PubChem Structure Search
PubChem Structure Search allows
the
PubChem Compound Database
to be queried by chemical structure or chemical structure pattern. The
PubChem Sketcher allows a
query to be drawn manually.
Users may also specify the structural query input by
PubChem Compound Identifier (CID),
SMILES,
SMARTS,
InChI,
Molecular Formula,
or by upload of a
supported structure file format.
|
Search Input |
 |
To perform a chemical structure search you must provide an appropriate query.
There are several forms of structure input allowed:
- SMILES/SMARTS Input
SMILES
-- Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System,
a chemical structure line notation (a typographical method using printable characters) for
entering and representing molecules. SMILES strings can be
imported or exported from many molecular editors. SMILES can include wildcard
atoms using a "*" for the atom. For example, the SMILES of
gleevec is
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5.
SMARTS --
SMILES ARbitrary Target Specification, a
chemical structure query line notation. SMILES is a subset of SMARTS. As such,
a valid SMILES is a valid SMARTS. All standard SMILES features,
including stereochemistry and isotope labeling, and all
standard SMARTS extensions, including recursive SMARTS, are recognized.
- InChI Input
InChI -- IUPAC International Chemical Identifier,
a chemical structure line notation.
For example, the InChI string of
aspirin is InChI=1/C9H8O4/c1-6(10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7(8)9(11)12/h2-5H,1H3,(H,11,12)/f/h11H.
- CID Input
CID -- PubChem Compound Identification, a non-zero integer PubChem accession
identifier for a unique chemical structure.
For example, the CID of
aspirin is 2244.
- Molecular Formula Input
Molecular Formula (MF) -- Specification of the count of each element in a
compound. For example,
ethyl alcohol has the MF C2H6O.
The general MF query syntax consists of a series of valid atomic symbols (please consult
your periodical chart), each optionally followed by either a number or a range. An "*" may be
used as a wildcard in the place of a number. The generic range syntax is "[atomic
symbol][low count]-[high count]", repeated for every specified element. Elements may be written in
arbitrary order.
Examples:
| 1. C7-8: |
represents compounds with seven or eight carbons. |
| 2. C-7: |
represents compounds with up to seven carbons. |
| 3. C7-: |
represents compounds with seven or more carbons |
| 4. C or C1: |
represents compounds with exactly one carbon |
| 5. C-: |
represents any number of carbons, including none. |
Please note that two-letter elements must be written with the second letter in
lowercase, otherwise "Cu" (one copper) and "CU" (one carbon, one uranium) would not be
distinguishable.
- File Input
A chemical structure file or a molecular formula file on your computer may be uploaded as a query.
For multiple molecular formulas, this is one MF query per line. For
multiple chemical structures in a file, all structures must be of the same
format (e.g., mixing of SMILES/SMARTS and InChI is not allowed). If a
line notation is being used, only one chemical structure or chemical
structure query is allowed per line.
"SDF"
formatted files (both v2000
and v3000) are also allowed. While chemical structure formats other than those
listed above may work, they are not supported.
When multiple queries within the same file are provided, the final result is
an "OR" of each query result.
|
Search Type |
 |
PubChem Structure Search
provides various chemical search types and options. On the top of structure
search page there are several tabs. Each of these tabs is dedicated to a
particular search type. Click one of the tabs to perform the desired
search type.
|
Name/Text Search |
 |
To search the
PubChem Compound Database
using a
textual query
(and not by a chemical structure query), please click the Name/Text tab
to go to the appropriate query form:
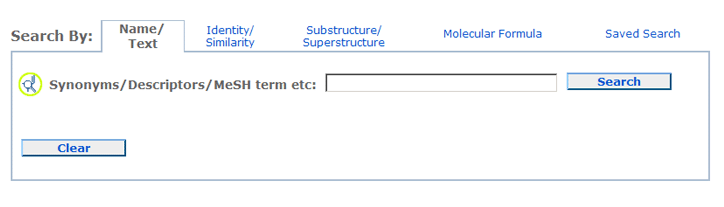
A Name/Text query allows one to locate chemical structures using one or more
textual keywords. For example, synonyms, descriptors, or MeSH terms can be entered for searching.
