1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzofuran
PubChem CID
50612
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
- 1,2,4,6,8,9-HEXACHLORODIBENZOFURAN
- 69698-59-5
- Dibenzofuran, 1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachloro
- UNII-31P7B35C0V
- Dibenzofuran, 1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachloro-
Molecular Weight
374.9 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Dates
- Create:2005-03-27
- Modify:2024-12-28
Description
Chlorinated dibenzofurans (CDFs) are a family of chemical that contain one to eight chlorine atoms attached to the carbon atoms of the parent chemical, dibenzofuran. The CDF family contains 135 individual compounds (known as congeners) with varying harmful health and environmental effects. Of these 135 compounds, those that contain chlorine atoms at the 2,3,7,8-positions of the parent dibenzofuran molecule are especially harmful. Other than for laboratory use of small amounts of CDFs for research and development purposes, these chemicals are not deliberately produced by industry. Most CDFs are produced in very small amounts as unwanted impurities of certain products and processes utilizing chlorinated compounds. Only a few of the 135 CDF compounds have been produced in large enough quantities so that their properties, such as color, smell, taste, and toxicity could be studied. (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
Chemical Structure Depiction
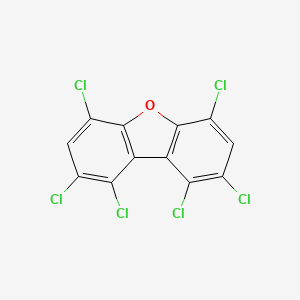
1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachlorodibenzofuran
Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
InChI=1S/C12H2Cl6O/c13-3-1-5(15)11-7(9(3)17)8-10(18)4(14)2-6(16)12(8)19-11/h1-2H
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
FGZCXIPKUCJGHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C1=C(C2=C(C3=C(O2)C(=CC(=C3Cl)Cl)Cl)C(=C1Cl)Cl)Cl
Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
C12H2Cl6O
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
69698-59-5
- 1,2,4,6,8,9-HEXACHLORODIBENZOFURAN
- 69698-59-5
- Dibenzofuran, 1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachloro
- UNII-31P7B35C0V
- Dibenzofuran, 1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachloro-
- 31P7B35C0V
- 1,2,4,6,8,9-HxCDF
- PCDF 127
- DTXSID70219985
- 3,4,6,10,12,13-hexachloro-8-oxatricyclo(7.4.0.02,7)trideca-1(13),2,4,6,9,11-hexaene
- 3,4,6,10,12,13-hexachloro-8-oxatricyclo[7.4.0.02,7]trideca-1(13),2,4,6,9,11-hexaene
- DTXCID20142476
- 1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexa-chlorodibenzofuran
- NS00121307
- Q27256072
Property Name
Property Value
Reference
Property Name
Molecular Weight
Property Value
374.9 g/mol
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
XLogP3
Property Value
7
Reference
Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Rotatable Bond Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Exact Mass
Property Value
373.820731 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Monoisotopic Mass
Property Value
371.823681 Da
Reference
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Topological Polar Surface Area
Property Value
13.1Ų
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Heavy Atom Count
Property Value
19
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Formal Charge
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Complexity
Property Value
323
Reference
Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.10.14)
Property Name
Isotope Atom Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count
Property Value
0
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count
Property Value
1
Reference
Computed by PubChem
Property Name
Compound Is Canonicalized
Property Value
Yes
Reference
Computed by PubChem (release 2021.10.14)
Semi-standard non-polar
2685, 2686, 2686
Follow these links to do a live 2D search or do a live 3D search for this compound, sorted by annotation score. This section is deprecated (see here for details), but these live search links provide equivalent functionality to the table that was previously shown here.
Similar Compounds (2D)
Similar Conformers (3D)
Same Count
No information on the metabolism of dibenzofuran in mammalian organisms was found in the available literature. The bacteria Sphingomonas, Brevibacterium, Terrabacter, and Staphylococcus auricularis degrade dibenzofuran to 2,2',3-trihydroxybiphenyl via dibenzofuran 4,4a-dioxygenase. (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
CDFs are created from production of coal tar and during incineration. They are used as insecticides, in the production of PVC, and in industrial bleaching. (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
Halogenated dibenzofurans (PCDFs and PBDFs) bind the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which increases its ability to activate transcription in the XRE (xenobiotic resoponse element) promoter region. Specifically AhR binds to the PCDF, translocates it to the nucleus and together with hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (ARNT) and xenobiotic responsive element (XRE) increases the expression of CYP1A1 and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (CYP1B1). AhR signaling also increseases conversion of arachidonic acid to prostanoids via cyclooxygenase-2, alters Wnt/beta-catenin signaling downregulating Sox9 and alters signaling by receptors for inflammatory cytokines. AhR signalling also alters proteasomal degradation of steroid hormone receptors, alters cellular UVB stress response and changes the differentiation of certain T-cell subsets. The resulting AhR mediated activation and alteration leads to body weight loss, cancer and thymic atrophy (characteristic of immune and endocrine disruption) which are common toxic responses to PCDFs and related toxic halogenated aryl hydrocarbons.
Carcinogen Classification
3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (L135)
CDFs cause vomiting and diarrhea, anemia, more frequent lung infections, numbness and other effects on the nervous system, and mild changes in the liver. However, there were no permanent liver changes or definite liver damage found in people who ingested CDFs. (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
Inhalation (L952) ; dermal (L952) ; oral (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
Skin and eye irritations, especially severe acne, darkened skin color, and swollen eyelids with discharge are the most obvious health effects of the CDF poisoning. (L952)
L952: Wikipedia. Dibenzofuran. Last Updated 1 June 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dibenzofuran
- ChemIDplus1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzofuranhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0069698595ChemIDplus Chemical Information Classificationhttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/ChemIDplus
- EPA DSSTox1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzofuranhttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70219985CompTox Chemicals Dashboard Chemical Listshttps://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/
- FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS)LICENSEUnless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required.https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/about-website/website-policies#linking1,2,4,6,8,9-HEXACHLORODIBENZOFURANhttps://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/31P7B35C0V
- Japan Chemical Substance Dictionary (Nikkaji)
- NIST Mass Spectrometry Data CenterLICENSEData covered by the Standard Reference Data Act of 1968 as amended.https://www.nist.gov/srd/public-lawDibenzofuran, 1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachlorohttp://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm
- SpringerMaterials1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexa-chlorodibenzofuranhttps://materials.springer.com/substanceprofile/docs/smsid_kokjahrydyxvcmtm
- Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)LICENSET3DB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (T3DB) and the original publication.http://www.t3db.ca/downloads1,2,4,6,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzofuranhttp://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D2174
- Wikidata1,2,4,6,8,9-hexachlorodibenzofuranhttps://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q27256072
- PubChem
- NORMAN Suspect List ExchangeLICENSEData: CC-BY 4.0; Code (hosted by ECI, LCSB): Artistic-2.0https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NORMAN Suspect List Exchange Classificationhttps://www.norman-network.com/nds/SLE/
- MolGenieMolGenie Organic Chemistry Ontologyhttps://github.com/MolGenie/ontology/
CONTENTS