target Treehttps://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/g/#browse/targets
- ClinicalTrials.govLICENSEThe ClinicalTrials.gov data carry an international copyright outside the United States and its Territories or Possessions. Some ClinicalTrials.gov data may be subject to the copyright of third parties; you should consult these entities for any additional terms of use.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/terms-conditions#Use
- Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD)LICENSEIt is to be used only for research and educational purposes. Any reproduction or use for commercial purpose is prohibited without the prior express written permission of NC State University.http://ctdbase.org/about/legal.jsp
- DailyMed
- EPA Chemical and Products Database (CPDat)EPA CPDat Classificationhttps://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/chemical-and-products-database-cpdat
- EU Clinical Trials Register
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)LICENSEPermission from WHO is not required for the use of WHO materials issued under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Intergovernmental Organization (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO) licence.https://www.who.int/about/policies/publishing/copyrightLUTEIN from TAGETES ERECTAhttps://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/Home/Chemical/4904
- FDA Regulatory Status of Color Additives
- FDA Substances Added to FoodLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- FooDBLICENSEFooDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (FooDB) and the original publication.https://foodb.ca/about
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-law
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- KEGGLICENSEAcademic users may freely use the KEGG website. Non-academic use of KEGG generally requires a commercial licensehttps://www.kegg.jp/kegg/legal.htmlPhytochemical compoundshttp://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?br08003.keg
- LIPID MAPSLipid Classificationhttps://www.lipidmaps.org/
- Natural Product Activity and Species Source (NPASS)
- MarkerDBLICENSEThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.https://markerdb.ca/
- MassBank of North America (MoNA)LICENSEThe content of the MoNA database is licensed under CC BY 4.0.https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/documentation/license
- Metabolomics Workbench
- National Drug Code (NDC) DirectoryLICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking
- Nature Chemical Biology
- NIPH Clinical Trials Search of Japan
- SpectraBaseLutein, all-trans-https://spectrabase.com/spectrum/J0M7ecJ80vY(all-E,3R,3'R,6'R)-beta,xi-Carotene-3,3'-diolhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/5SI4xlx1kgbLUTEIN;(3R,3'R,6'R)-BETA,EPSILON-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOLhttps://spectrabase.com/spectrum/HeYwsds5BJK
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/LuteinNORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB)LICENSEData files contained in the PDB archive (ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org) are free of all copyright restrictions and made fully and freely available for both non-commercial and commercial use. Users of the data should attribute the original authors of that structural data.https://www.rcsb.org/pages/policies
- Rhea - Annotated Reactions DatabaseLICENSERhea has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). This means that you are free to copy, distribute, display and make commercial use of the database in all legislations, provided you credit (cite) Rhea.https://www.rhea-db.org/help/license-disclaimer
- Springer Nature
- Thieme ChemistryLICENSEThe Thieme Chemistry contribution within PubChem is provided under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
- Wikidata
- WikipediaAzobisisobutyronitrilehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Azobisisobutyronitrile
- Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)LICENSEWorks produced by the U.S. government are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any such works found on National Library of Medicine (NLM) Web sites may be freely used or reproduced without permission in the U.S.https://www.nlm.nih.gov/copyright.html
- PubChem
- GHS Classification (UNECE)GHS Classification Treehttp://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_welcome_e.html
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
- PATENTSCOPE (WIPO)SID 388371981https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/388371981