To search for a phrase or a name with non-alphanumeric characters (i.e., not of
a-z, A-Z, or 0-9), please use double quotes around the query (for example, "4-guanidinobutyramide"). There are various
indexes that
can be individually searched by suffixing the text phrase or keyword with an
appropriate index and by using brackets (for example, to search a particular IUPAC name:
"4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butanamide"[iupacname]). One may also perform
numeric range searches
of appropriate index fields using a ":" delimiter (for example: 100.5:200[molecularweight]
for a molecular weight range search between 100.5-200.0 g/mol ).
Queries may be combined using the Boolean operators "AND", "OR", and "NOT".
Please note that these Boolean operators must be capitalized.
Examples:
- Which compound has a CID equal to 123?
Enter 123[cid] or 123[uid] in the text box, and click
the Search button.
- Which compounds have a molecular weight between 100 and 200 daltons?
Enter they query 100:200[molecularweight] or 100:200[mw] in the text box, and click
the Search button.
- Which compounds have "aspirin" or "gleevec" as keywords in their synonyms?
Enter aspirin[synonym] OR gleevec[synonym] in the text box, and click Search button.
|
Identity and Similarity Search |
 |
To locate a particular chemical structure or to find chemical structures similar
to another chemical structure, please click the Identity/Similarity tab
to go to the appropriate query form:
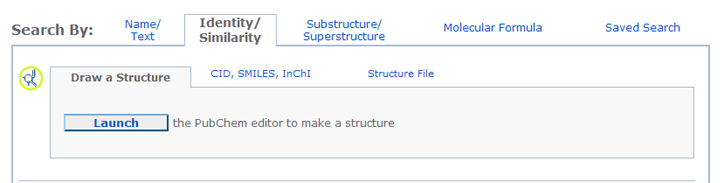
All queries for identity search and similarity search must be valid chemical
structures and will be subjected to the same PubChem chemical structure
standardization processing used to create the PubChem Compound database from the
PubChem Substance database. This "standardization" procedure will
normalize the chemical structure query for resonance and tautomeric form
invariance to make it consistent with its PubChem representation, thus
increasing the likelihood of finding a particular chemical structure in PubChem.
Invalid or incompletely defined chemical structure queries may not provide
intended results.
Please note that if explicit hydrogen atoms are not provided in the chemical
structure query, PubChem
will use the most likely valence state for the atoms in the provided chemical
structure. To achieve desired and consistent results, it is best to provide all explicit hydrogens in chemical structure queries of this
search type.
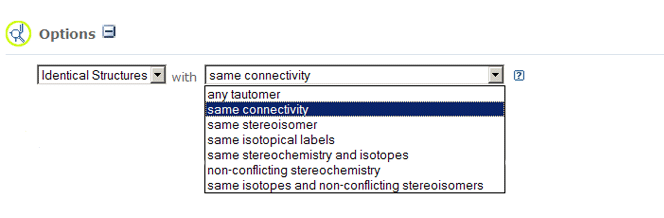
- Identical Structures search allows you to locate records that are
identical to
the provided chemical structure with different notions of chemical structure identity.
Additional search options allow you to choose the degree of "sameness":
- Any Tautomer provides tautomeric form invariance and returns chemical structures that are
tautomers of the provided chemical structure. This option ignores stereochemical or isotopic differences.
- Same Connectivity provides isotopic and stereocenter form invariance and returns
chemical structures that exactly match the connectivity and valence-bond form
(i.e., same bond orders) of the provided chemical
structure. This option ignores differences in isotopic or stereochemical information.
- Same Stereoisomer provides isotopic form invariance and returns chemical structures that
exactly match the connectivity, valence-bond, and stereochemical form of the provided chemical structure.
This option ignores isotopic differences.
- Same Isotopic Labels provides stereochemical form invariance and returns chemical
structures that exactly match the connectivity, valence bond, and isotopic form of the provided chemical
structure. This option ignores stereochemical differences.
- Same Stereochemistry and Isotopes provides chemical structures that exactly match the
connectivity, valence bond, stereochemical, and isotopic form of the provided chemical structure.
This option should be used in most cases and can be considered an "exact
match" to a chemical structure.
- Same Isotopes and Nonconflicting Stereoisomers returns chemical structures
that exactly match the connectivity, valence bond, and isotopic form but allows either the same
or unspecified stereo at each defined stereocenter in the provided chemical structure
query.
- Nonconflicting Stereoisomers provides isotopic form invariance and returns chemical
structures that exactly match the connectivity and valence bond form but allows
either the same or unspecified stereo at each defined stereocenter of the provided
chemical structure query.
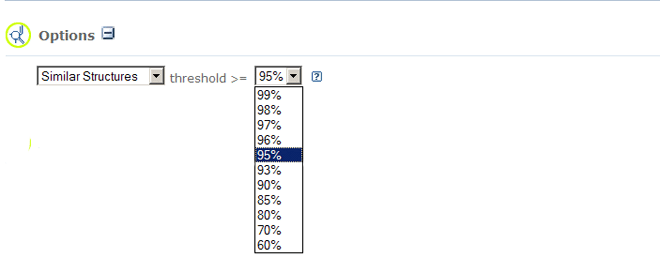
- Similar Compounds search type allows you to locate records that are similar
to a chemical
structure query using pre-specified similarity thresholds. Similarity is measured using the
Tanimoto equation and
the PubChem dictionary-based
binary fingerprint.
This fingerprint consists of series of chemical substructure "keys". Each key denotes
the presence or
absence of a particular substructure in a molecule. The fingerprint does not consider variation in
stereochemical or isotopic information. Collectively, these binary keys provide a "fingerprint" of a
particular chemical structure valence-bond form.
The degree of similarity is dictated by the Threshold parameter.
A threshold of "100%" effectively acts as an "exact match" to the provided chemical structure
query (ignoring stereo or isotopic information), while a threshold of "0%" would return all chemical structures
in the PubChem Compound database. Various predefined thresholds between 99-60%
are allowed.
To work properly, both Identity and Similarity search types require a completely
defined structure. A SMILES string with wildcards or a SMARTS string containing
substructure patterns may not provide intended results for Identity and Similarity search
types.
To perform an Identity or Similarity search, please click the
Identity/Similarity tab in the Search By section to choose the above described search
types and method for providing a chemical structure:
- To draw a chemical structure, click the Launch button to open the PubChem Sketcher.

- To provide a chemical structure by CID, SMILES or InChI click on the CID, SMILES, InChI
tab.
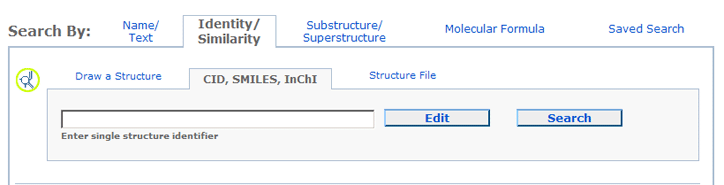
- To Upload a structure file (e.g., in SDF format), click the Structure File tab.

Finally, select a desired option for your search job.
- The default search option is "Identical Structures" with several choices for
finding "Similar Compounds".
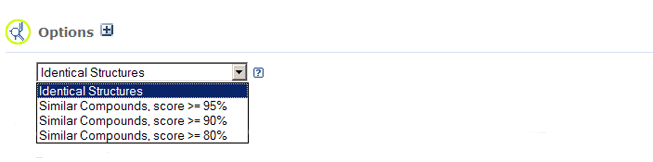
- By clicking on
 to expand the Option section, more options will appear for Identity search. to expand the Option section, more options will appear for Identity search.
- By clicking on
 to expand the Option section, more options will appear for
Similar Structure search. to expand the Option section, more options will appear for
Similar Structure search.
A number of filters are also available under "Filter" section.
When an Identity/Similarity search is submitted, the provided structure will be
validated and standardized, prior to performing the query.
|
Substructure and Superstructure Search |
 |
To locate a chemical structures using a particular chemical structure pattern,
please click the Substructure/Superstructure tab to go to the appropriate
query form:

The presence of explicit hydrogen atoms can be a complicating factor for
substructure and superstructure queries, considering the hydrogen atoms become
part of the pattern being searched. When a CID is provided as the
structure input method, by default explicit hydrogens are removed prior to
search.
To perform a Substructure or Superstructure search, please click the
Substructure/Superstructure tab in the Search By section and choose
one the above described search
input type tabs. Same as for Identity and Similarity
search types, one can draw a chemical structure or provide a chemical structure by CID, SMILES/SMARTS, InChI,
or upload a structure file (e.g., in SDF format).
Finally, select a desired search type option for the search job.
- Default search options allow: single or double bonds in the query can match aromatic bonds,
chain bonds match both ring and chain bonds, and, when CID is the input type, all
explicit hydrogen atoms in the query are automatically stripped.
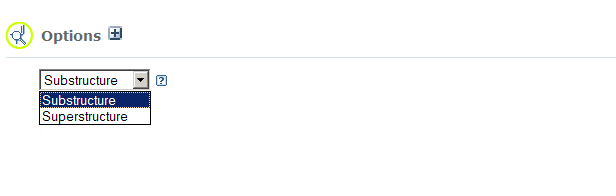
- By clicking
 to expand the Option section more options will appear for these search types. to expand the Option section more options will appear for these search types.

When an Substructure/Superstructure search is submitted, the
provided structure will be displayed as an image for user's preview.
|
Molecular Formula Search |
 |
To locate a chemical structures by a particular molecular formula pattern, please click the Molecular Formula tab to go to the appropriate query form:
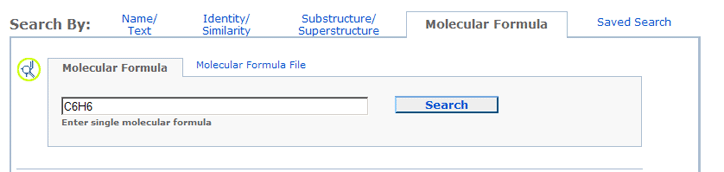
Molecular Formula search allows one to locate records that contain a certain number and type of atomic elements.
For example, a query of "C6H6" will return all structures containing six (6) carbon atoms and six (6) hydrogen atoms.
Molecular Formula search is specifically designed for queries
that are either a single molecular
formula or a molecular formula file, containing one or more molecular formulas,
one per line. A CID may also be used to provide the input molecular formula.
By default, the search results from a Molecular Formula search will exactly match the
entered stoichiometry. One may allow other elements in the returned results by
click on the  following the Options, and select
"allow other element". following the Options, and select
"allow other element".
|
3D Conformer Search |
 |
To locate a chemicals structurally similar to a 3D conformer, please click the 3D Conformer tab to go to the appropriate query form:
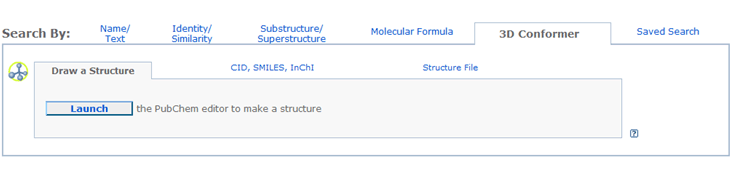
The 3D conformer search can take either a 2D or 3D chemical structure as input. A 3D structure may be submitted only through a SDF. The search database consists of pre-calculated 3D conformers of compounds in the PubChem Compound database. Currently, up to 3 conformers per compound are in the search database. A 3D conformer search job will look for the chemicals in the PubChem Compound database that have 3d conformers structurally similar to the query conformer. The threshold of the shape similarity is 80%, and of the feature similarity is 50%.
When the input is a 2D structure, if the input is a CID, the pre-calculated default conformer of that CID is chosen to search for similar conformers; otherwise, the theoretical 3D conformers of the query will be generated by OpenEye software Omega, and only a single conformer withenergy-minimum is utilized as the query conformer. A 3D input structure will be directly used to search for similar conformers.
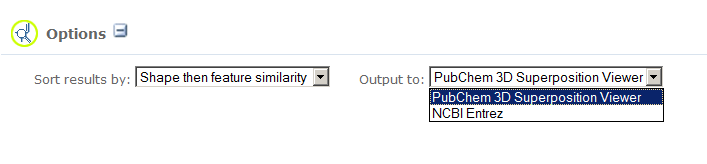
The search results can be sorted. The pull-down menu in the Option section allows you to specify the sorting of search results:

The search results can be sent into the PubChem web-based 3D conformer superposition viewer to understand the details of the similarities and superpositions between similar conformers. They can also be sent and displayed into NCBI Entrez search engine for further investigations via utilization of various NCBI scientific resources. Choosing a destination from the "Output to: " pull-down menu in the Option section to decide where your search results will be displayed:
|
Search with Saved Query |
 |
PubChem Structure Search allows queries to be imported and exported via
PUG XML.
These saved queries can be sent to colleagues or used to repeat a search at a
later date without having to reenter the query or options. After entering
a chemical structure and selecting appropriate options for Identity/Similarity,
Substructure/Superstructure, or Molecular Formula search, you have
the option of saving your query. This is achieved by clicking Save Query button at the bottom of the
corresponding submission page. The saved query file is in XML format based on the
PUG XML schema for
PubChem Structure Search. This saved query can be also used as input for the
PUG service.
Users can directly upload a saved query file for repeating a previously
saved search. To upload the saved search, one needs to click on the Saved Query tab in the Search By section, and click on
Browse button on the page like the one below to select a file for upload.
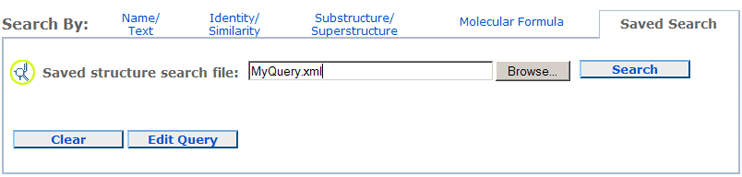
It is possible to modify a saved query by clicking the Edit Query
button depicted in the image above. Data from the saved search file will be used to fill the query form. In that form,
one can
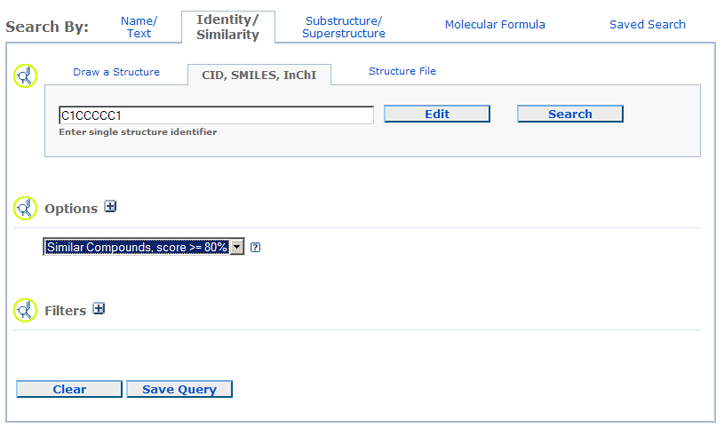
modify any settings so that the query is modified. For example, if a query file contains the data for
an 80% similarity search of C1CCCCC1, after you input the query file and click the Edit Query,
a query form like the one below will be ready for you to change your query.
|
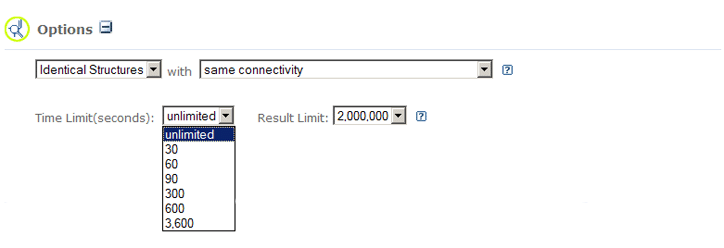
Time Limit and Result Limit |
 |
By default, there is no time limit for a structure search to be performed. A
time limit can be imposed on
the duration of chemical structure query. One may modify this limit by clicking the
 following the Option on a submission page. If the query does not
finish within allowed time period, all hits found up to that time period (and within the hit limit
specified), will be returned.
By default, the maximum number of results returned by the chemical structure query is currently
limited to two million. One may modify this limit by clicking the
 following
the Option on a submission page. following
the Option on a submission page.
For example, these are what the Time Limit and Result Limit
option interface looks like for an Identity search.
|
Query Preview |
 |
For Identity/Similarity and Substructure/Superstructure searches, submitted queries
are first validated. Validation, in PubChem terminology, includes standardization processing of
Identity/Similarity queries, much like the processing of chemical structures used to create the
PubChem compound database from depositors' original structures.
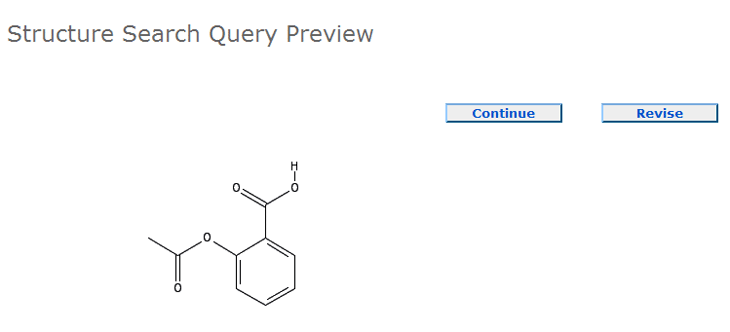
Structure Search Query Preview allows you to review the structure query being submitted to
PubChem. This step provides an image of each query structure. Clicking the "Continue" button will
allow the search job to proceed. To revise or resubmit a query, please click the "Review"
button.
Here is a typical Structure Search Query Preview:
When multiple chemical structure queries are provided, these navigation buttons (first, previous, next,
last, respectively):
  enable you to review each.
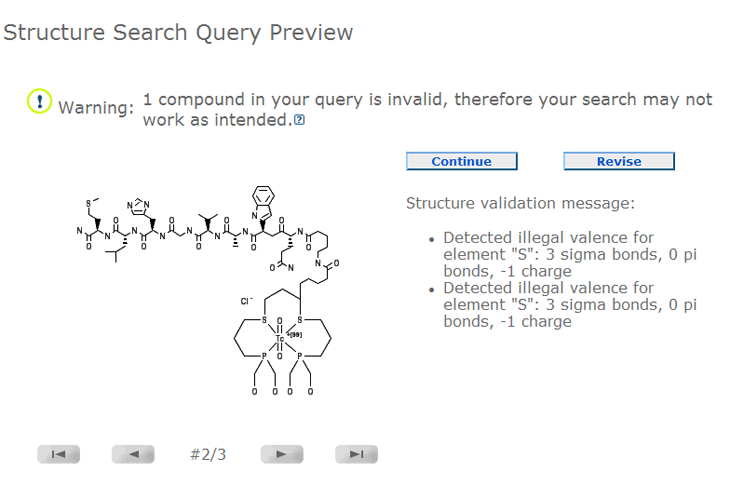
Below is a Query Preview of an SDF file for a similarity search containing one invalid chemical
structure and two valid chemical structures. The number "#2/3" means the structure currently displayed
is the 2 nd structure of three in the submission
(#n th/total). The Query Preview may contain one or more message
containing structure query validation information.
|
Filters |
 |
Results of a structure search may be further narrowed using various filters. By clicking
 following the Filters section, one may select from
many filter types.
The list of filter types is presented below:
- Compound Subset
One may search an explicitly specified subset of the PubChem Compound
database. After selecting the desired subset type, one can
specify any subset-specific option. There are three subset types available:
- PubChem Compound Search History
One may use a
previously performed chemical structure query or PubChem Compound search result
for further refinement. Click Retrieve to obtain a current
search history list, if none is present. If a search history result is found
(or if one already exists), a pull-down menu will appear offering to select
a particular history item. Click Refresh to refresh available history items. Please keep in mind that
a search history
expires after eight hours of inactivity.
- CID List
A CID (PubChem Compound ID) list may be provided for subsetting a search. To search using a list of
CIDs, select the CID List radio button, and input (for example, via copy/paste from a document)
a list of CIDs. One may use whitespace (e.g., a space, newline, etc.), a comma (","), or semicolon (";") as a delimiter.
- CID File
User can upload a text file containing a particular CID list. To search using such
a CID file, select the
CID File radio button, and browse to find the file that contains a list of CIDs
(again, separated by
either whitespace, comma (","), or semicolon (";") as a delimiter) on your
computer.
- Property
PubChem computes various properties of chemical structures. The
property filter allows you to restrict the search to chemical structures
with particular computed property
ranges. All ranges must be bounded. To bound an open-ended range, please enter a large value in the
open-ended part of the text box, e.g., -999999 for a minimum value or 999999 for a maximum value.
- Stereochemistry
Used for restricting search to chemical structures with particular stereochemical specificity,
when stereochemistry is possible. Pull-down menus are available for specifying chiral centers and
E/Z bonds:
- Fully Specified -- All stereochemical information must be fully specified
- Partially Specified -- All stereochemical information must be partially specified
- Fully Unspecified -- All stereochemical information must be fully unspecified
- Not Fully Specified -- All stereochemical information must not be fully specified
- Not Partially Specified -- All stereochemical information must not be partially specified
- Not Fully Unspecified -- All stereochemical information must not be fully unspecified
- BioActivity
Used for restricting search to chemical structures with particular bioactivity.
Pull-down menu is available to specify the type of information available in
PubChem BioAssay with the following choices:
- Tested -- Compound has a PubChem BioAssay result
- Active -- Compound is active in a PubChem BioAssay
- Inactive -- Compound is inactive in a PubChem BioAssay
- Not Tested -- Compound does not have a PubChem BioAssay result
- Links
Used for restricting search to chemical structures with particular cross-link types. User can filter the
type of links for a compound by selecting the appropriate radio button with the choices by column:
- Require -- Compound must have a link of this type
- Disallow -- Compound must not have a link of this type
- Allow -- Compound can have a link of this type
- Chemical Elements
Used for restricting search to chemical structures containing particular chemical elements. Please check
the boxes of the elements that must be present in the result set.
- Depositor's Category
Used for restricting search to chemical structures matching a particular
depositor category classification.
User can filter the type of depositor category for a compound by selecting the appropriate radio button
with the choices by column:
- Require -- Compound must have a depositor category of this type
- Disallow -- Compound must not have a depositor category of this type
- Allow -- Compound can have a depositor category of this type
- Data Source
Used for restricting search to chemical structures deposited by certain depositor(s). User can specify
one or more data sources that are allowed or disallowed by selecting individual
depositors in the scrollable text boxes:
- From -- Compound resulted from data provided by selected depositors
- Not from -- Compound did not result from data provided by selected depositors
|
Structure Search URL-based Interface |
 |
PubChem Structure Search can be used directly without the need to fill out
an input form. This is achieved by formulating an appropriate URL with the
input already provided. The URL consists of a base (see below), being the
same as that required to invoke the PubChem Structure Search with a "?cmd=search"
at the end. There are a series of parameters that may be provided to
indicate the query type (q_type), the input query (q_data), and the search type.
The parameters are described in more detail below.
Formulating the URL for a structure search is rather straightforward.
Each parameter may be provided in any order and must have "=" after the
parameter name and a "&" character between parameters. All query data
input must be properly
URL-encoded
to enable proper interpretation.
- Base URL:
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/
- URL parameters:
- Query data type (q_type):
- single CID, InCh, or SMILES: q_type=dt
- molecular formula:
q_type=mf
- structure file: q_type=str_file
- molecular
formula file: q_type=mf_file
- saved query: q_type=xml
- Query data (q_data):
Combined with q_type, user can enter a CID, SMILE/SMARTS or InChI string, or a molecular
formula by using this parameter. For example, to input CID 123, user has to give
"q_type=dt&q_data=123" as part of your URL; to input a molecular formula
"C6H6", user has to give
"q_type=mf&q_data=C6H6" as part of your URL.
- Search type (simp_schtp):
- Identity search: simp_schtp=fs (means full structure)
- Similarity search: simp_schtp=(%similarity)
(for example, simp_schtp=90 means
a 90% similarity structure search)
- Substructure search: simp_schtp=subsch
- Superstructure search: simp_schtp=supsch
- Molecular Formula search: simp_schtp=mf
Examples:
|




 A Name/Text query allows one to locate chemical structures using one or more
textual keywords. For example, synonyms, descriptors, or MeSH terms can be entered for searching.
To search for a phrase or a name with non-alphanumeric characters (i.e., not of
a-z, A-Z, or 0-9), please use double quotes around the query (for example, "4-guanidinobutyramide"). There are various
indexes that
can be individually searched by suffixing the text phrase or keyword with an
appropriate index and by using brackets (for example, to search a particular IUPAC name:
"4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butanamide"[iupacname]). One may also perform
numeric range searches
of appropriate index fields using a ":" delimiter (for example: 100.5:200[molecularweight]
for a molecular weight range search between 100.5-200.0 g/mol).
Queries may be combined using the Boolean operators "AND", "OR", and "NOT".
Please note that these Boolean operators must be capitalized.
A Name/Text query allows one to locate chemical structures using one or more
textual keywords. For example, synonyms, descriptors, or MeSH terms can be entered for searching.
To search for a phrase or a name with non-alphanumeric characters (i.e., not of
a-z, A-Z, or 0-9), please use double quotes around the query (for example, "4-guanidinobutyramide"). There are various
indexes that
can be individually searched by suffixing the text phrase or keyword with an
appropriate index and by using brackets (for example, to search a particular IUPAC name:
"4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butanamide"[iupacname]). One may also perform
numeric range searches
of appropriate index fields using a ":" delimiter (for example: 100.5:200[molecularweight]
for a molecular weight range search between 100.5-200.0 g/mol).
Queries may be combined using the Boolean operators "AND", "OR", and "NOT".
Please note that these Boolean operators must be capitalized.
 following the Option on a submission page. If the query does not
finish within allowed time period, all hits found up to that time period (and within the hit limit
specified), will be returned.
following the Option on a submission page. If the query does not
finish within allowed time period, all hits found up to that time period (and within the hit limit
specified), will be returned.


 enable you to review each.
Below is a Query Preview of an SDF file for a similarity search containing one invalid chemical
structure and two valid chemical structures. The number "#2/3" means the structure currently displayed
is the 2nd structure of three in the submission
(#nth/total). The Query Preview may contain one or more message
containing structure query validation information.
enable you to review each.
Below is a Query Preview of an SDF file for a similarity search containing one invalid chemical
structure and two valid chemical structures. The number "#2/3" means the structure currently displayed
is the 2nd structure of three in the submission
(#nth/total). The Query Preview may contain one or more message
containing structure query validation information.
 following the Filters section, one may select from
many filter types.
The list of filter types is presented below:
following the Filters section, one may select from
many filter types.
The list of filter types is presented below: